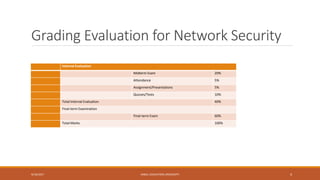
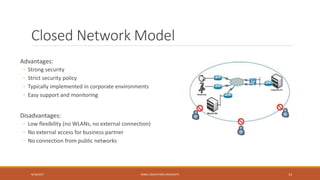
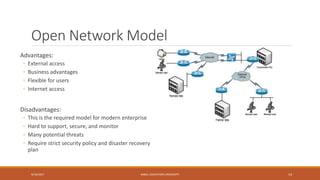
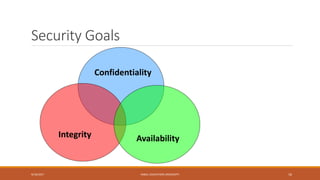
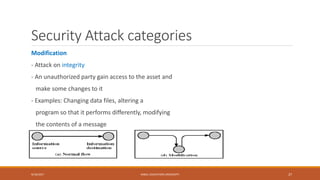
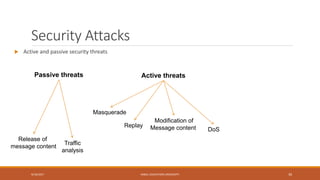
This document outlines the course content for a network security class at Kabul Education University. It includes an overview of topics to be covered in the first week such as network security background, definitions, why security became important, network models, and security goals. It also outlines the class policies on attendance and assignments. The grading evaluation breaks down the internal and final exam components. Several lecture slides provide more details on concepts like what security is, why network security is needed, security attack categories, and that security is best achieved through a process using multiple mechanisms rather than a single product.