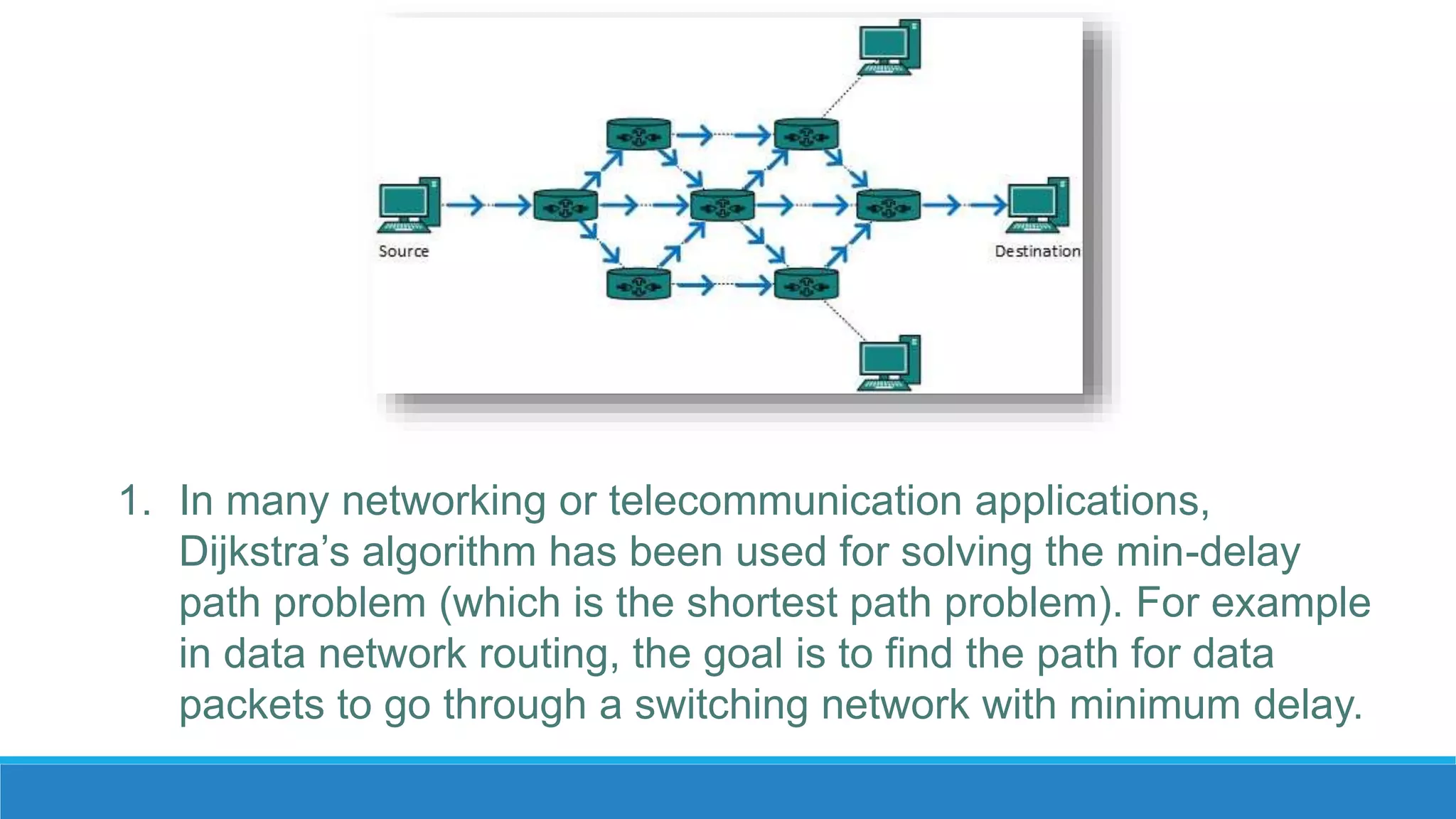
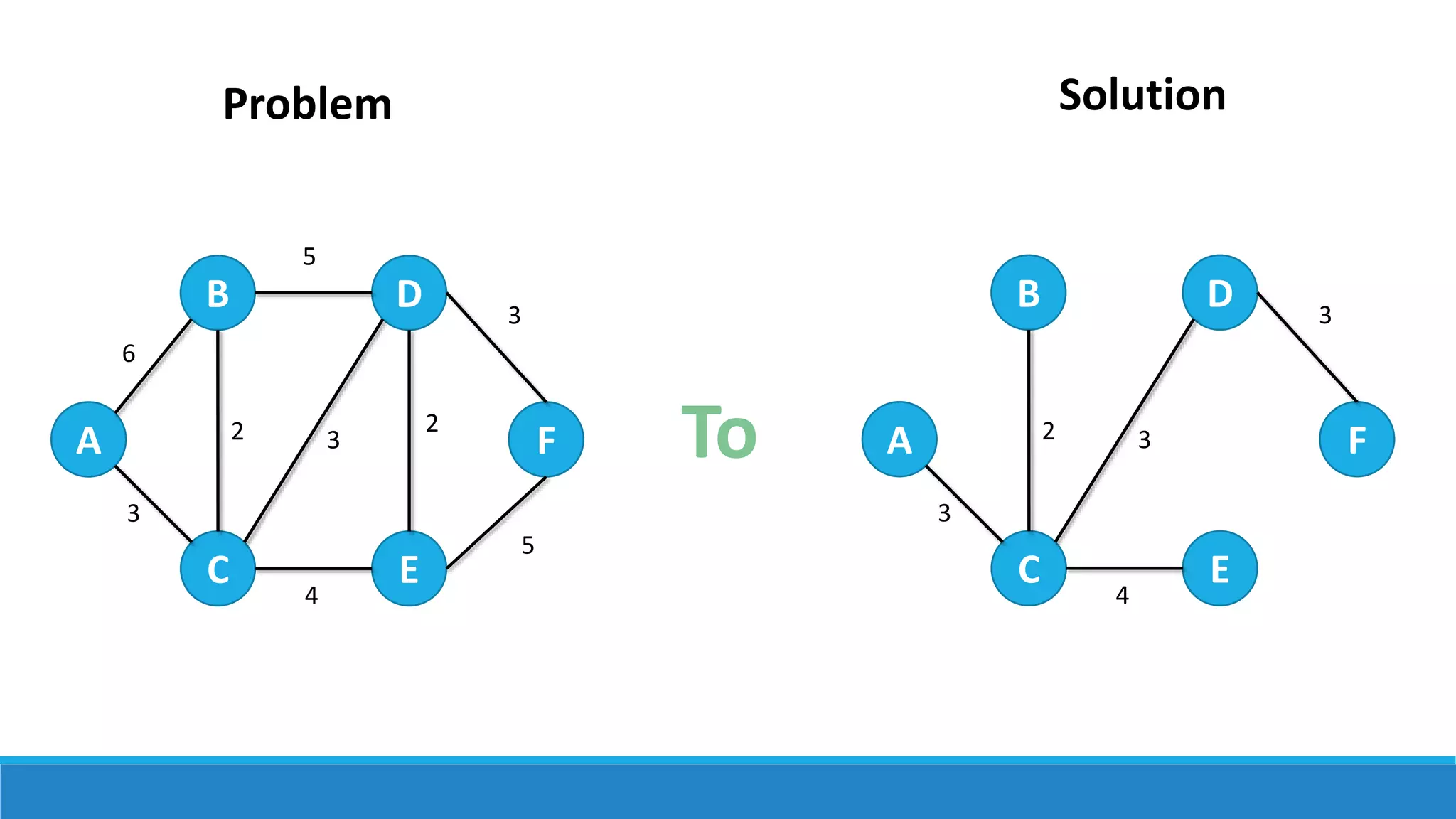
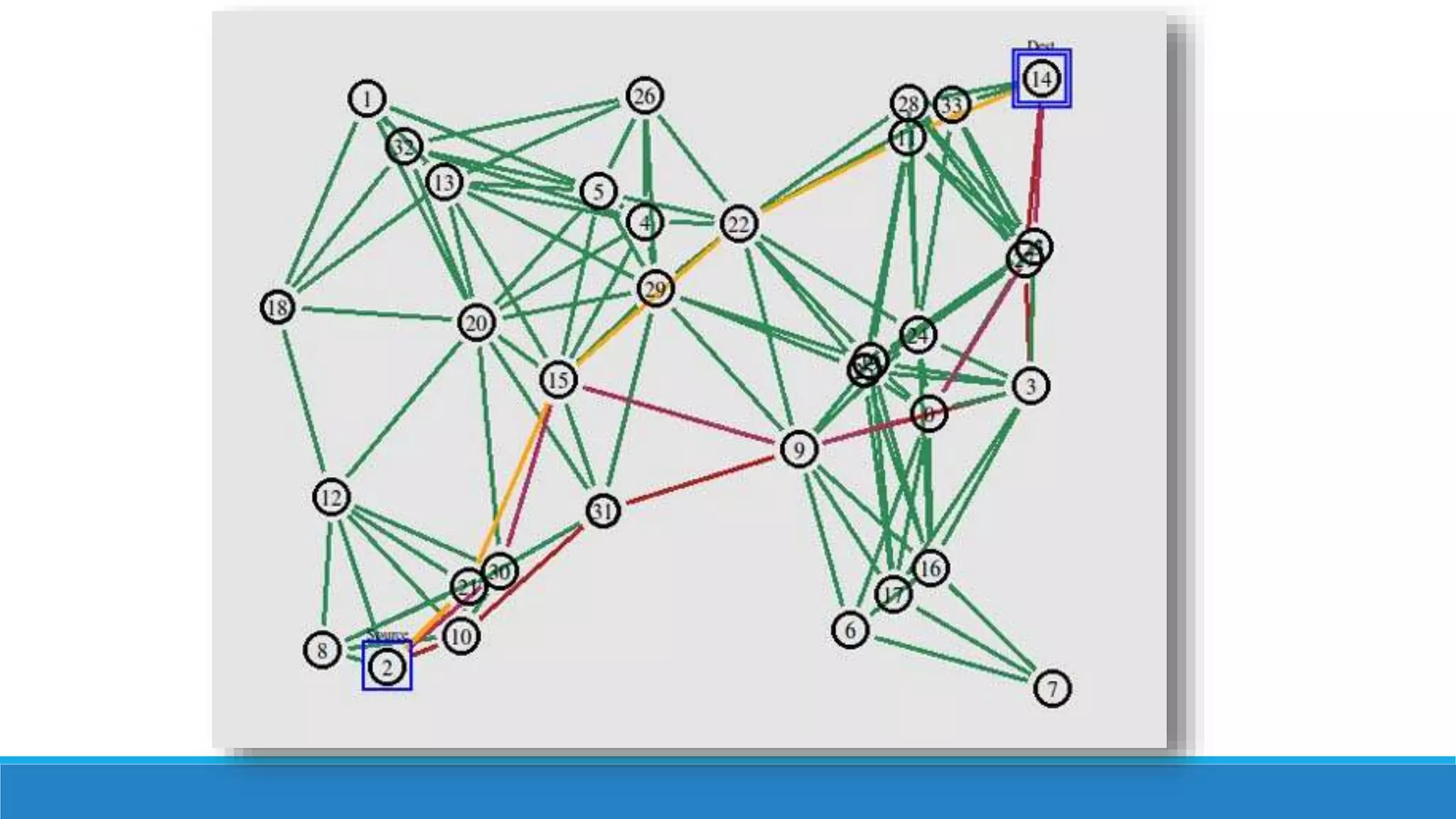
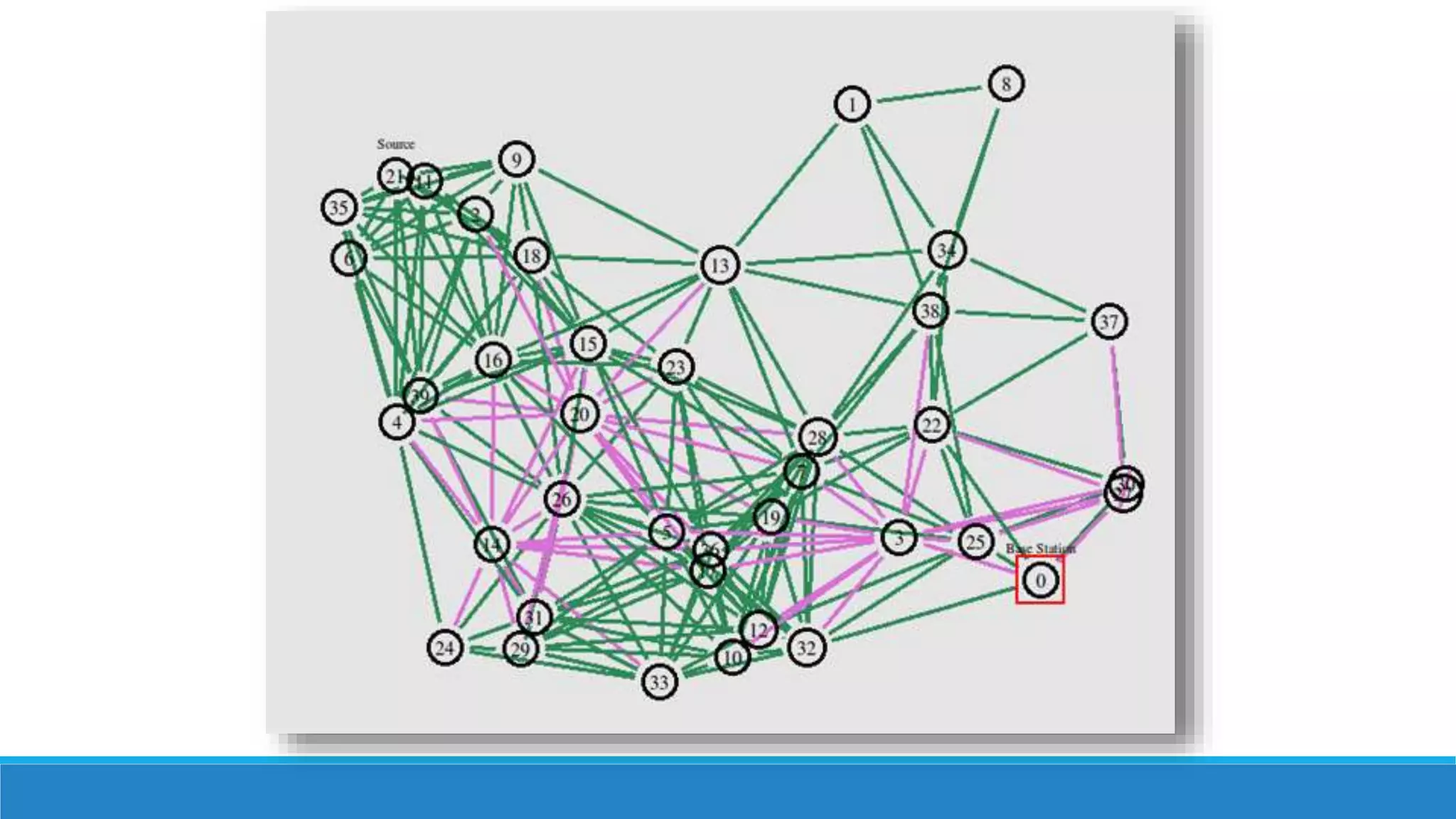
Dijkstra's algorithm is used to find the shortest path between nodes in a graph. It was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956. The algorithm finds the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in the graph. It is commonly used to find driving directions and for routing data packets through networks with minimum delay. The algorithm works by assigning distances or costs to the edges in the graph and finding the path with the lowest cost between two nodes. It cannot handle graphs with negative edges.