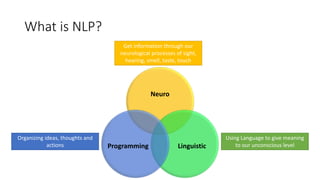
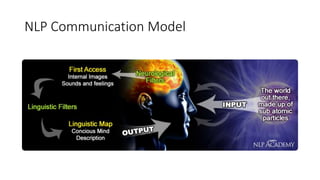
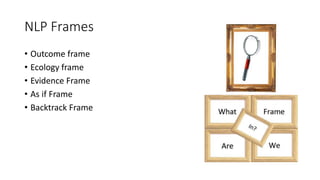
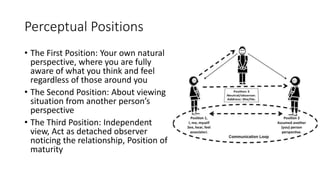
This document provides an overview of key concepts in Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP). It discusses the history and definition of NLP, focusing on how it uses language patterns and metaphors to communicate with the subconscious mind. Several core NLP concepts and techniques are then outlined, including the NLP communication model, different NLP frames, states, the meta model, perceptual positions, Disney's creative strategy, the TOTE model, and feedforward. The document aims to introduce readers to NLP and some of its fundamental principles and applications.