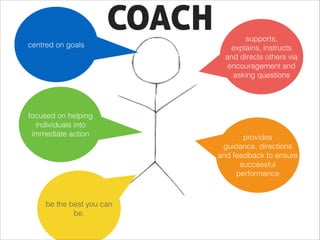
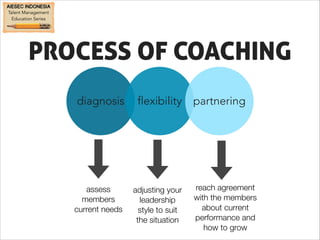
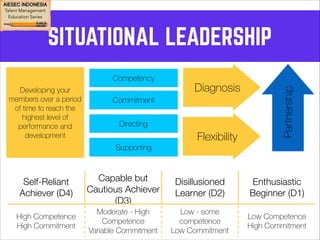
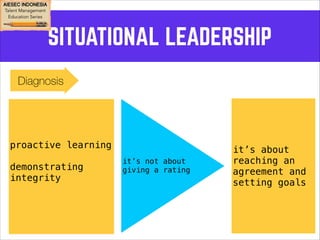
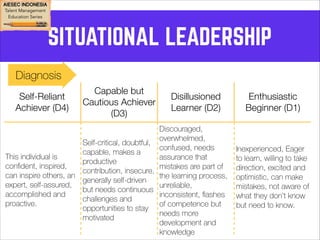
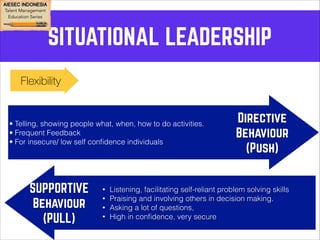
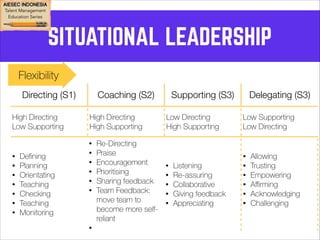
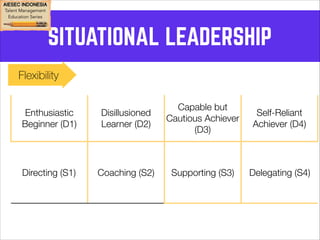
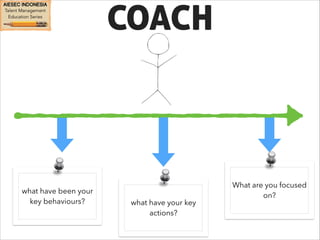
This document outlines coaching techniques for leaders in AIESEC Indonesia. It discusses that AIESEC Indonesia needs to produce more leaders and leadership experiences. It then defines what a coach is and says that every team leader in AIESEC Indonesia should be a coach. It introduces situational leadership theory and the four developmental levels of members. It explains the coaching process of diagnosis, flexibility in leadership style, and partnering with members to set goals. The overall document provides guidance to team leaders on how to coach members at different developmental levels through goal setting, feedback, and adjusting their leadership approach.