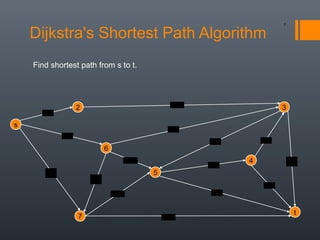
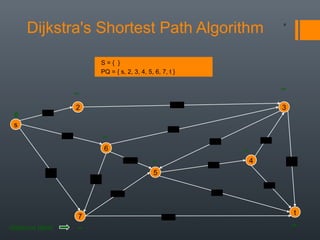
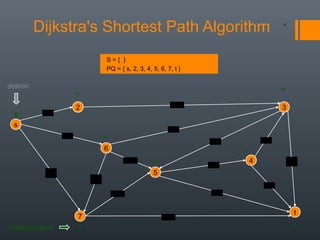
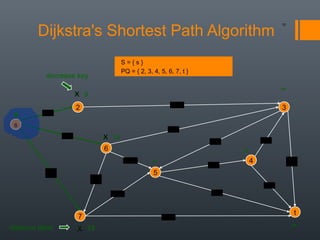
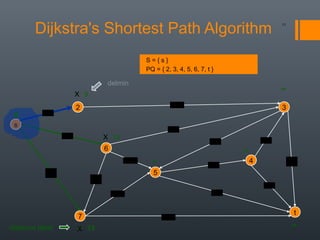
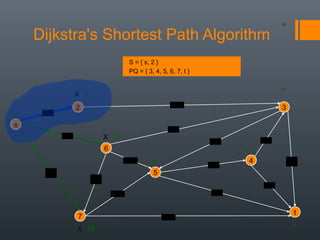
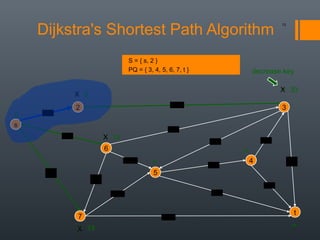
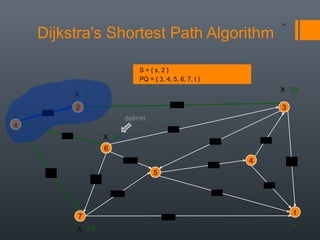
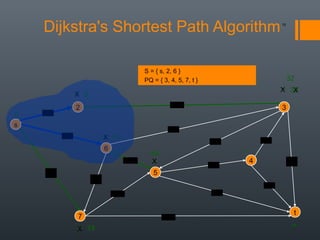
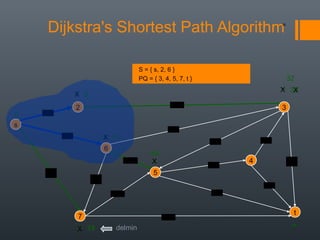
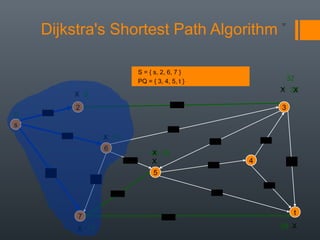
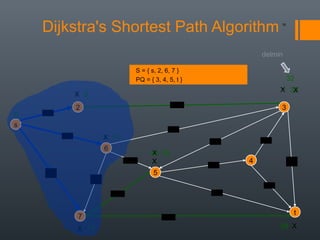
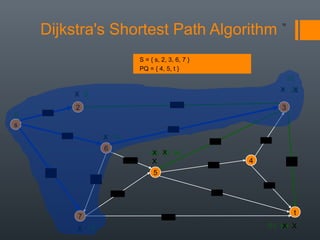
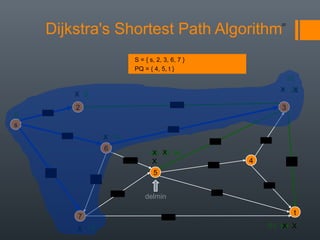
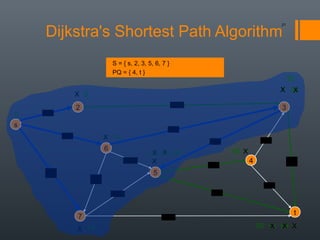
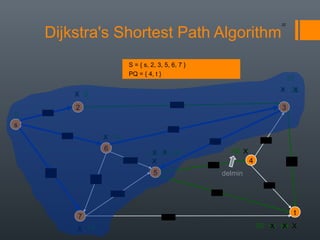
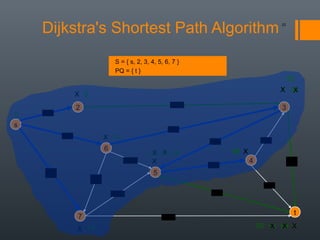
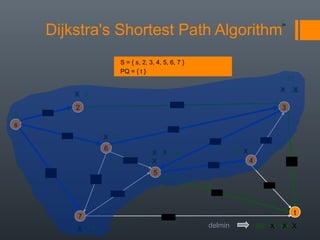
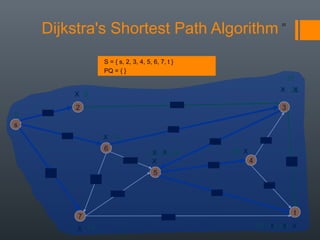
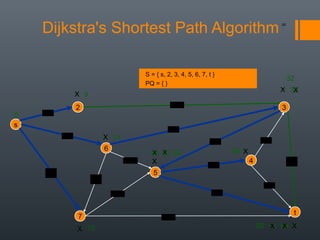
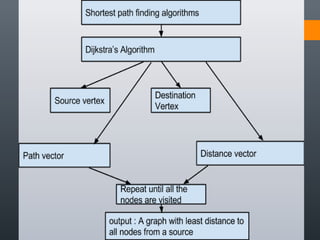
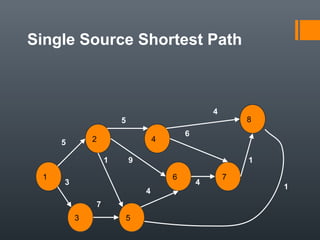
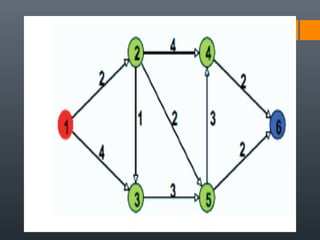
Dijkstra's algorithm is used to find the shortest path between a starting vertex and any other vertex in a graph with positive edge weights. It works by maintaining a distance label for each vertex, with the starting vertex's label set to 0. It then iteratively selects the unprocessed vertex with the smallest distance label and relaxes any incident edges that improve neighboring vertices' distance labels, until all vertices have been processed. Storing predecessor vertices allows reconstruction of the shortest path.


![Dijkstra's Algorithm
Input:
a weighted digraph G=(V,E) with positive edge weights
a source node s V∈
Initialization:
d[s]=0
for each vertex x V-s∈
d[x]=infinity
Mark all the vertices as unprocessed
Iteration:
for i=1 to |V|
Choose an unprocessed vertex x from V with minimum d[x]
Mark x as processed
for all y adj(x)∈
if d[y] > d[x]+w(x,y)
d[y] = d[x]+w(x,y)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150507094615-lva1-app6891/85/2-3-shortest-path-dijkstra-s-3-320.jpg)
![Dijkstra's Algorithm With PATH
Input:
a weighted digraph G=(V,E) with positive edge weights
a source node s V∈
Initialization:
d[s]=0 predecessor [ s ] = undefined
for each vertex x V-s∈
d[x]=infinity
Mark all the vertices as unprocessed
Iteration:
for i=1 to |V|
Choose an unprocessed vertex x from V with minimum d[x]
Mark x as processed
for all y adj(x)∈
if d[y] > d[x]+w(x,y)
d[y] = d[x]+w(x,y)
predecessor [ y ] = x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150507094615-lva1-app6891/85/2-3-shortest-path-dijkstra-s-4-320.jpg)
![Printing the Distance and path
for each vertex v
{
print Distance d[v]
print_path(v);
}
print_path(v)
{
if (v is undefined)
return;
else
print_path ( prdecessor[v] ); // note recursion
print v
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150507094615-lva1-app6891/85/2-3-shortest-path-dijkstra-s-5-320.jpg)
![C Code
for(i=1; i<=numofvertices; i++)
{
printf("nDistance : %d ::: Path: ",distance[i]);
print_path(i);
}
void print_path(int i)
{
if (i==-1)
return;
else
print_path(prdecessor[i]);
Assumes that vertices are
numbered from 1.
distance array and
predecessor array are
computed by dijkstra
algorithm
-1 is undefined vertex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150507094615-lva1-app6891/85/2-3-shortest-path-dijkstra-s-6-320.jpg)