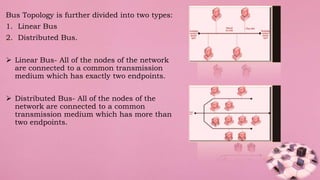
The document discusses various types of computer networks and topologies, including local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN), and wide area networks (WAN). It explains physical and logical topologies, detailing specific types like bus, ring, star, and their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, communication schemes such as contention and token passing are outlined, illustrating how data is transmitted across these networks.