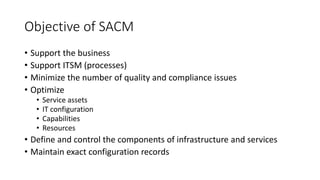
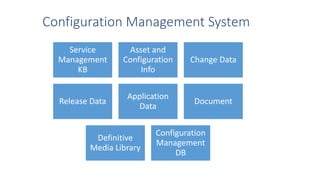
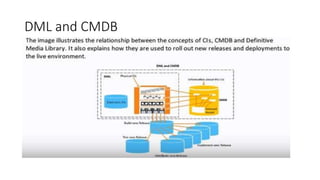
This document discusses Service Asset and Configuration Management (SACM) as part of ITIL. It defines key terms like configuration item, configuration management, and outlines the purpose, objectives and scope of SACM. The document also discusses how SACM supports IT service management processes by maintaining accurate information on IT assets, configurations and relationships in a Configuration Management Database to support incident and problem resolution.