Embed presentation
Downloaded 425 times

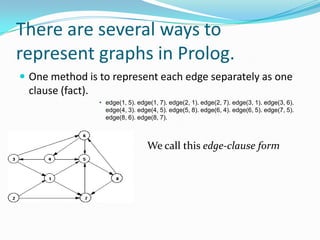







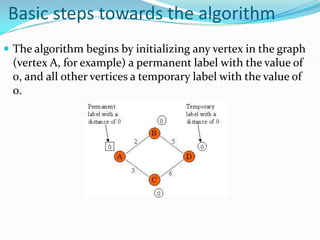
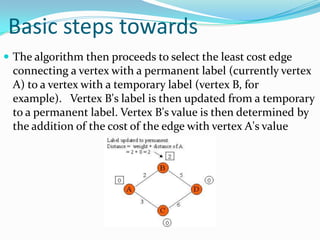
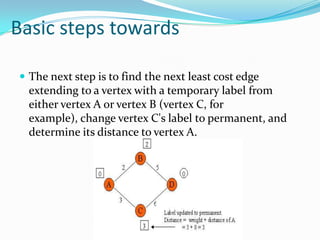
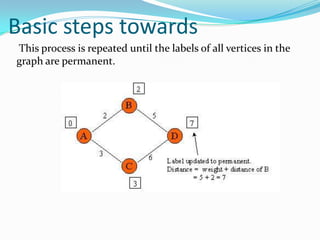
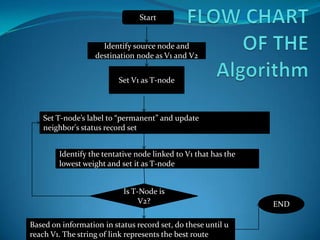







This document provides an overview of representing graphs and Dijkstra's algorithm in Prolog. It discusses different ways to represent graphs in Prolog, including using edge clauses, a graph term, and an adjacency list. It then explains Dijkstra's algorithm for finding the shortest path between nodes in a graph and provides pseudocode for implementing it in Prolog using rules for operations like finding the minimum value and merging lists.





















