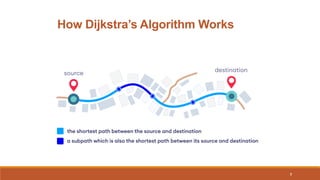
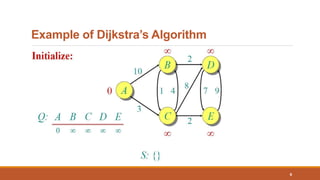
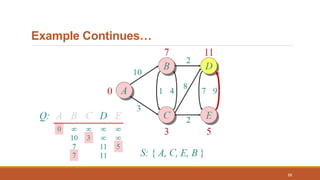
The document presents Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm, developed by Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956, which solves the single source shortest path problem in both directed and undirected graphs. It outlines the algorithm's complexity, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as its applications in fields like digital mapping and network routing. Additionally, the document includes detailed examples and pseudocode to illustrate how the algorithm operates.