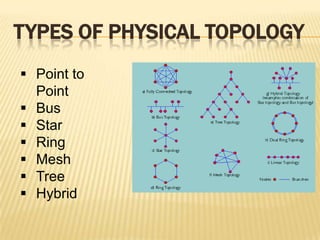
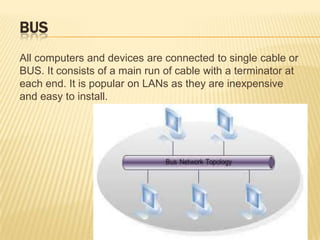
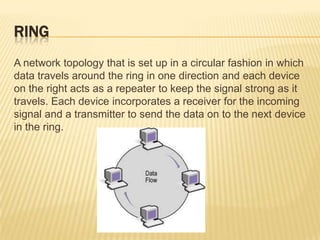
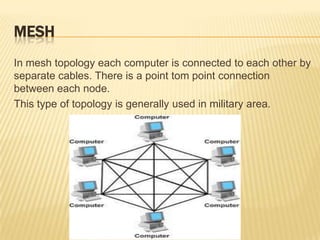
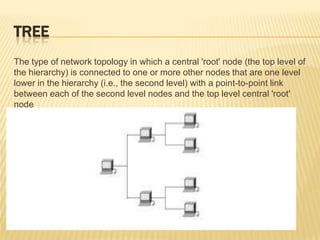
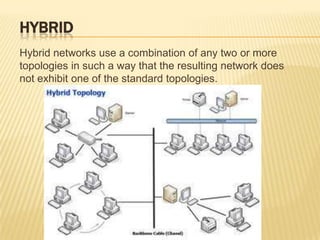
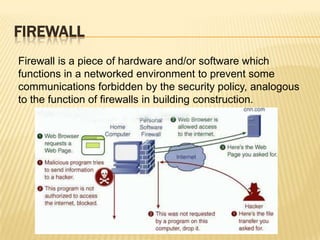
This document discusses computer networks and networking concepts. It defines what a computer network is and different types of networks like LAN, MAN, and WAN. It then covers network topologies, describing physical topologies like bus, star, ring, mesh, tree and hybrid topologies. It also discusses common networking devices like routers, switches, hubs, bridges and others. Finally, it covers some common networking cables used like coaxial cable, Ethernet cable and optical fiber cable.