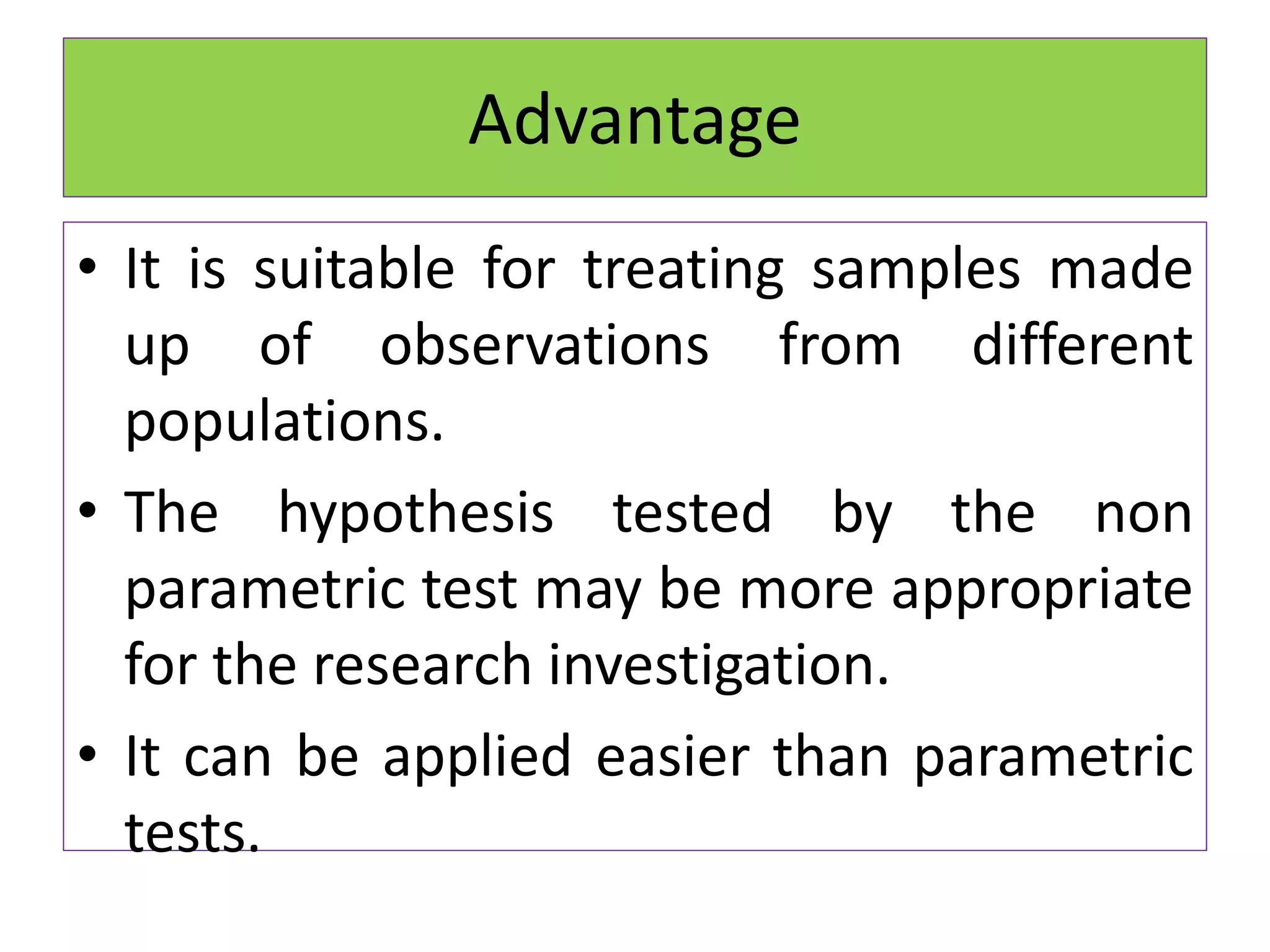
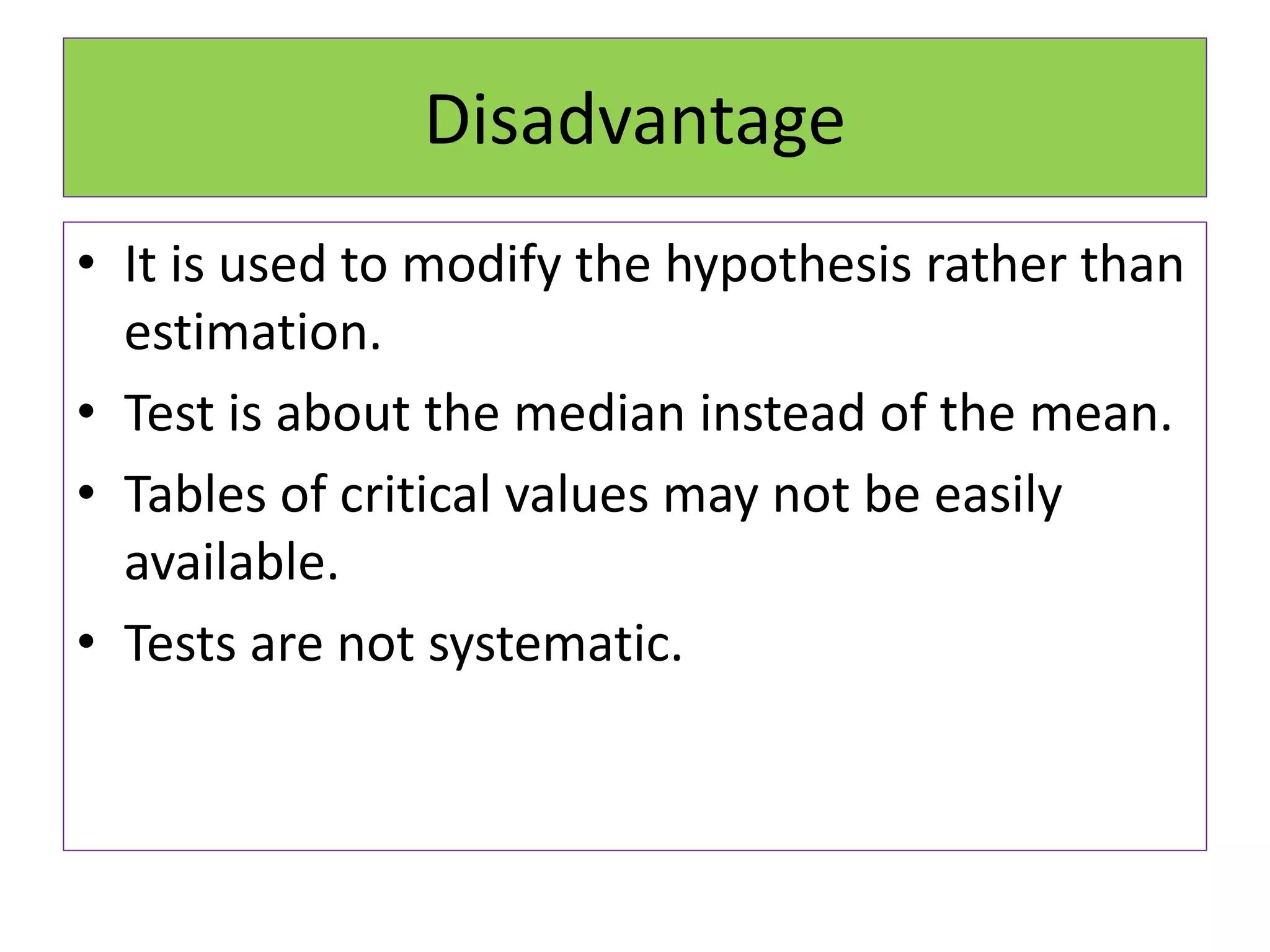
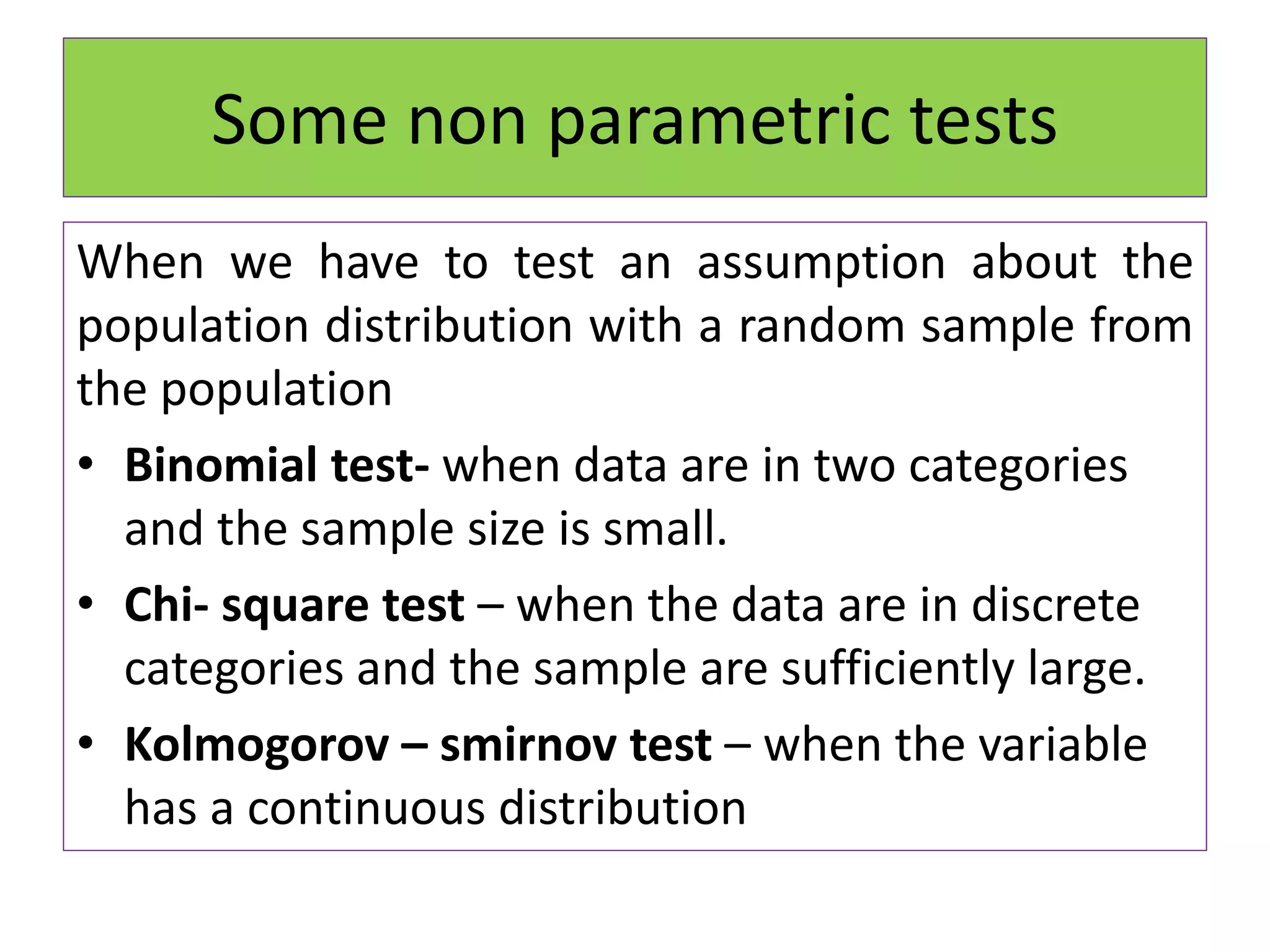
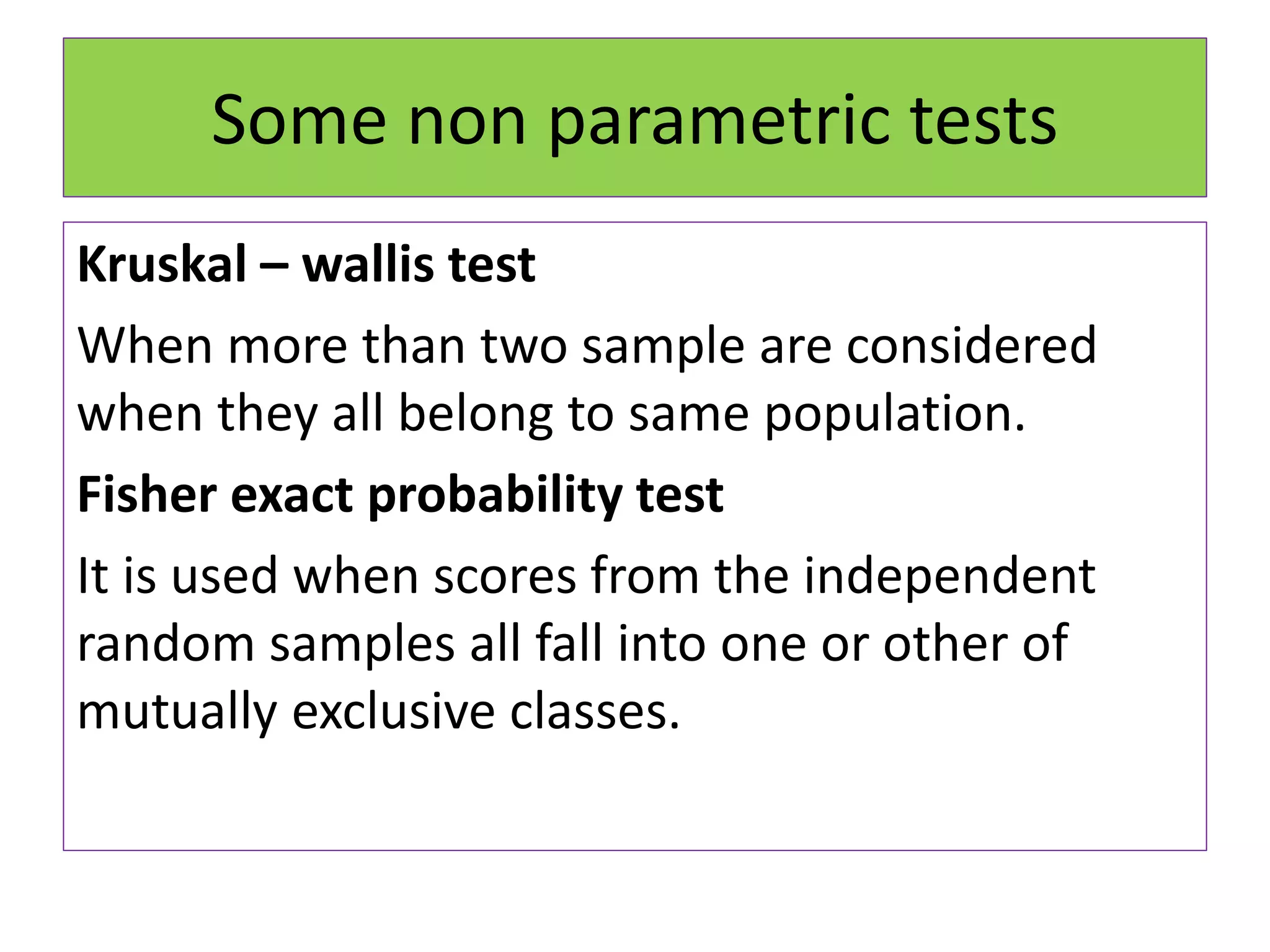
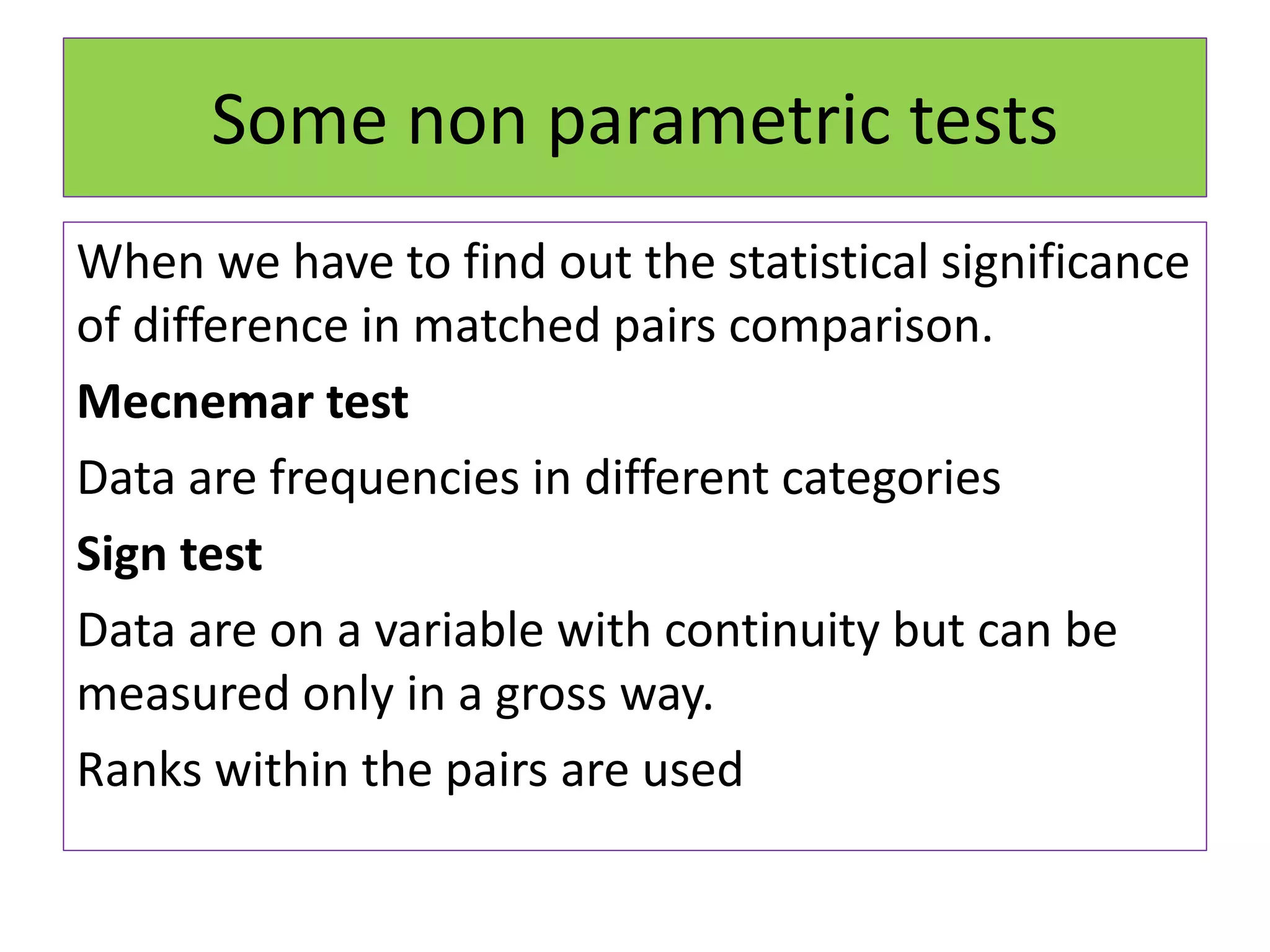
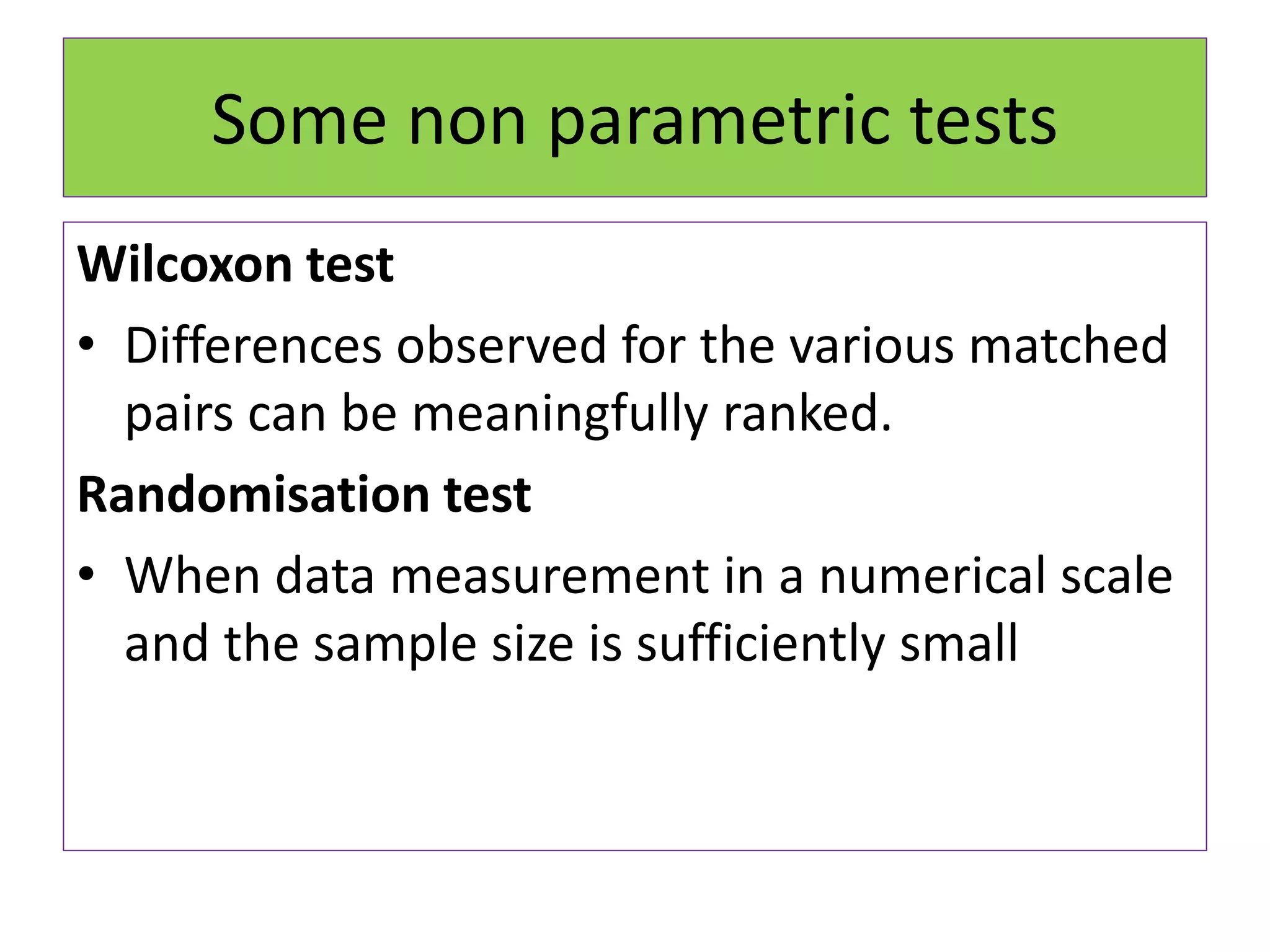
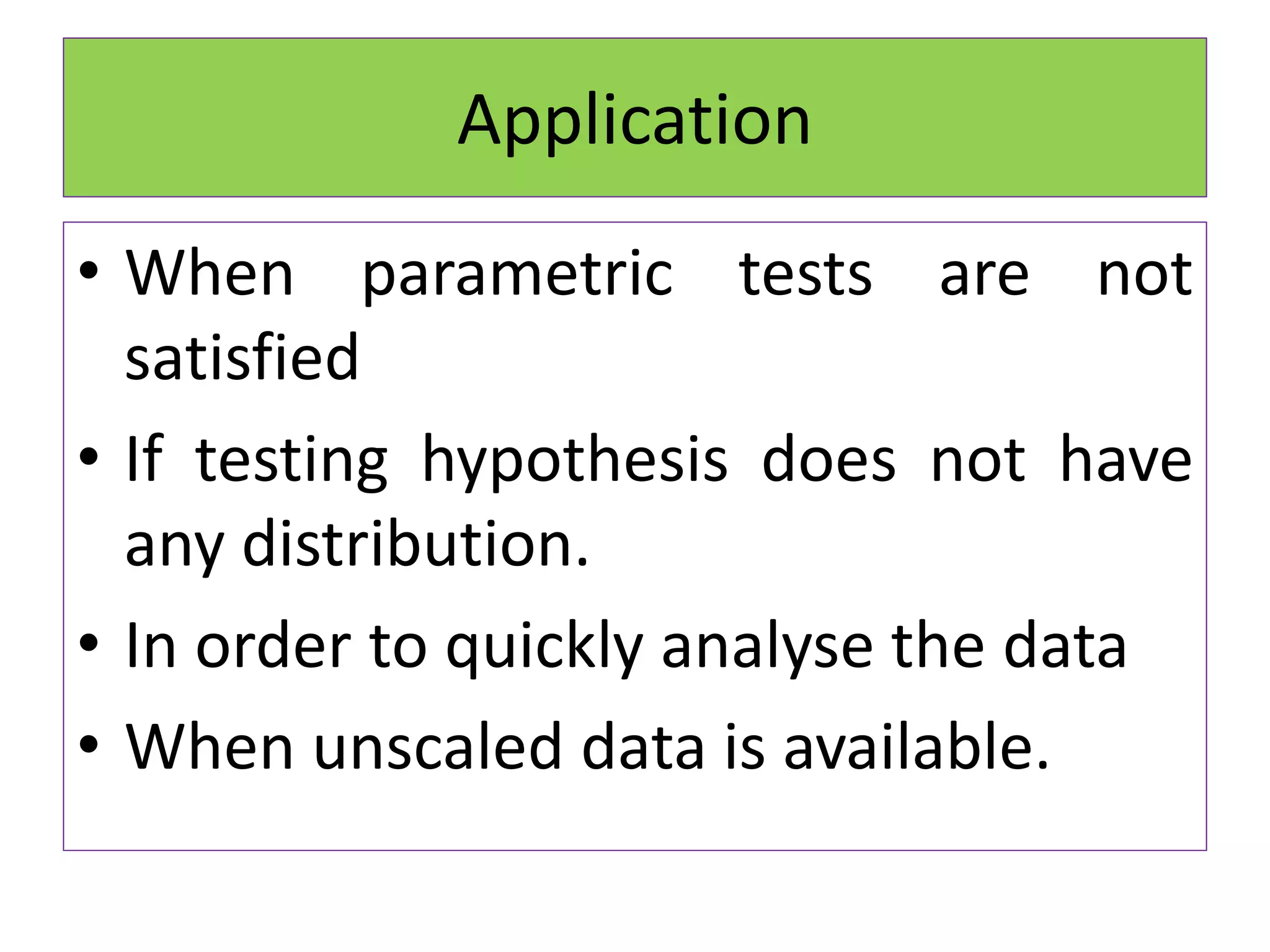
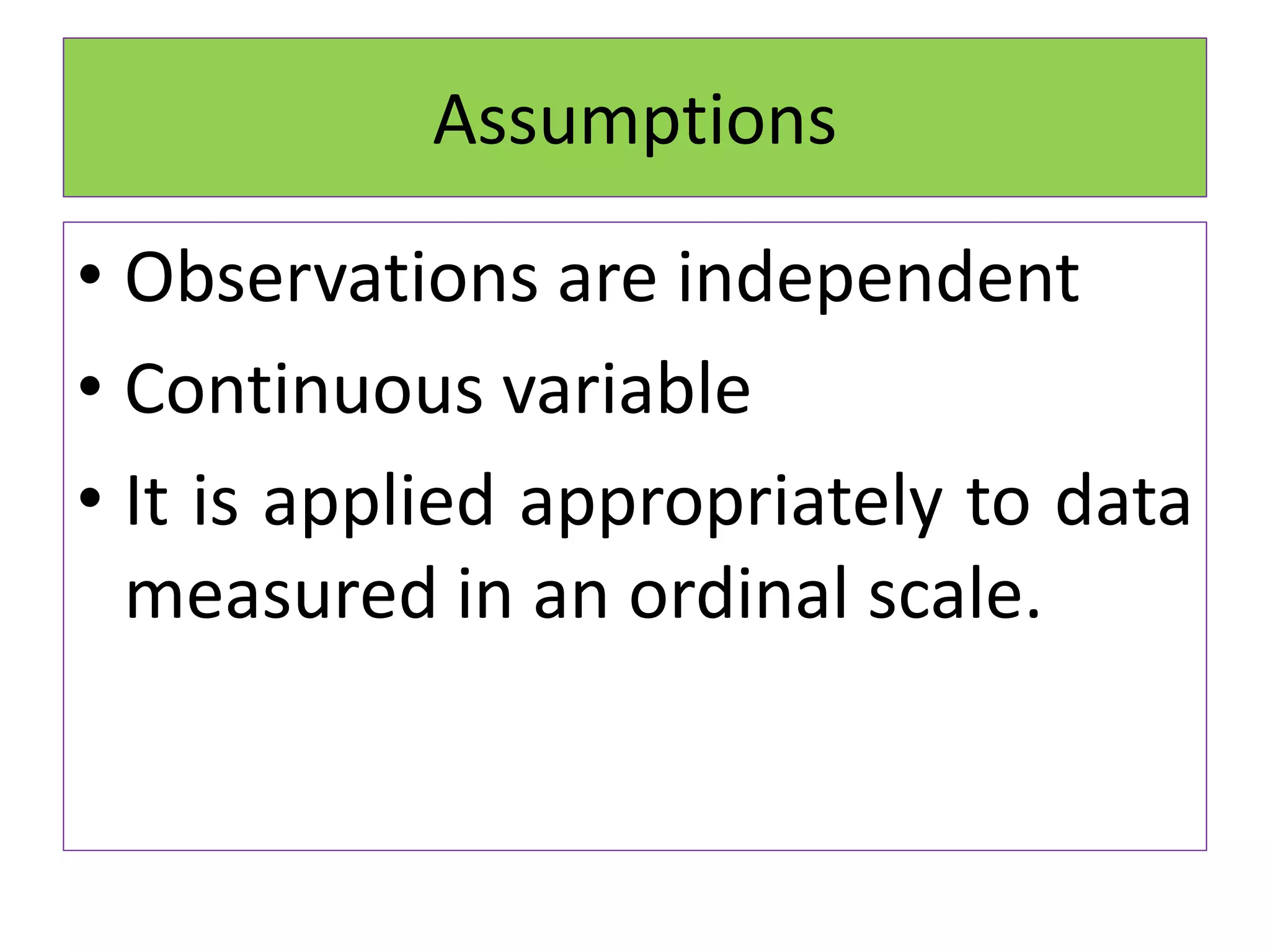
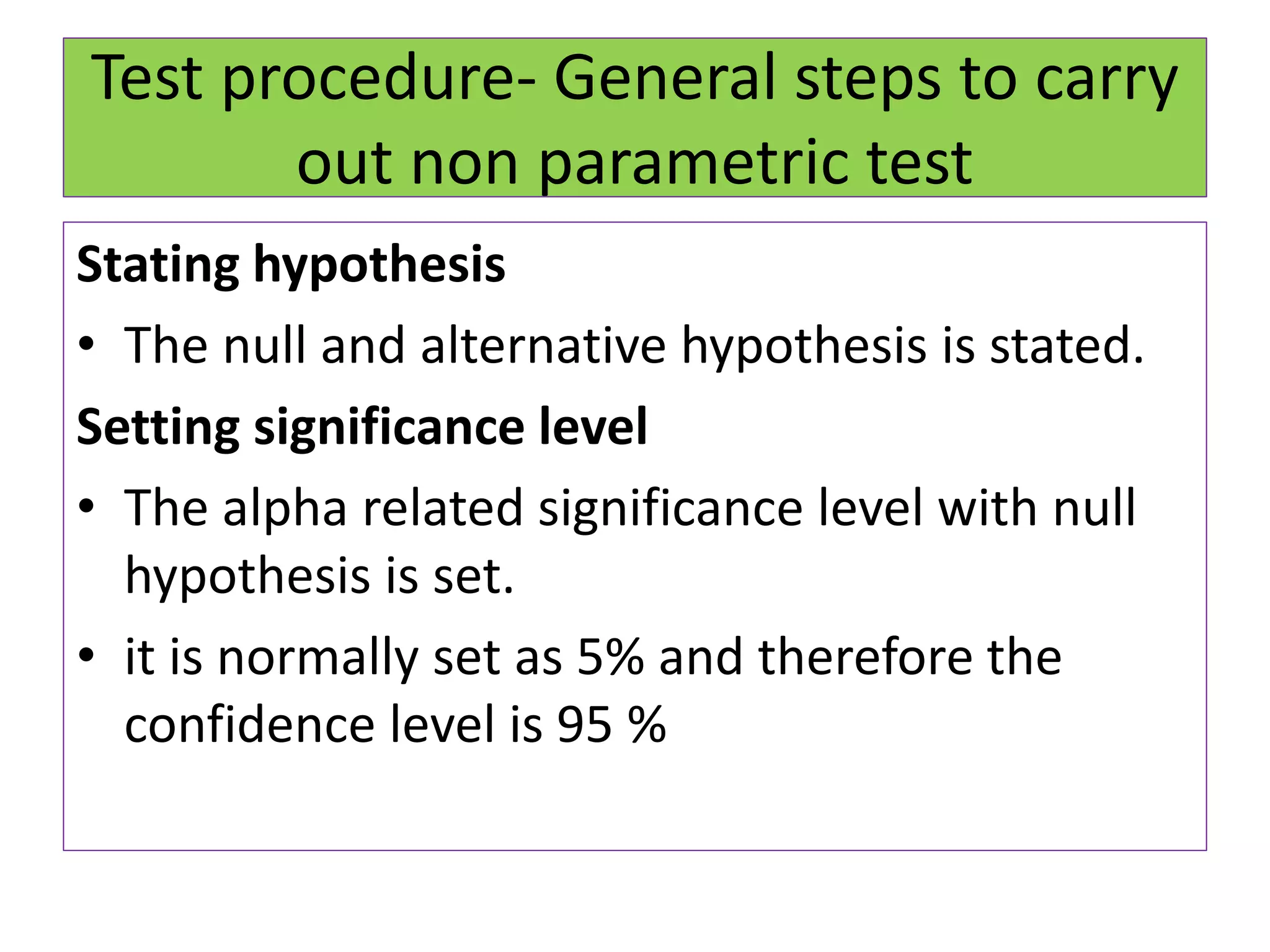
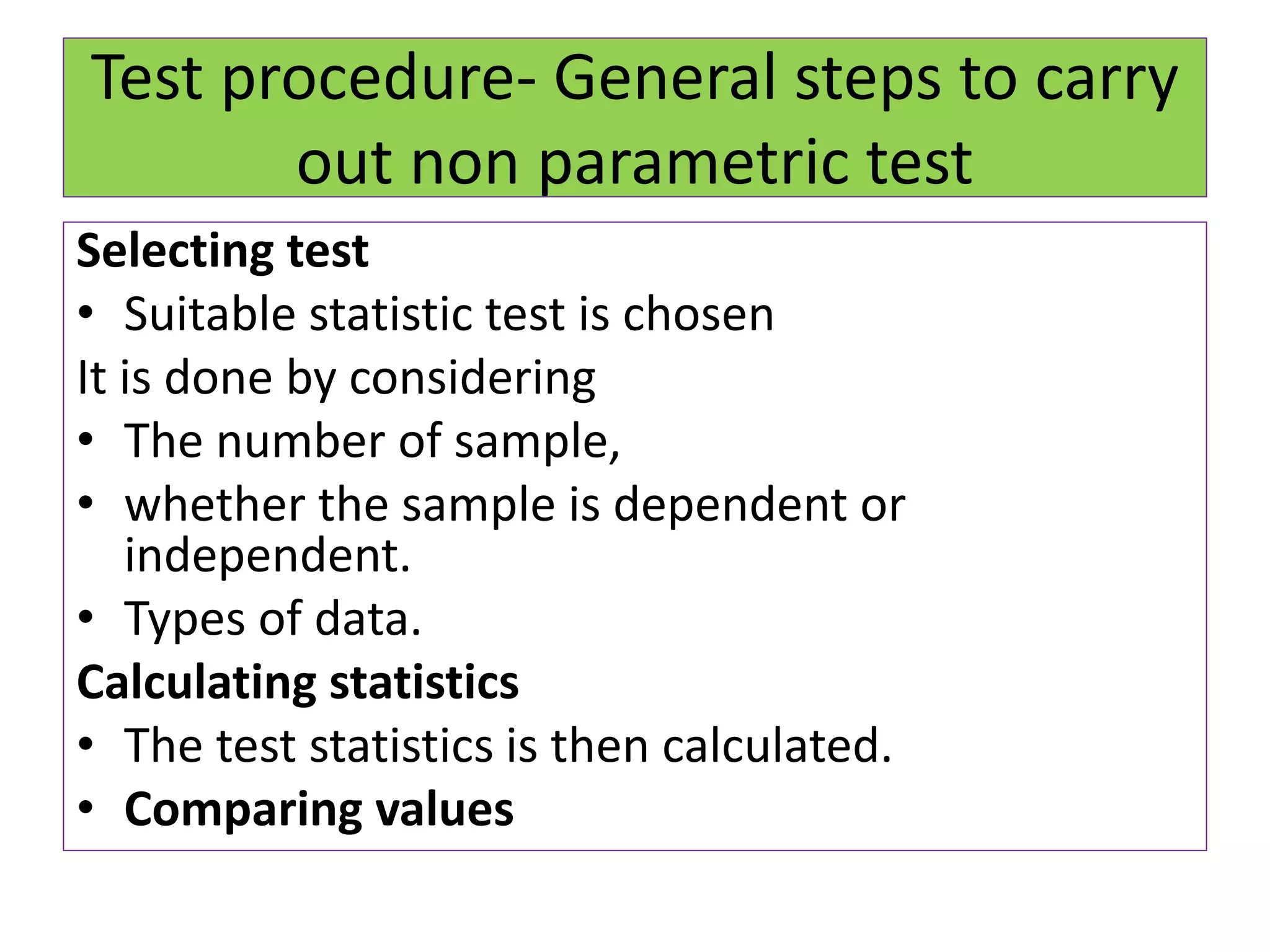
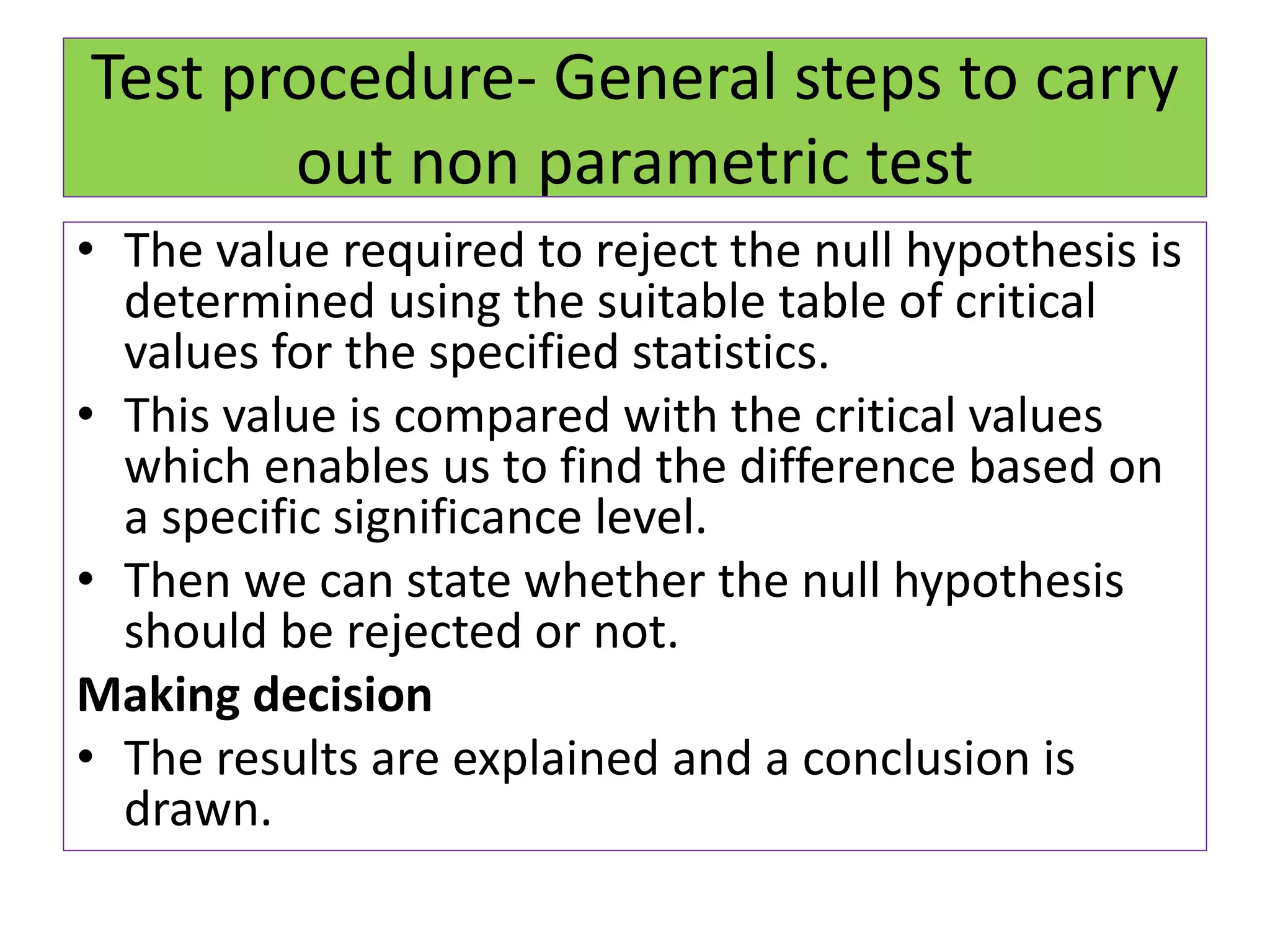
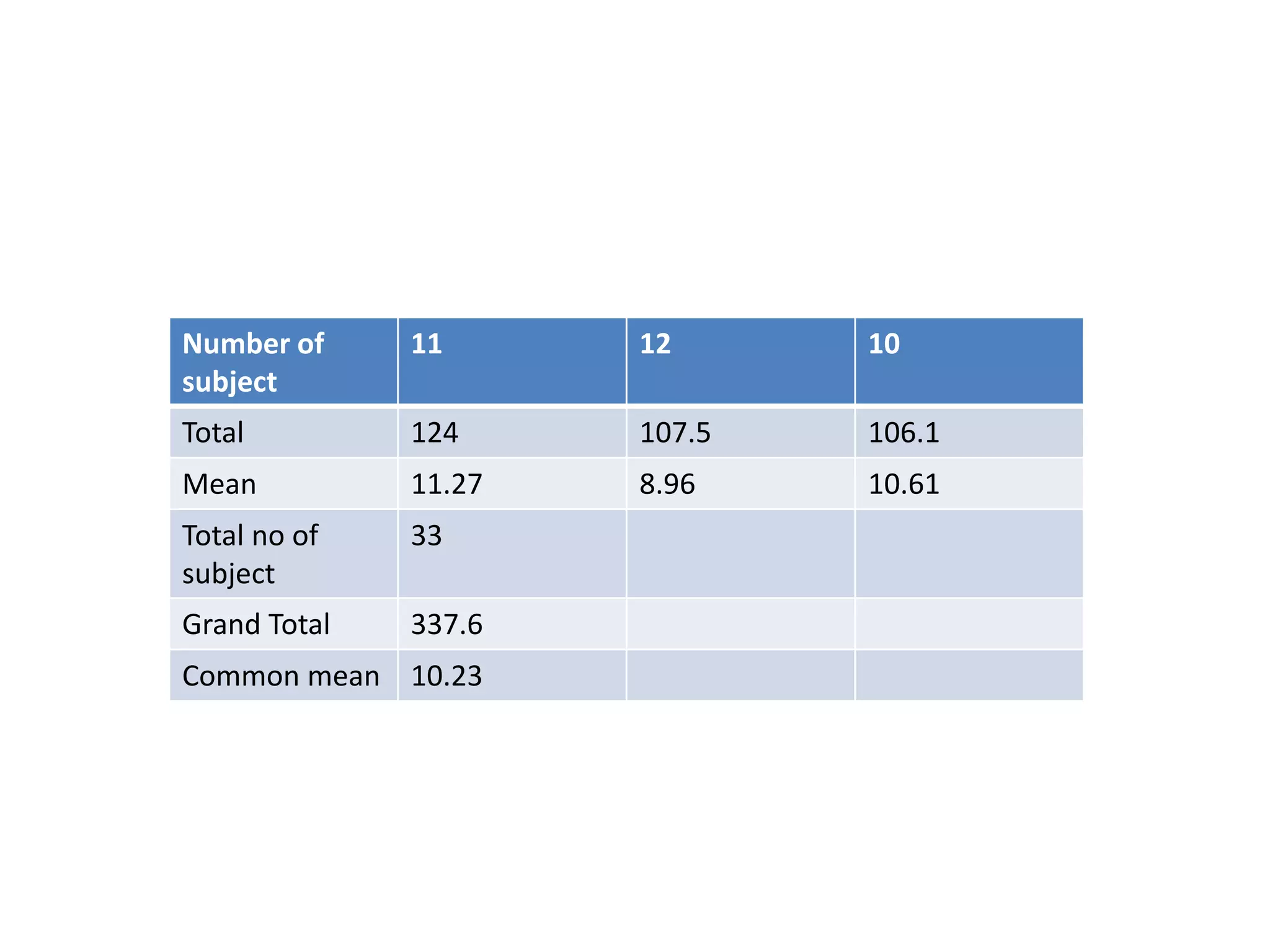
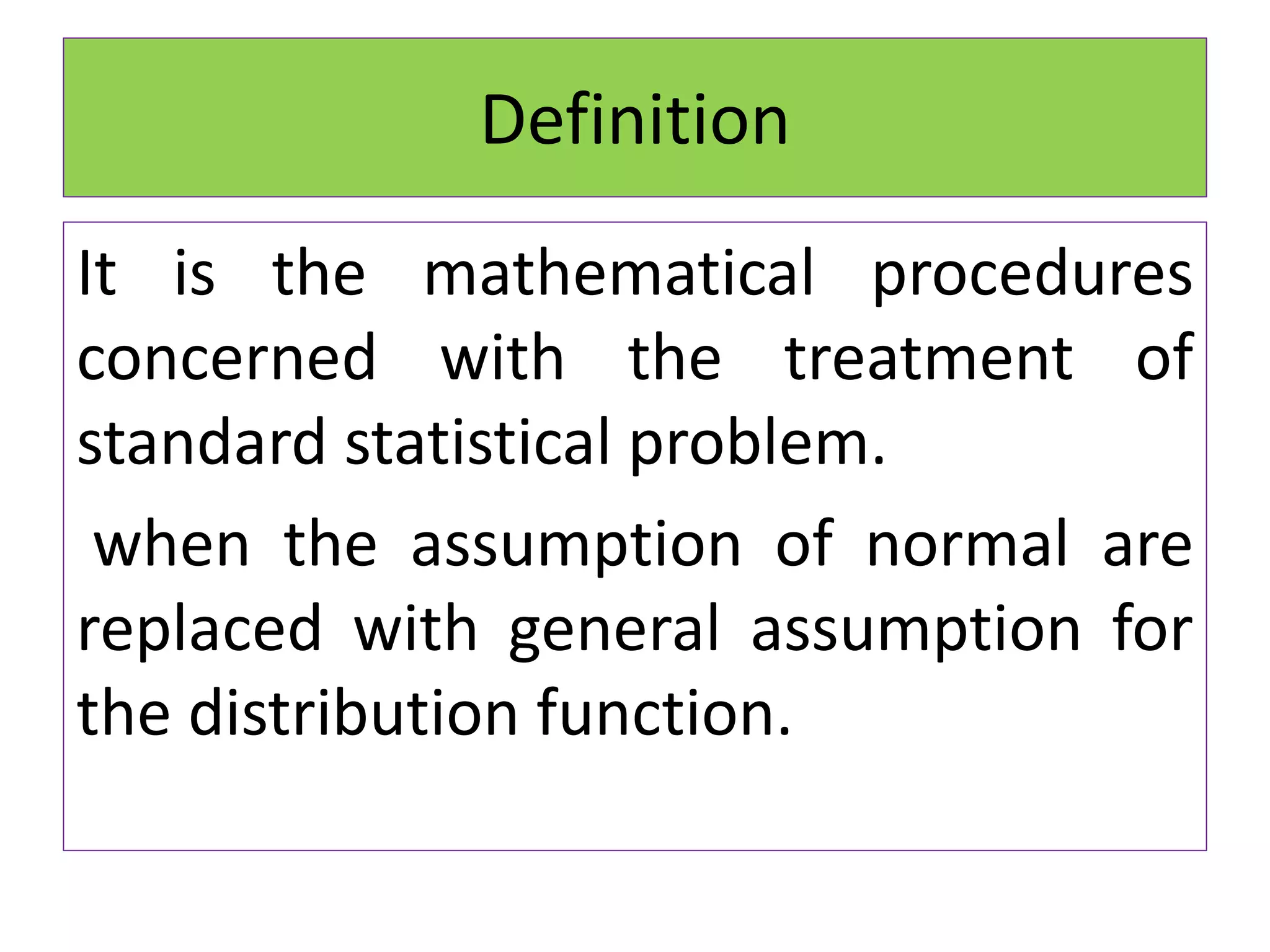
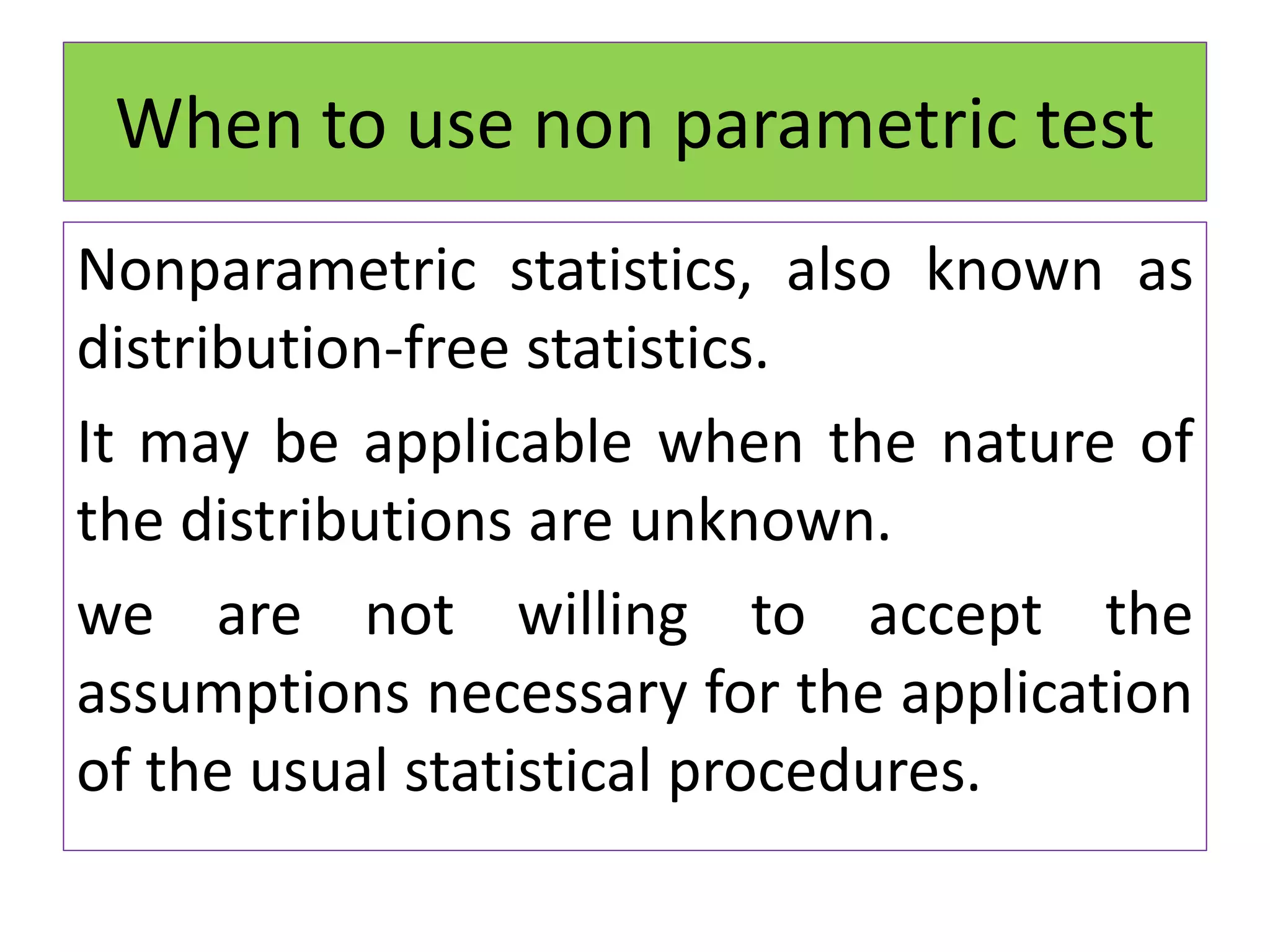
The document discusses non-parametric tests and provides information about when to use them. Non-parametric tests make fewer assumptions about the distribution of population values and can be used when sample sizes are small or the data is ordinal. Examples of non-parametric tests provided include the sign test, chi-square test, Mann-Whitney U test, and Kruskal-Wallis test. The general steps to perform a non-parametric test are also outlined.





![• If the sample size is small [as 6] there is no
alternative to use a non parametric test unless
the nature of population distribution is
precisely known.
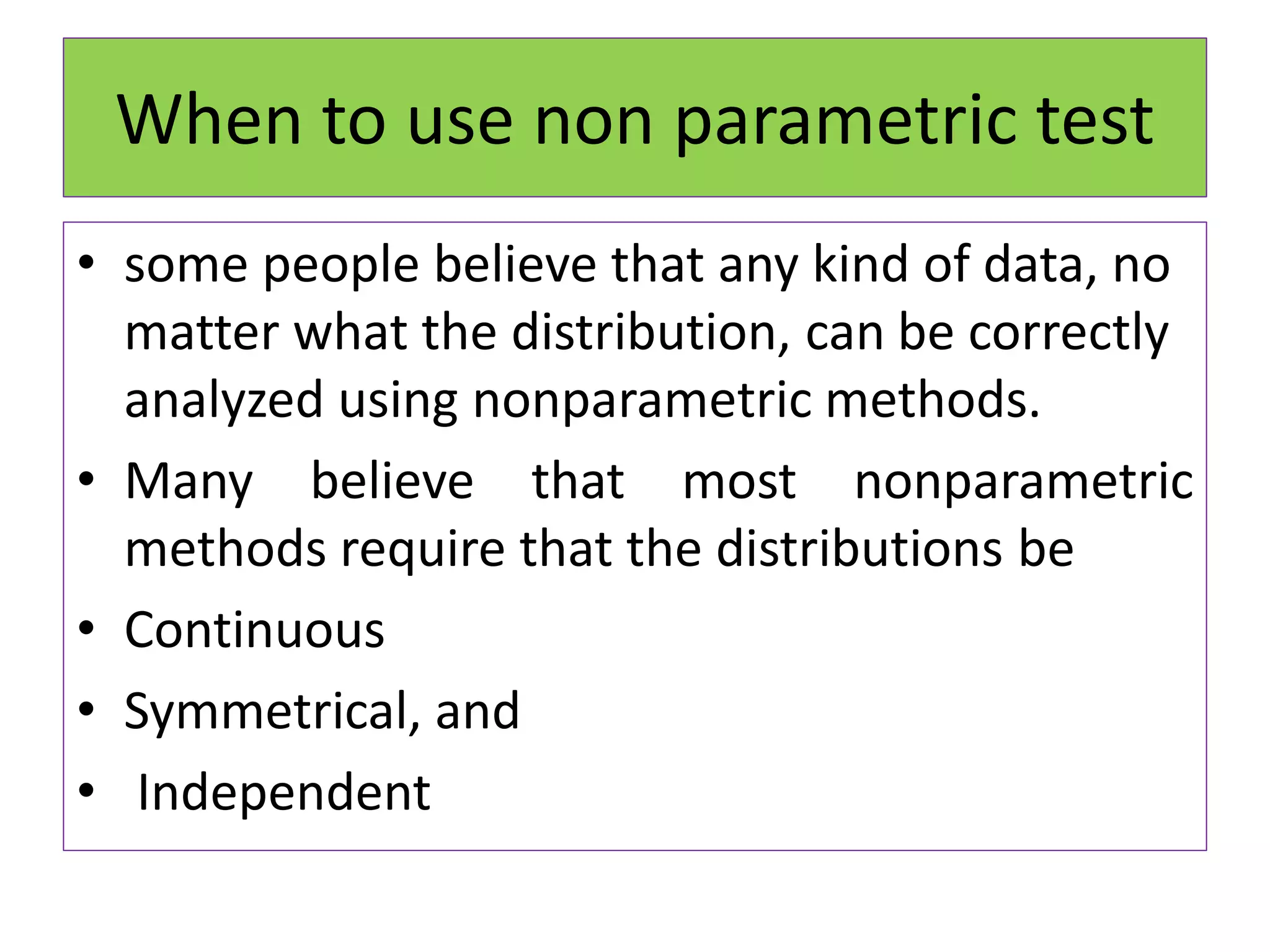
• Easy to learn
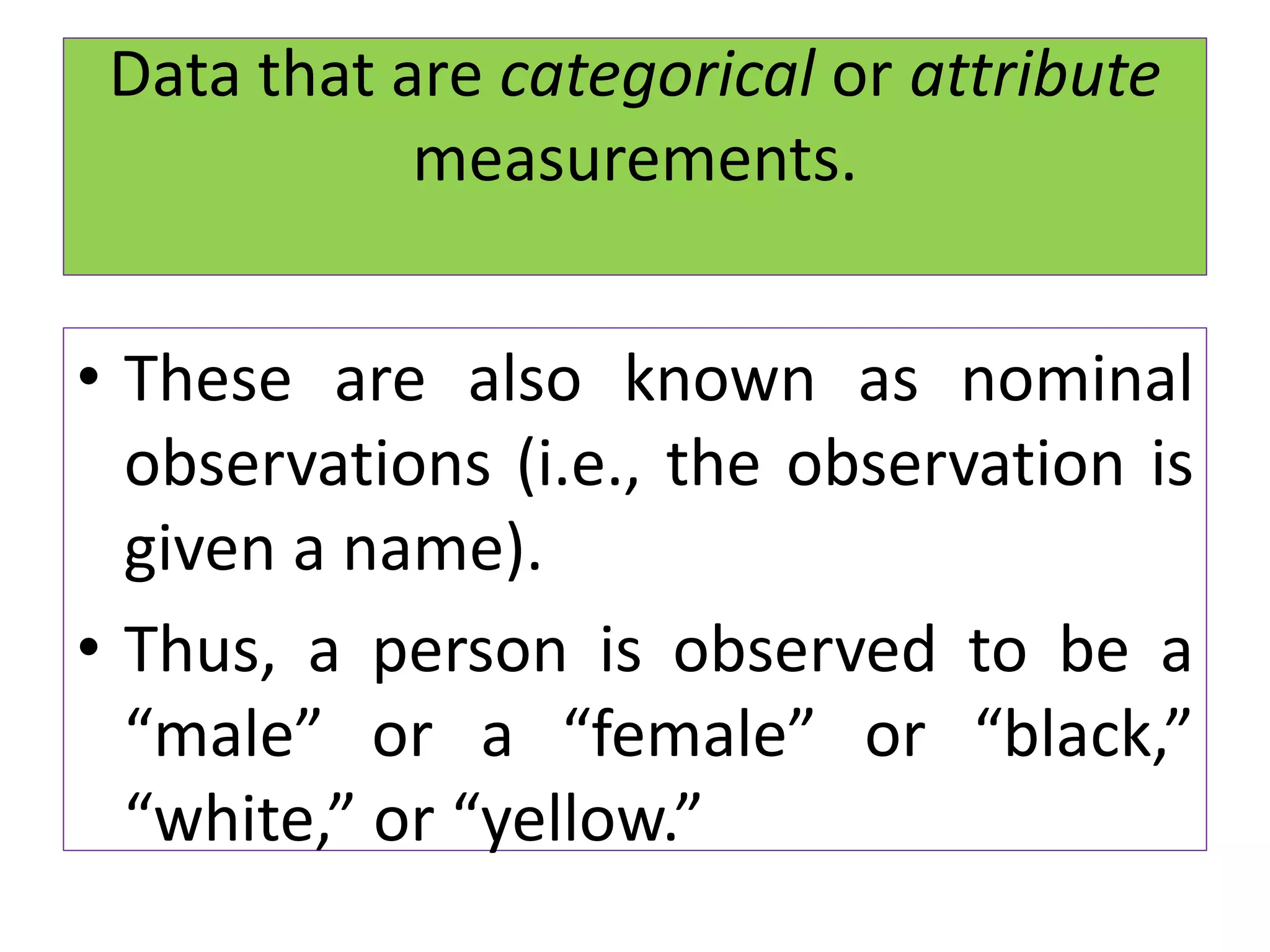
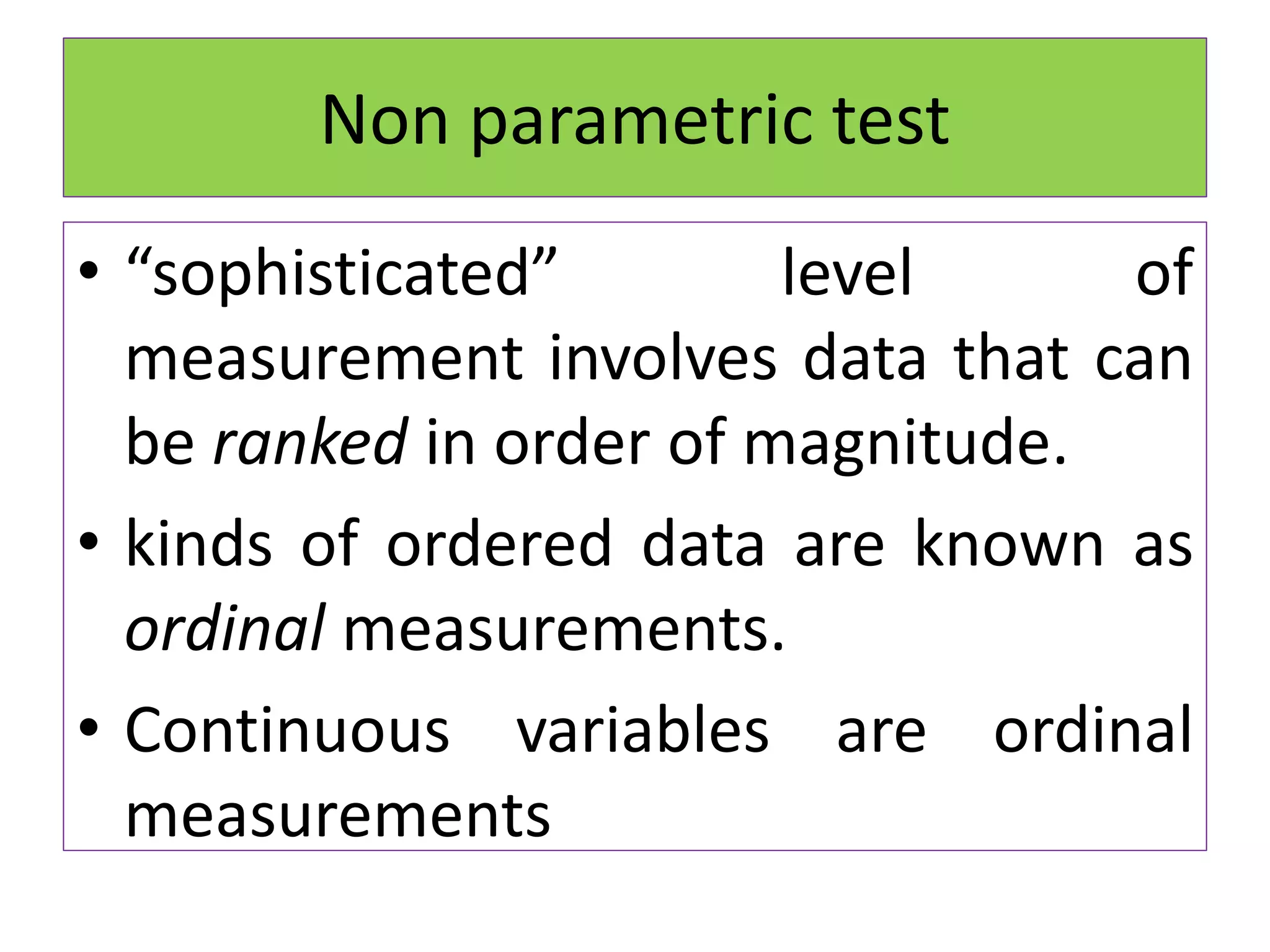
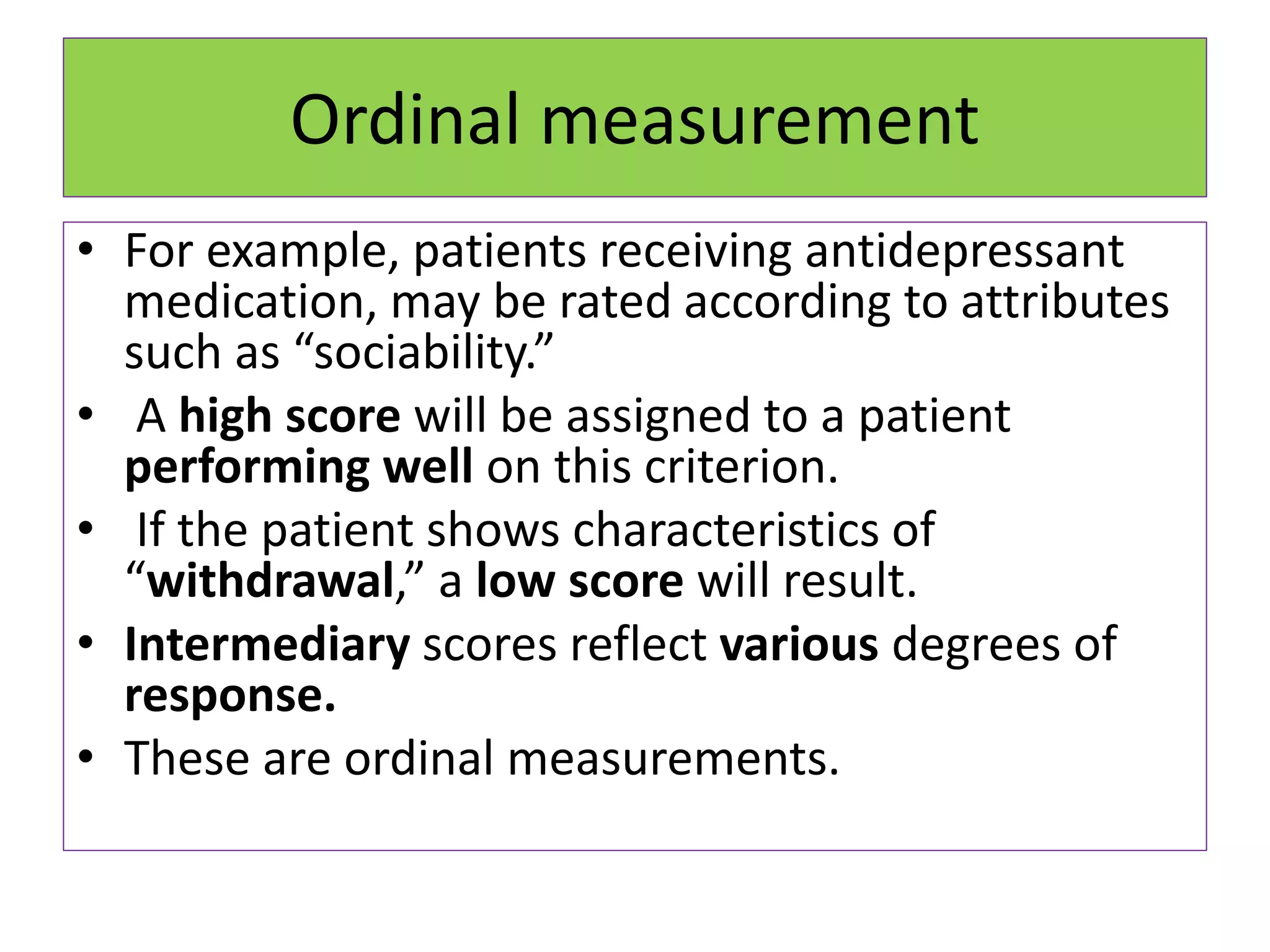
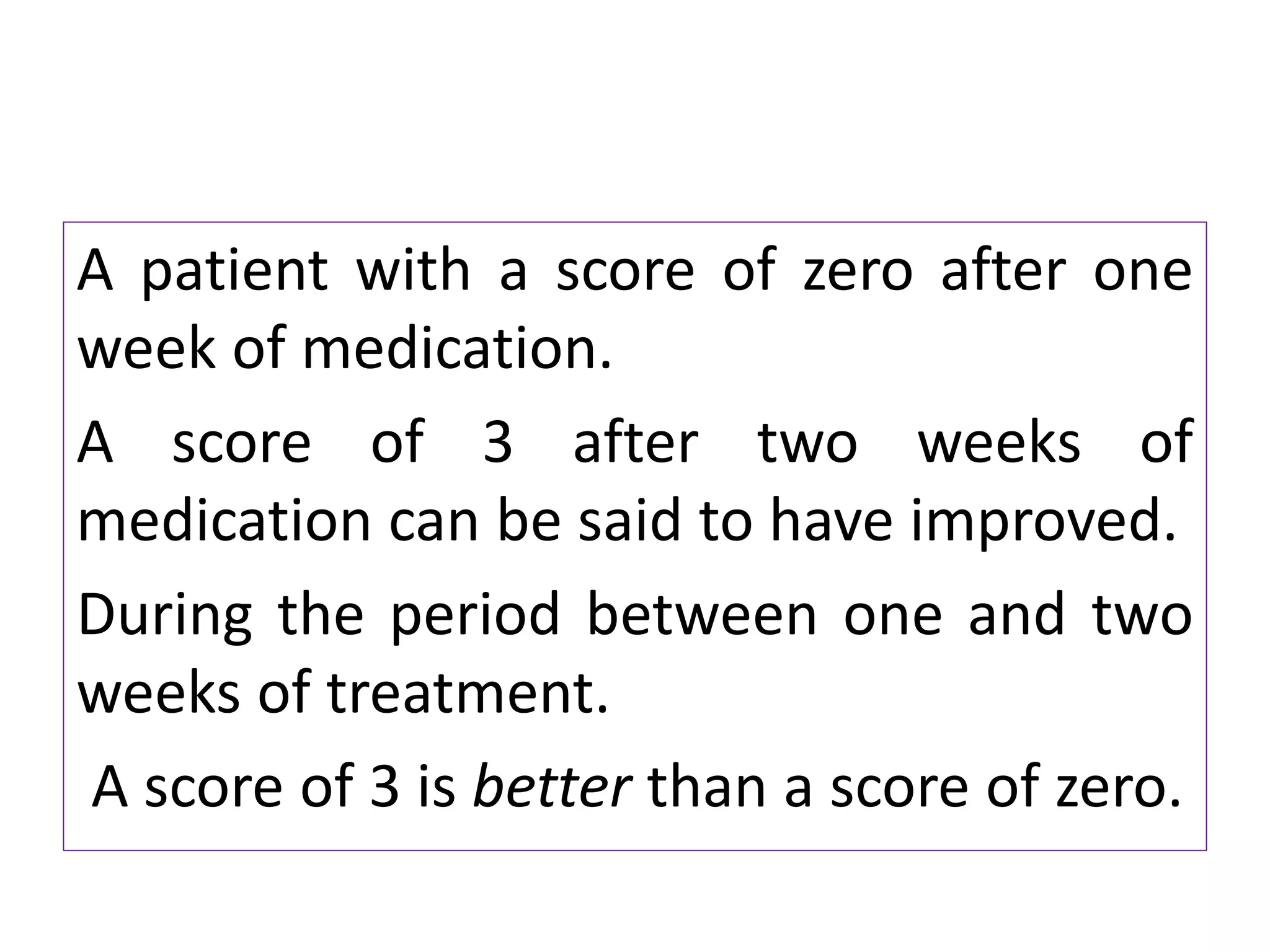
• It is applicable when the observation are
nominal, ordinal [ ranked ] , or measured
imprecisely
Advantage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nonparametrictest-210419073306/75/Non-parametric-test-17-2048.jpg)