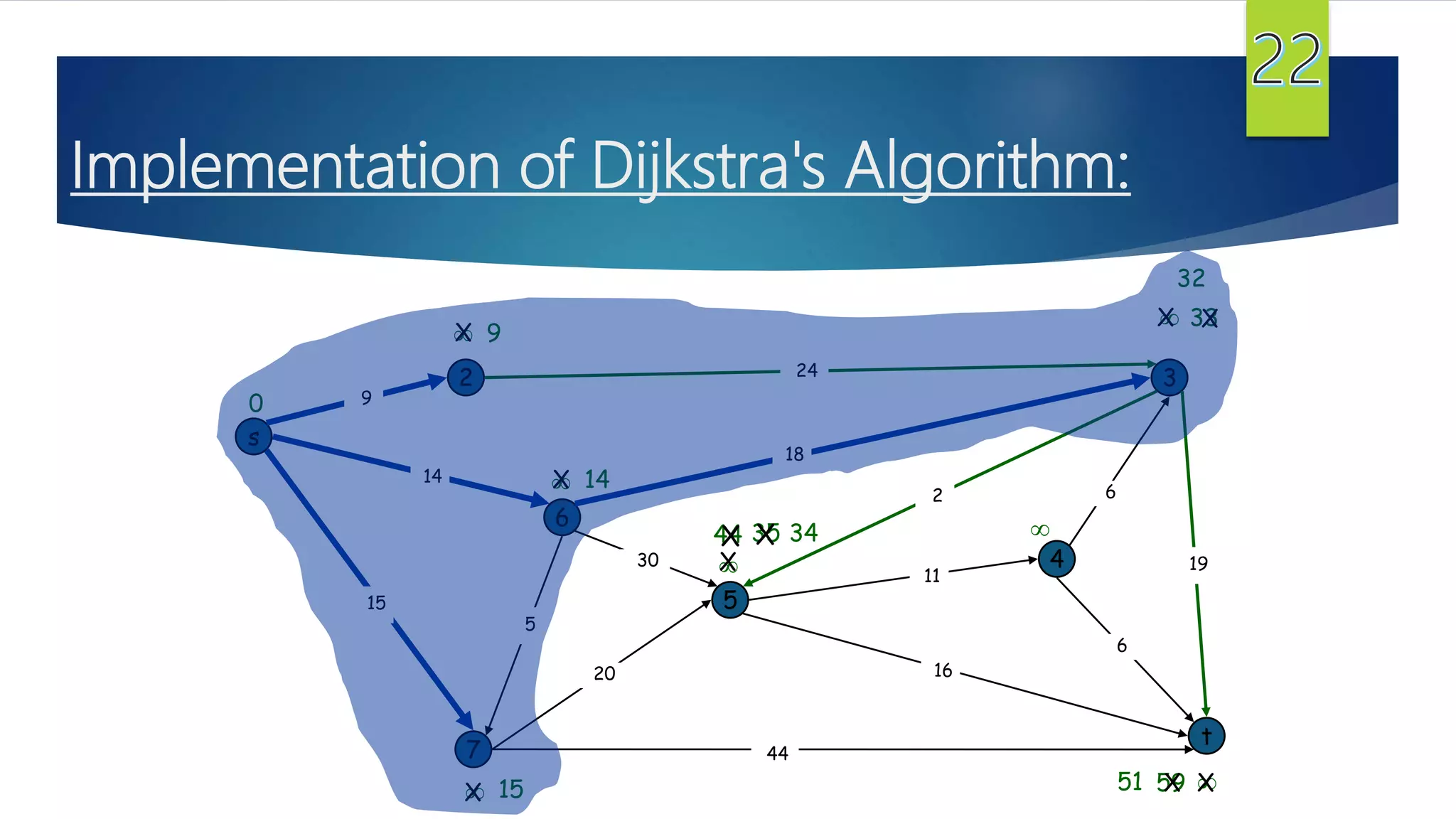
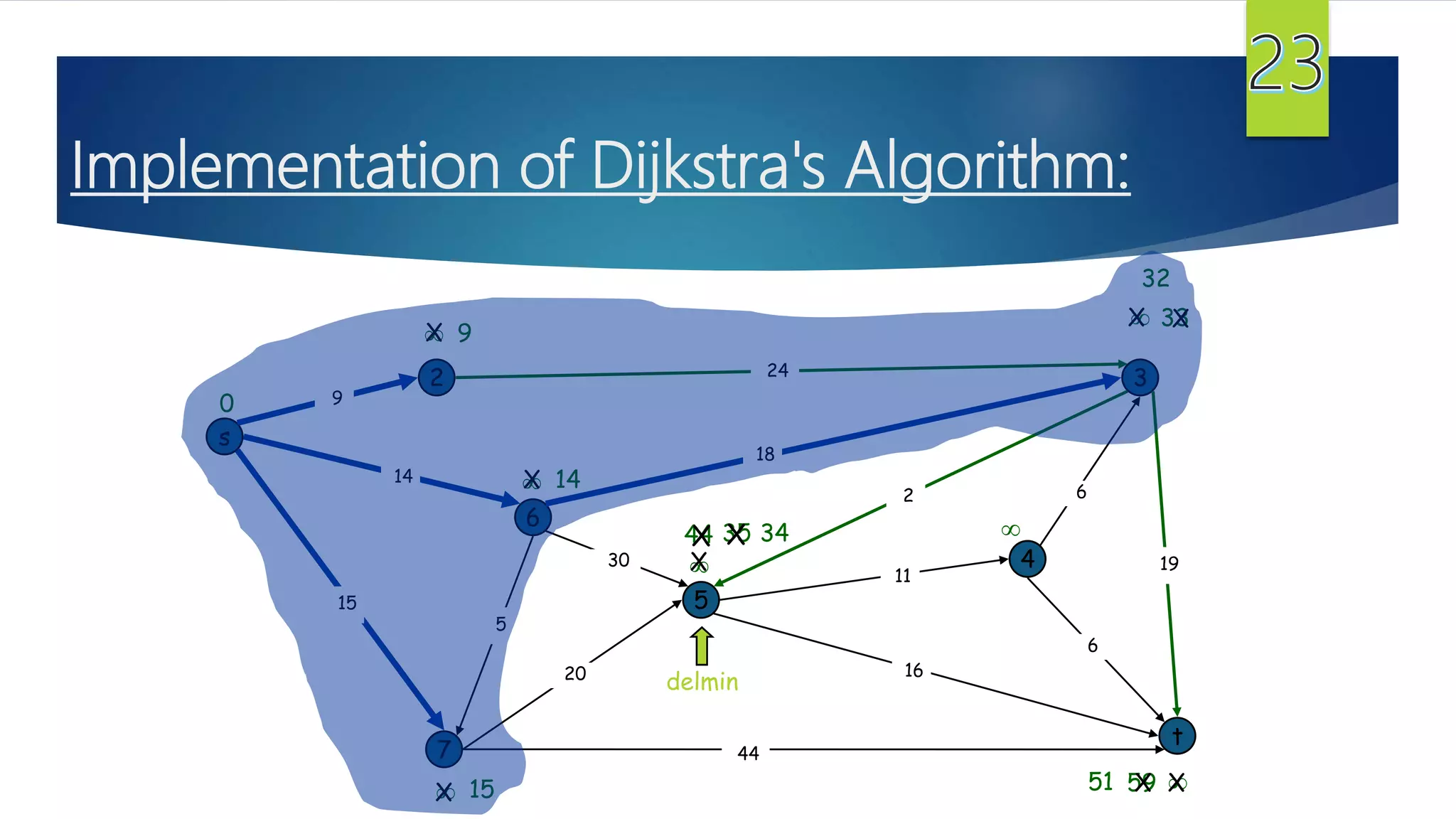
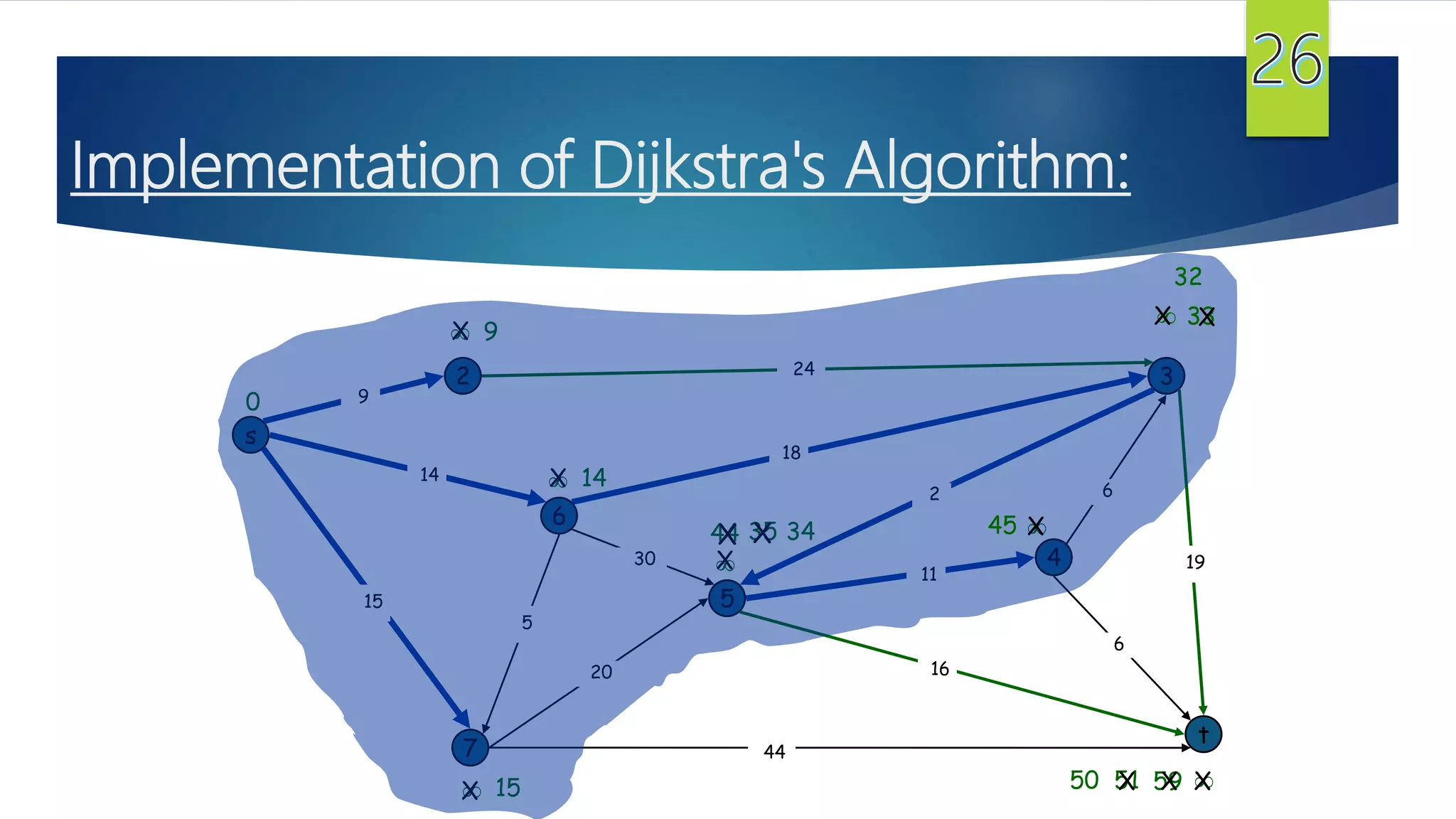
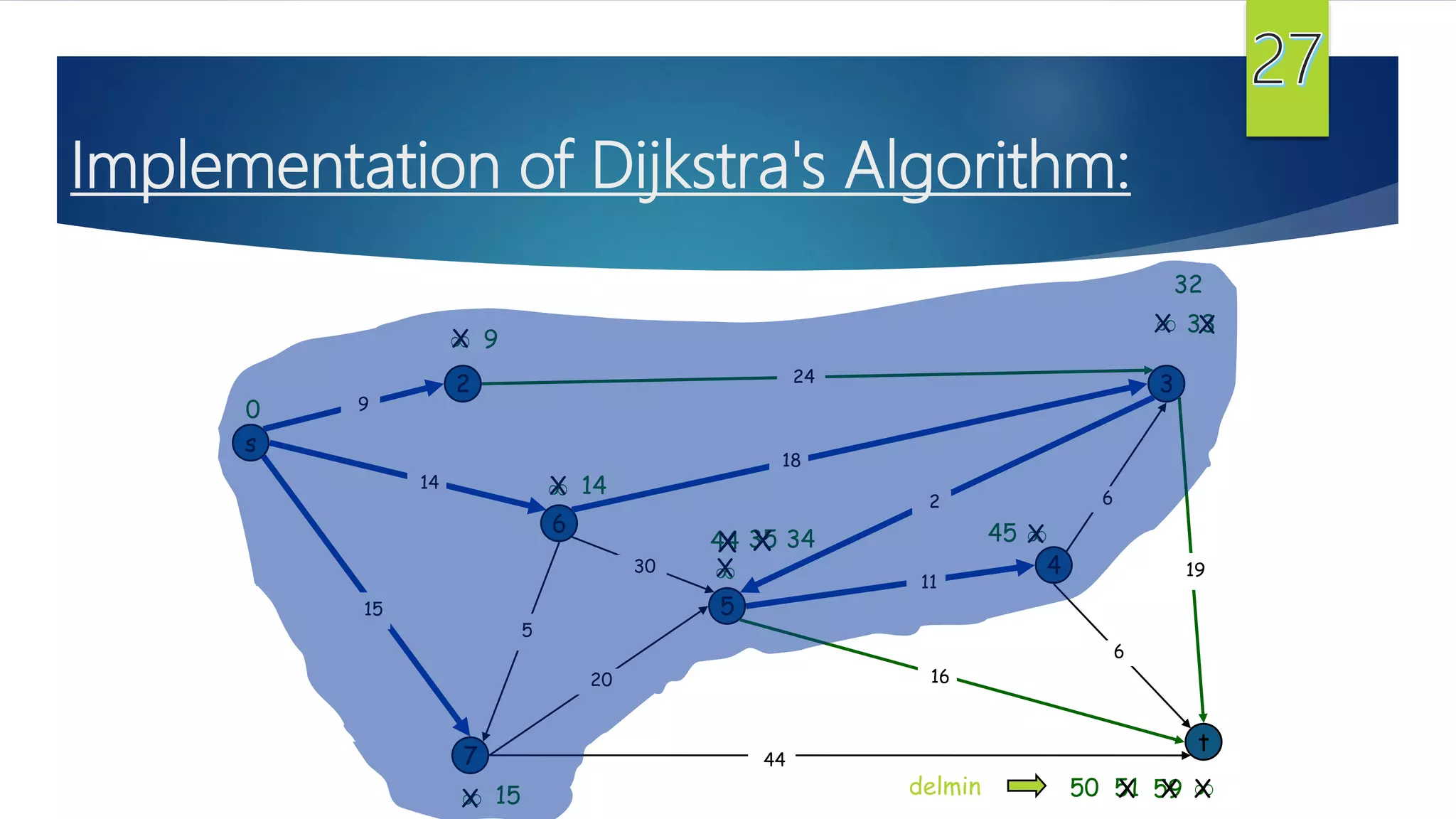
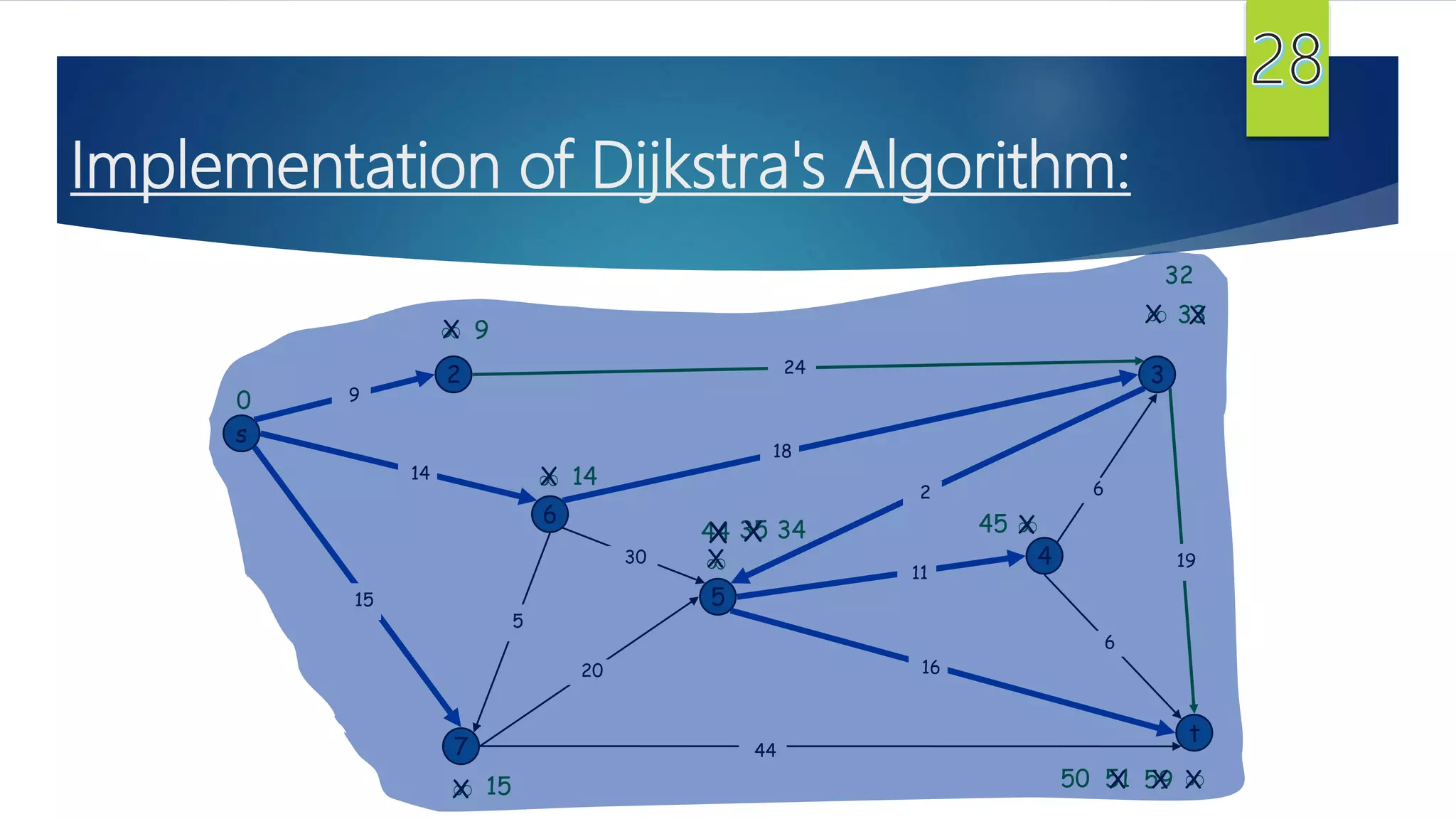
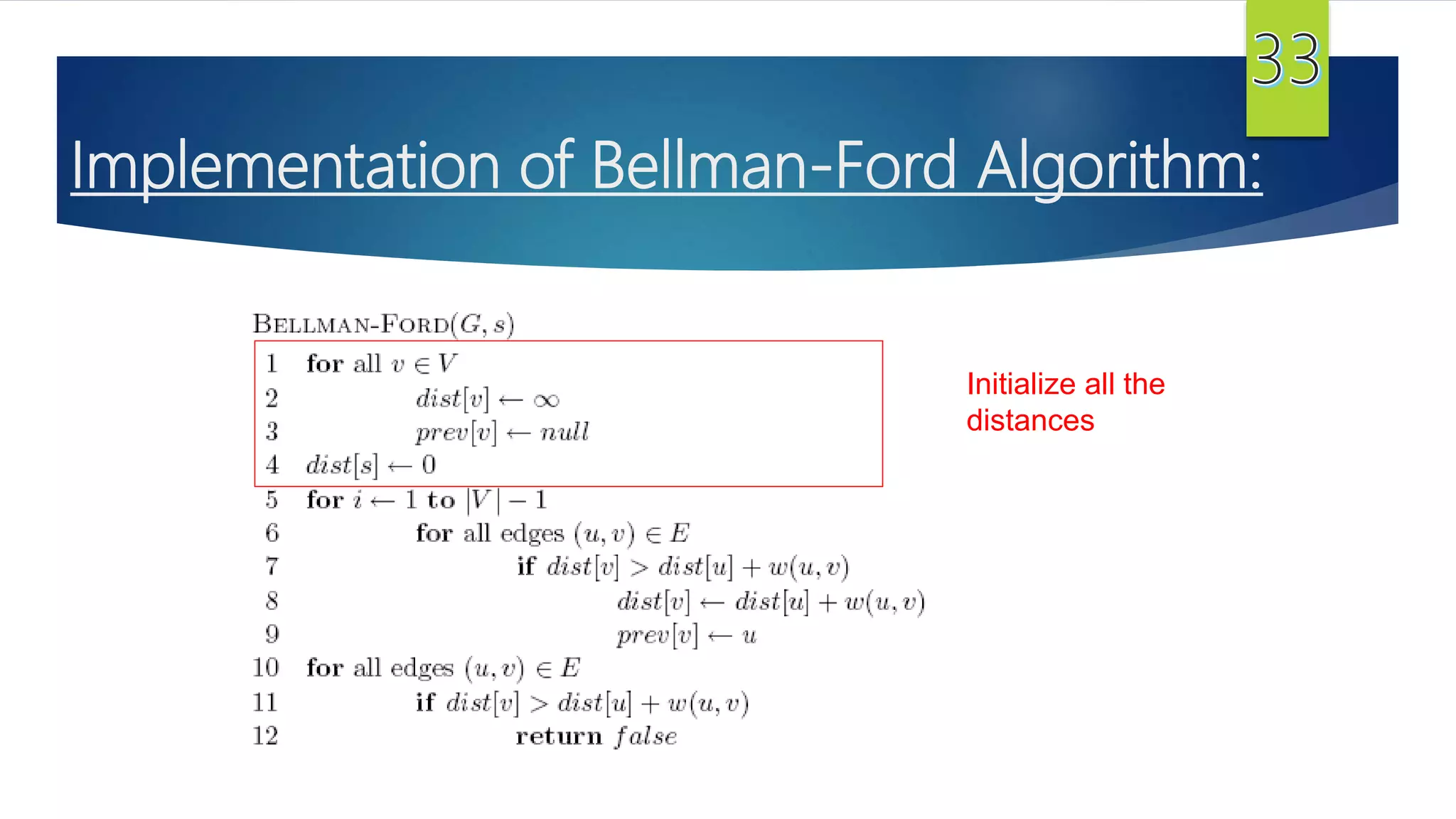
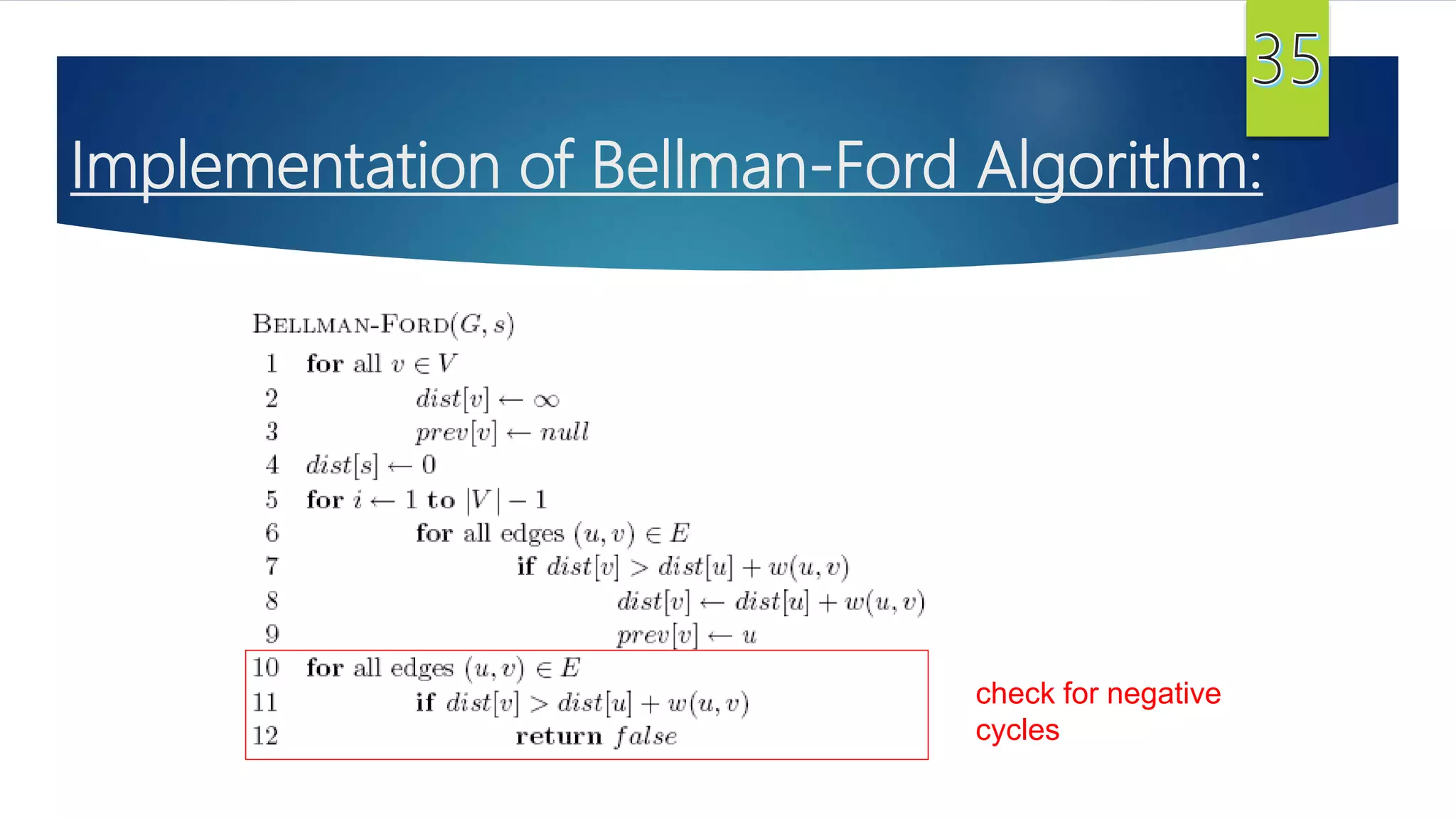
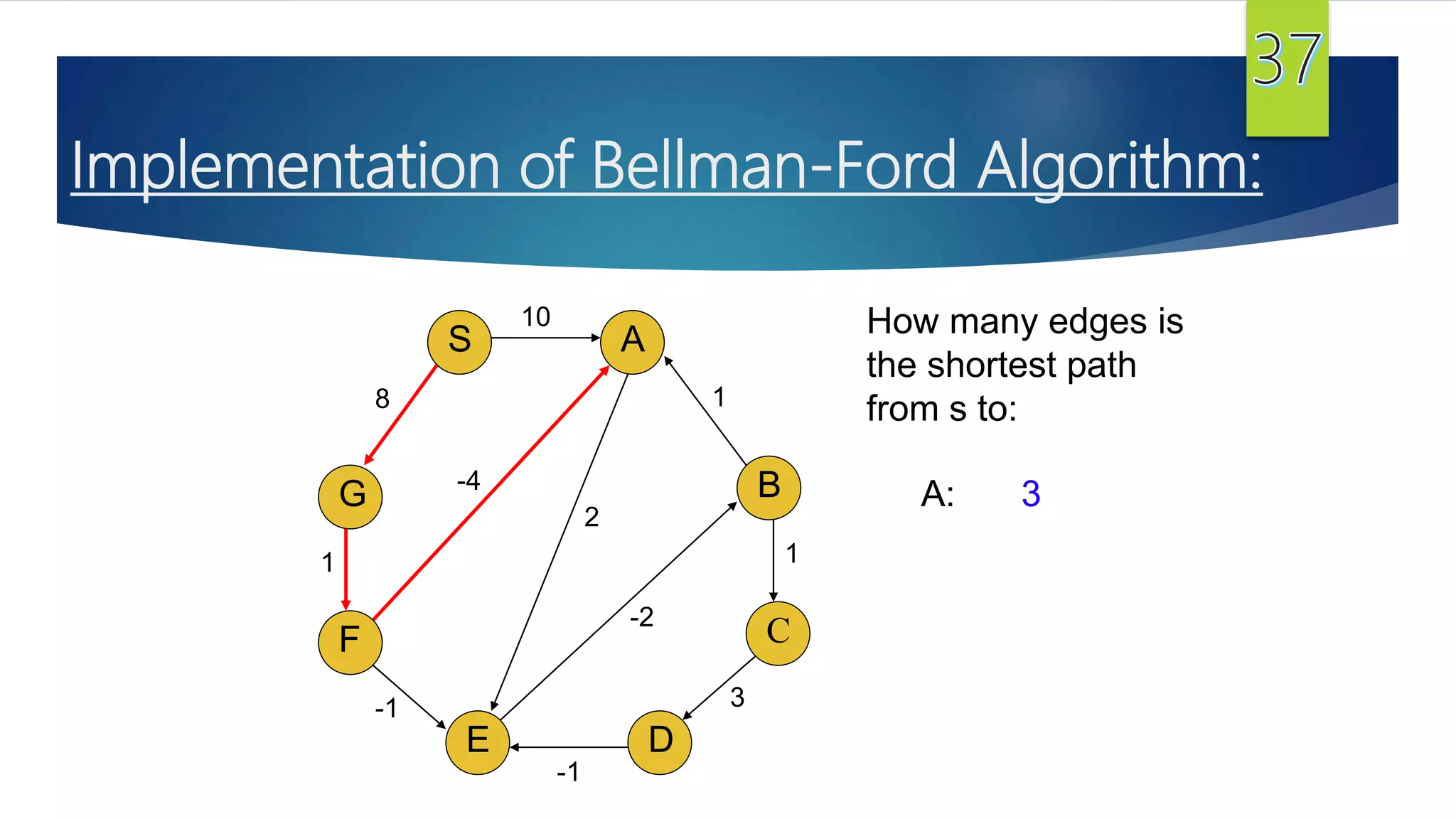
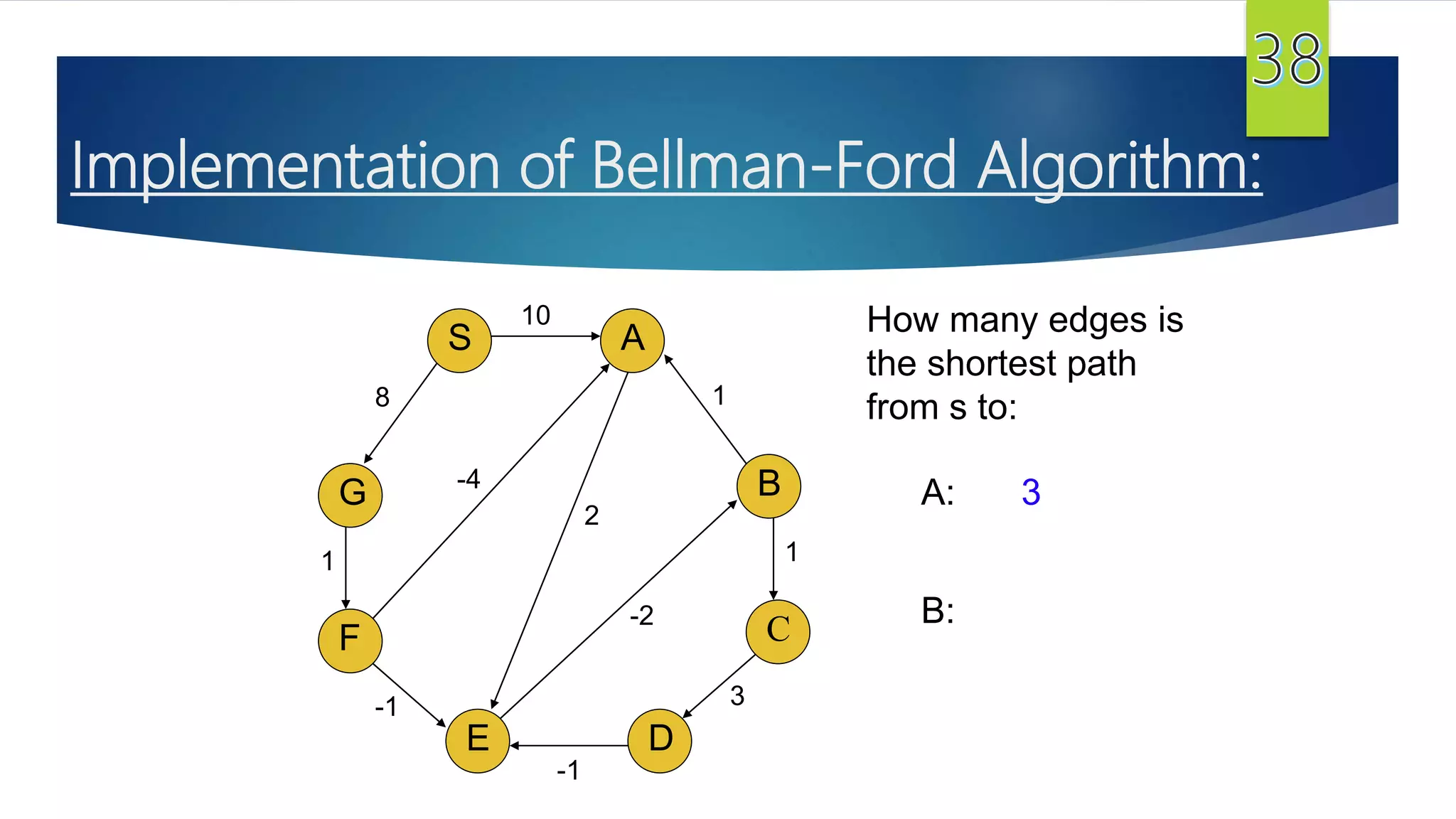
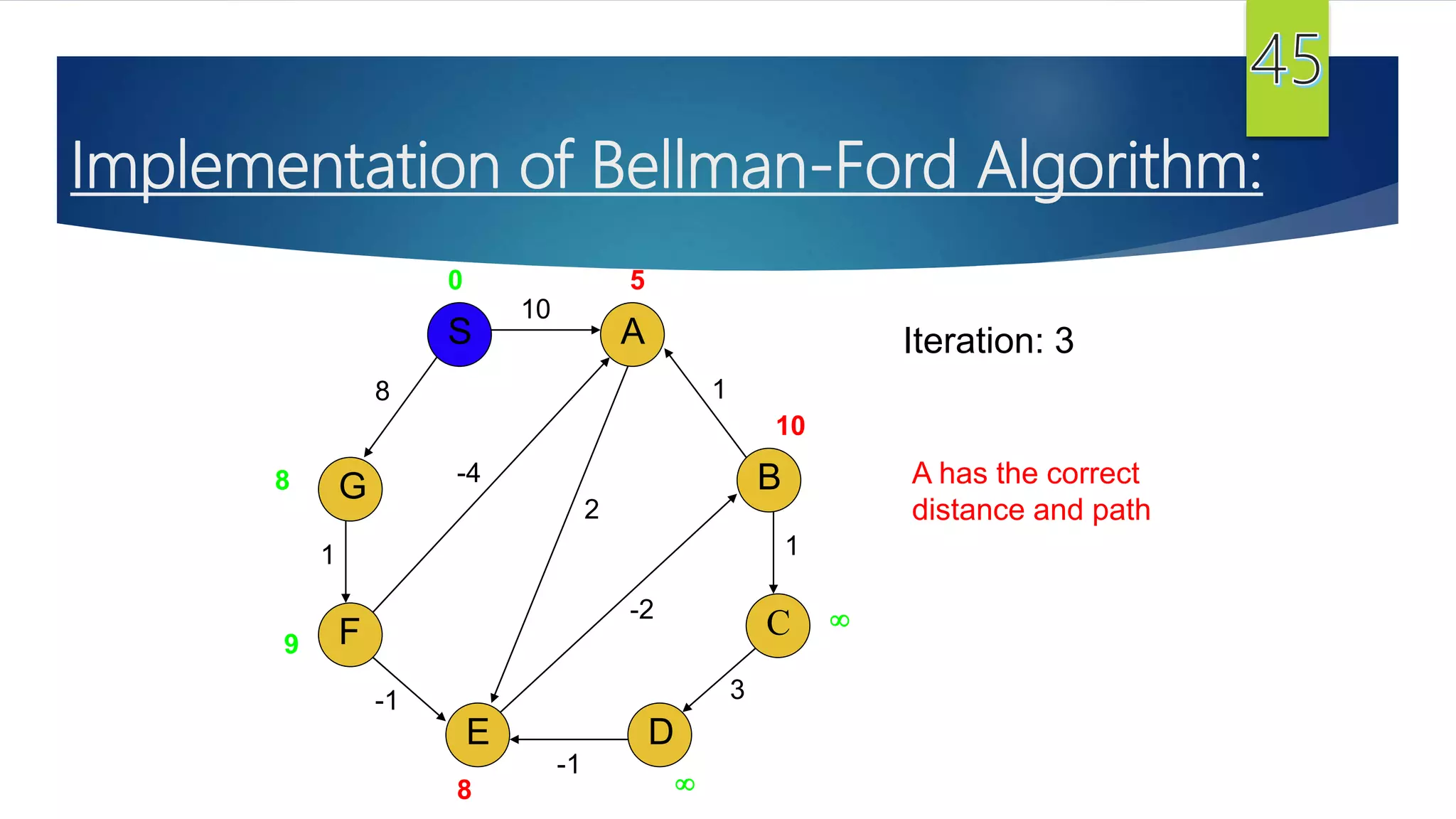
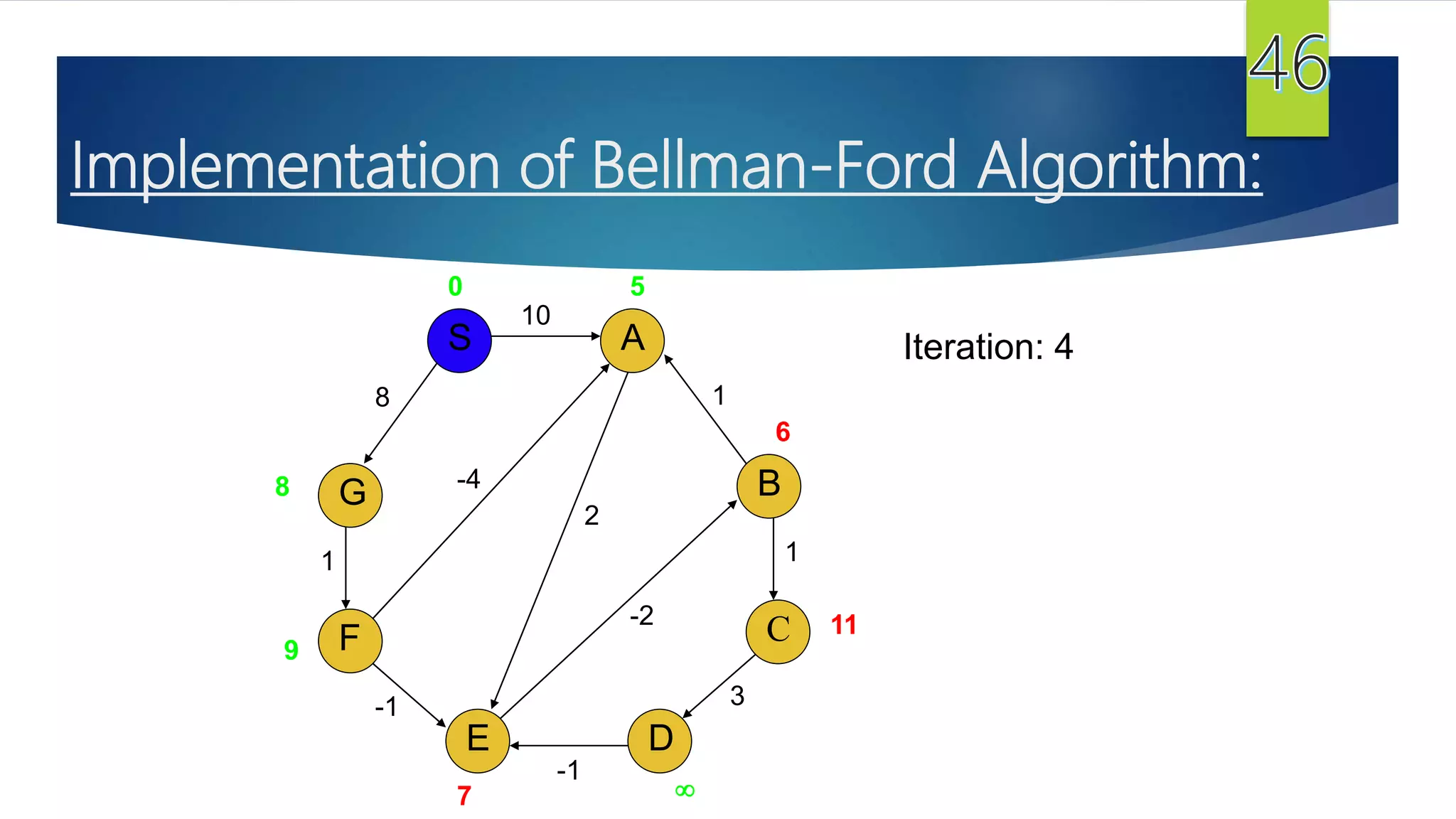
The document presents a detailed overview of the single-source shortest path problem, discussing algorithms such as Dijkstra's and Bellman-Ford, their implementations, and conditions for their effectiveness. It underscores that Dijkstra's algorithm fails in graphs with negative weight edges, while the Bellman-Ford algorithm is capable of handling such scenarios. The presentation includes initialization, relaxation techniques, and examples illustrating the algorithms' applications and limitations.




![Representation of Single Source Shortest Path:
For each vertex v V:
d[v] = δ(s, v): a shortest-path estimate
Initially, d[v]=∞
Reduces as algorithms progress
[v] = predecessor of v on a shortest path from s
If no predecessor, [v] = NIL
induces a tree—shortest-path tree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpathbyemad-200917190226/75/Single-sourceshortestpath-by-emad-6-2048.jpg)
![Initialization:
INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(V, s)
1. for each v V
2. do d[v] ←
3. [v] ← NIL
4. d[s] ← 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpathbyemad-200917190226/75/Single-sourceshortestpath-by-emad-7-2048.jpg)
![Relaxation:
Relaxing an edge (u, v) = testing whether we can improve the shortest path to v found so far by
going through u.
Example:
If d[v] > d[u] + w(u, v)
update d[v] and [v]
S 8
2
4
u
v
2 6
u v
4
RELAX(u,v,w)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/singlesourceshortestpathbyemad-200917190226/75/Single-sourceshortestpath-by-emad-8-2048.jpg)