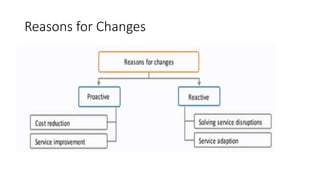
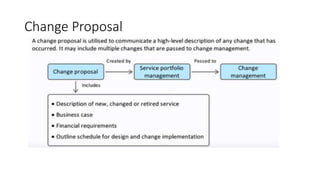
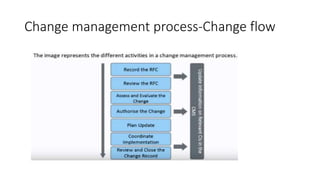
This document discusses various aspects of ITIL including IT service continuity management, information security management, change management, and service transitions. It provides details on topics such as business impact analysis, change types, the change advisory board, change proposals, change management processes, and change manager responsibilities. The presentation outlines key ITIL concepts to ensure the resumption of IT services within agreed timescales and introduce changes in a controlled manner to optimize business risk.