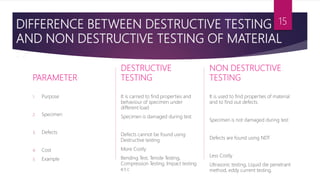
Destructive and non-destructive testing are two types of material testing. Destructive testing involves testing specimens until failure to understand material performance under loads, while non-destructive testing evaluates material properties without damage using techniques like ultrasound, dye penetrant, and eddy current. Common destructive tests include tensile testing and impact testing, while common non-destructive tests include ultrasound, dye penetrant, eddy current, and visual inspection. Destructive testing yields more information but is more costly, while non-destructive testing allows evaluation without compromising the sample.