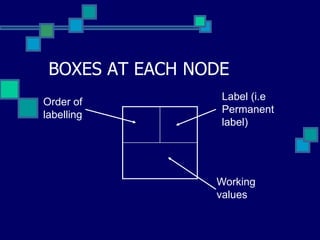
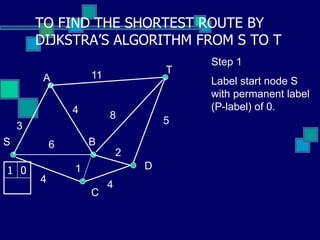
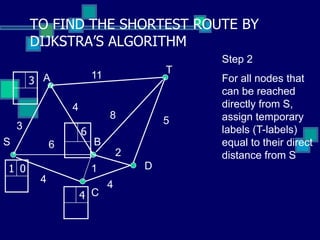
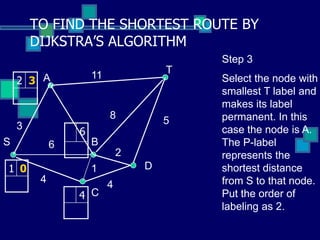
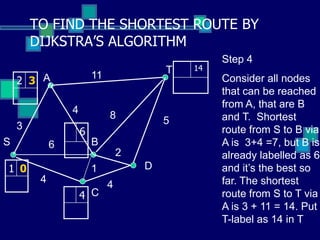
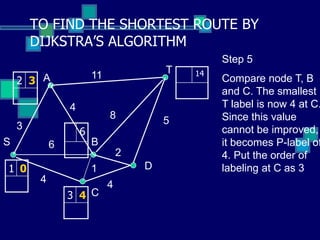
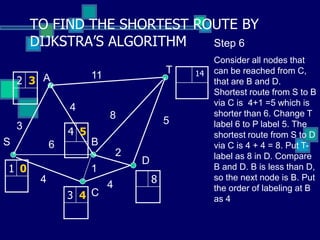
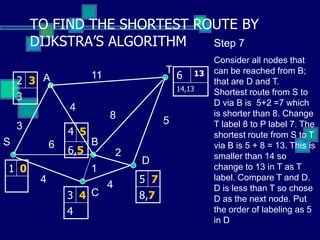
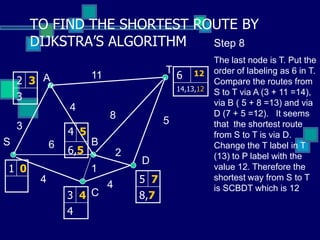
This document describes Dijkstra's algorithm, a greedy algorithm used to find the shortest paths between nodes in a graph. It explains that Dijkstra's algorithm works by assigning permanent labels to nodes starting with the source node, then iteratively assigning temporary labels to neighboring nodes to track the shortest path distances from the source. The algorithm is demonstrated on a sample graph with 6 nodes labeled A through T, showing how it progressively assigns labels to nodes in order to find the shortest path from node S to node T.