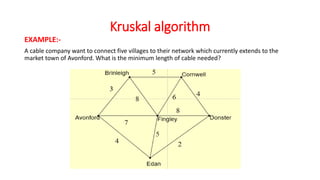
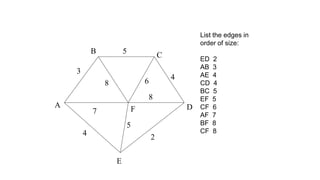
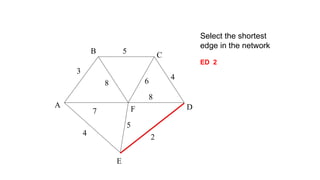
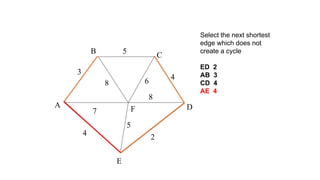
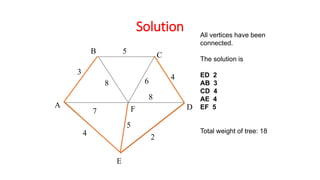
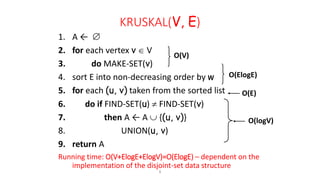
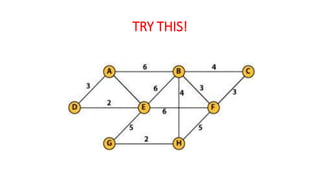
Kruskal's algorithm is a minimum spanning tree algorithm that finds the minimum cost collection of edges that connect all vertices in a connected, undirected graph. It works by sorting the edges by weight and then sequentially adding the shortest edge that does not create a cycle. The algorithm uses a disjoint set data structure to track connected components in the graph. It runs in O(ElogE) time, where E is the number of edges.