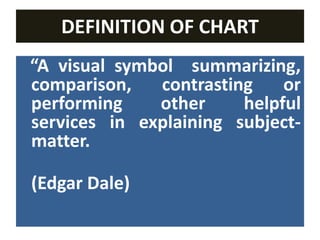
Charts are visual aids that use symbols, diagrams, and flow charts to represent data according to specific guidelines. They present facts, figures, content, abstract ideas and organizational structures in a concise manner to stimulate thinking and motivate learning. Common chart types include flow charts, cause-and-effect charts, timetables, and tree charts. Effective charts are easy to understand, carefully designed based on size and format guidelines, and educate the audience.