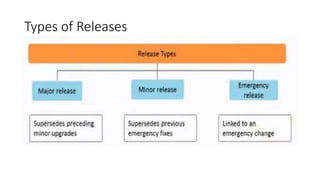
Release and Deployment Management (RDM) aims to build, test, and deliver new or changed IT services to customers. RDM plans, schedules, and controls the movement of service releases through testing and implementation. The goal of RDM is to deploy releases into operation and establish effective customer service while ensuring handover to operations and adequate documentation for support. RDM defines processes for packaging, building, testing, and deploying releases to production according to a release policy and governance.