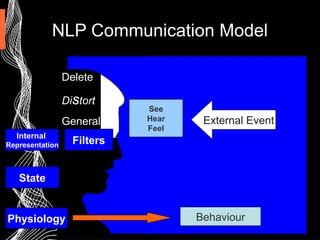
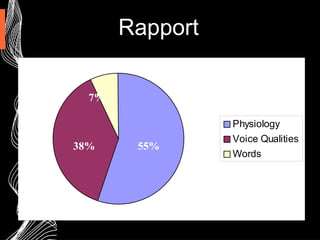
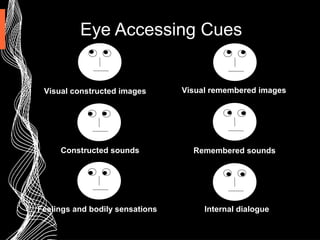
This document provides an introduction to Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) and sales excellence. It discusses that NLP focuses on how people think and communicate effectively to influence others and achieve desired outcomes. The key facets of NLP discussed are building rapport, focusing on outcomes, paying attention to sensory cues from others, and having flexible behaviors. Calibration, communication models, presuppositions, metaphors and modeling high performers are techniques presented to help improve sales skills.