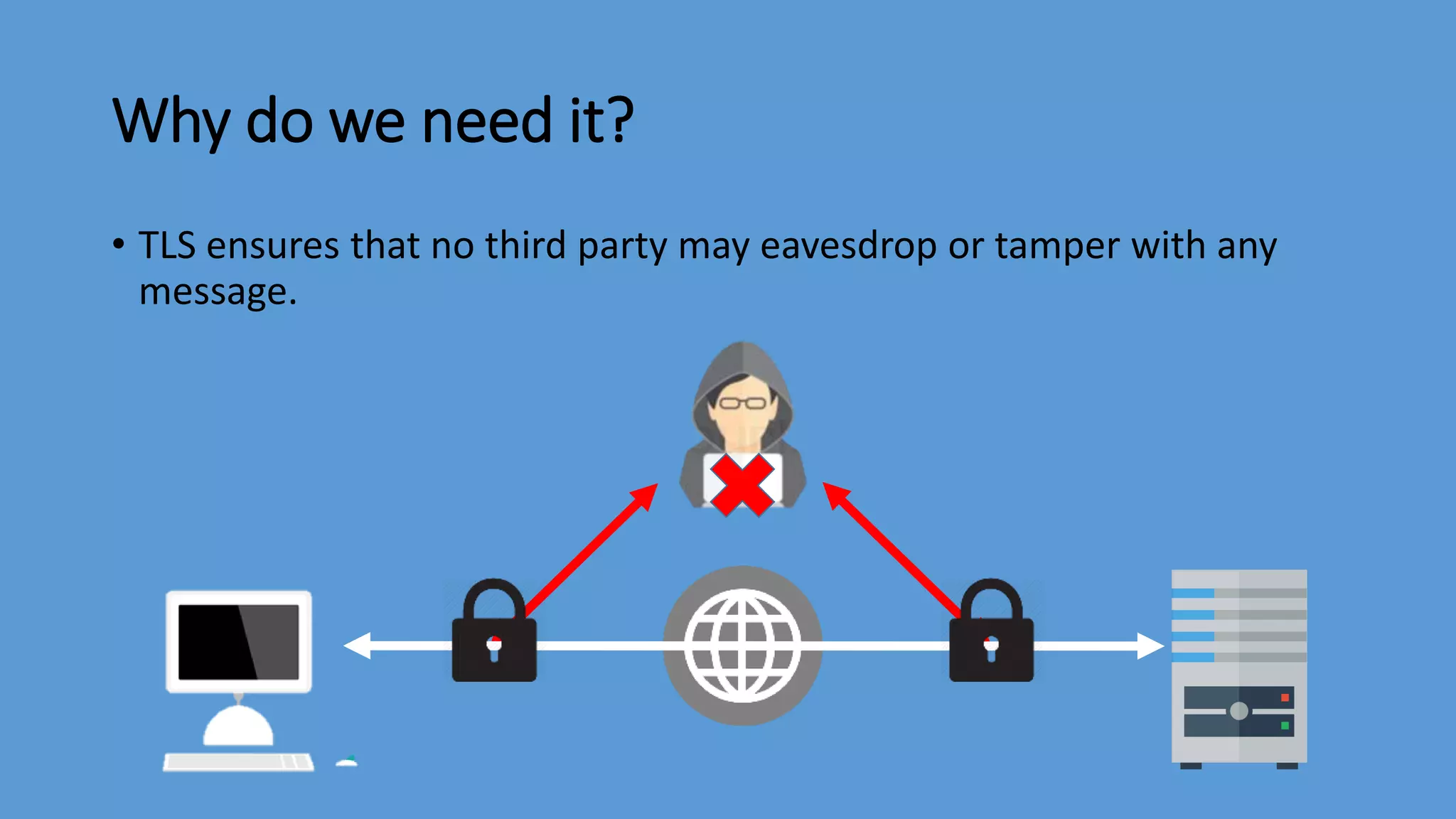
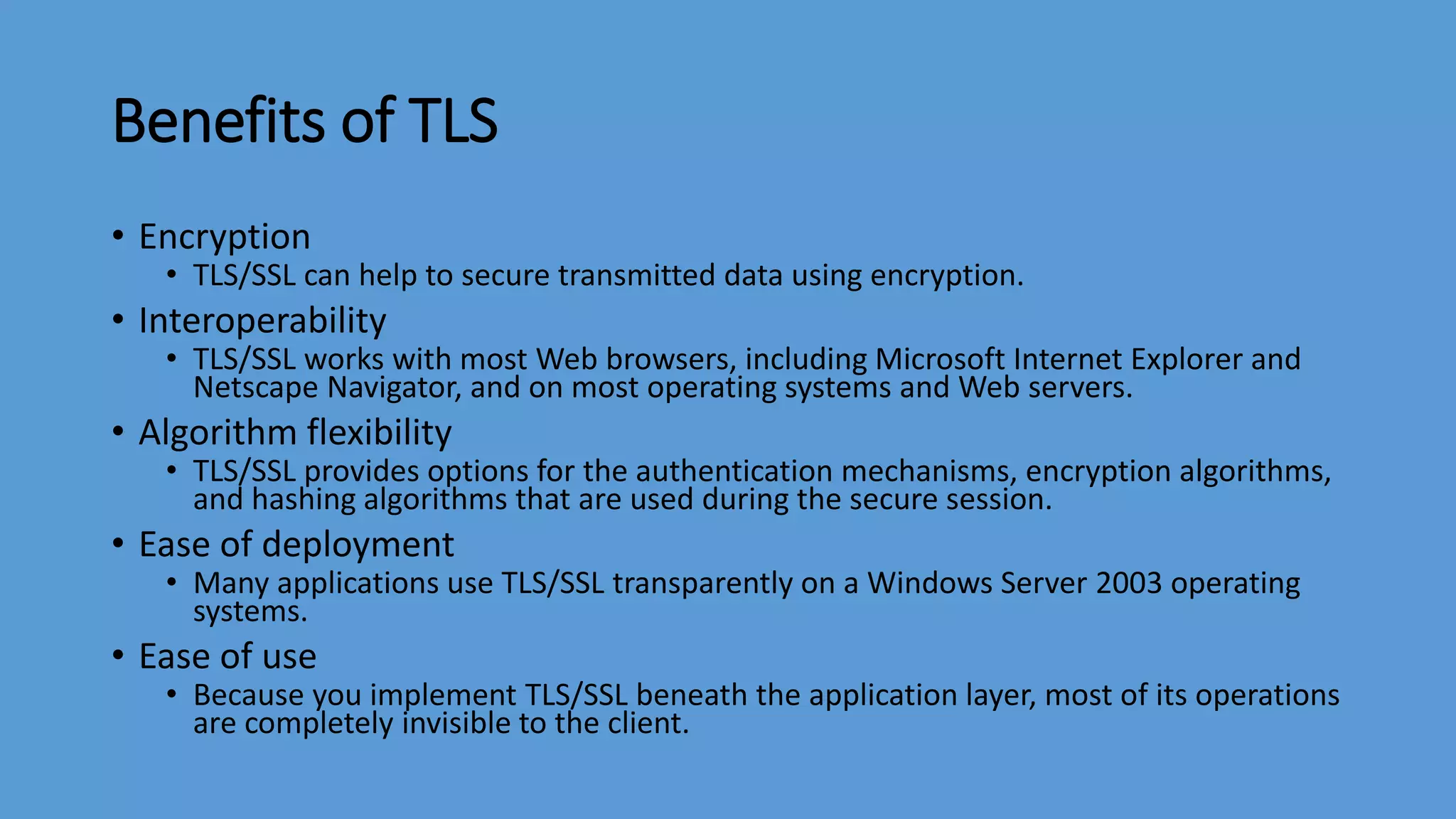
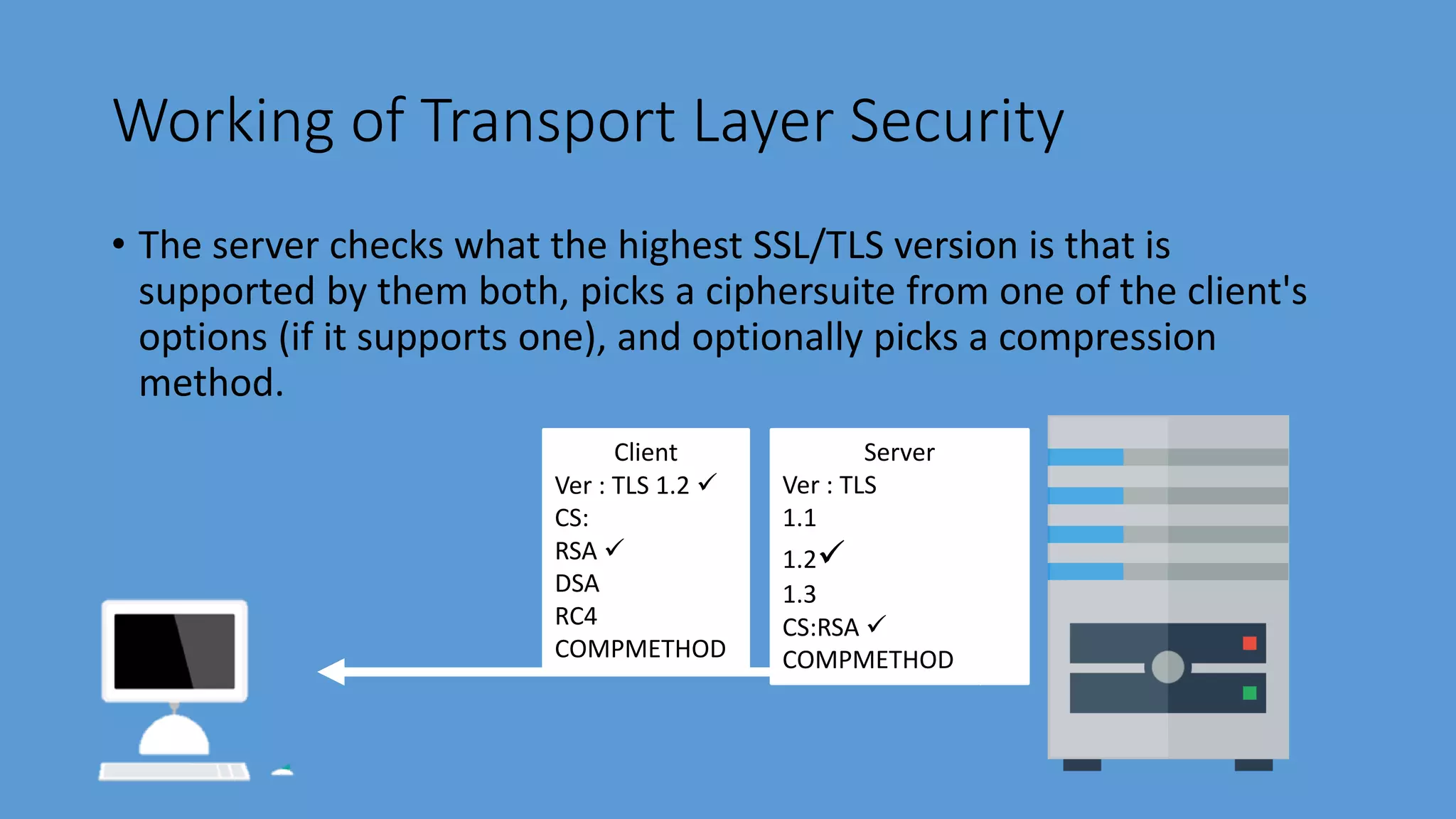
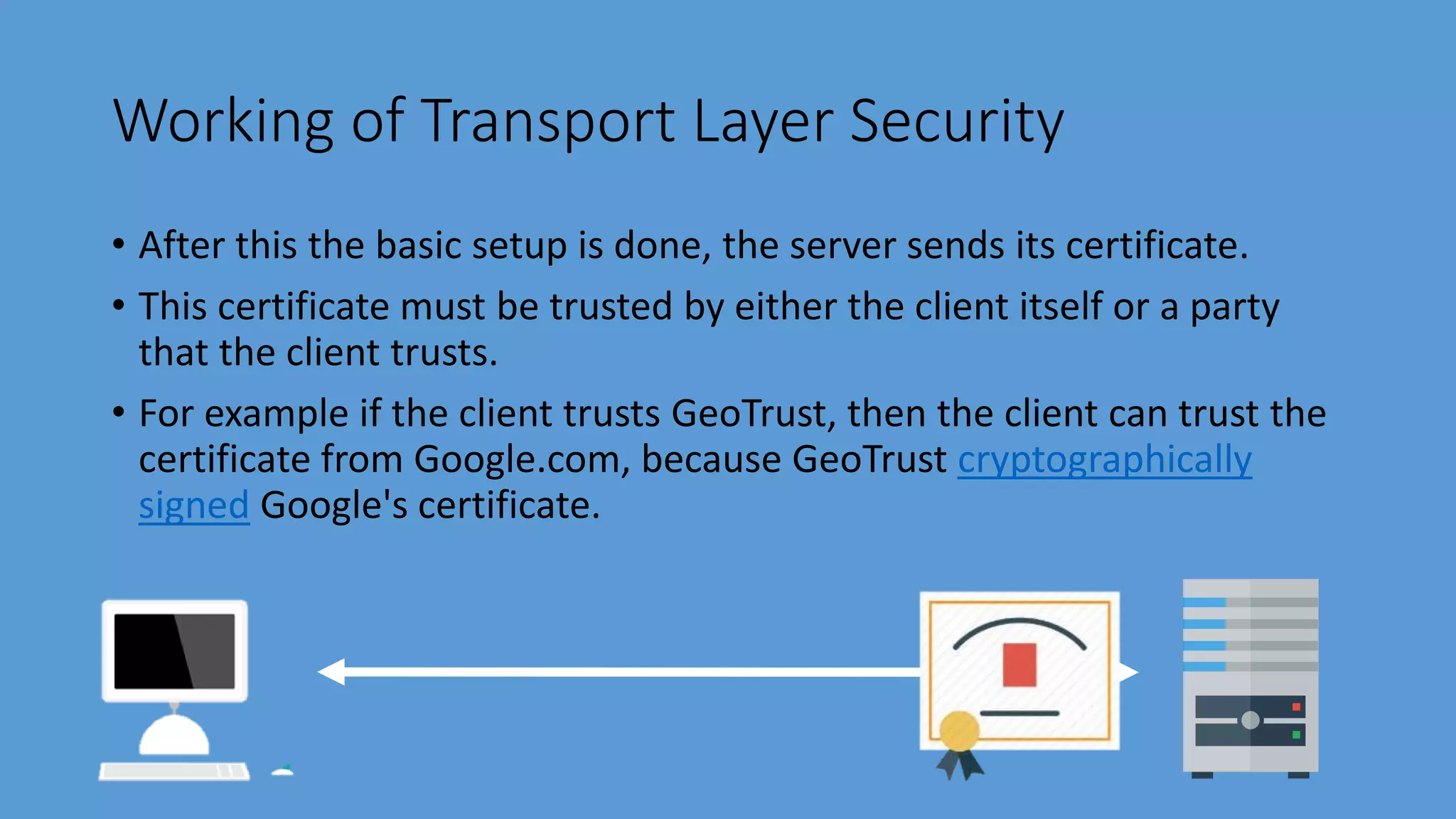
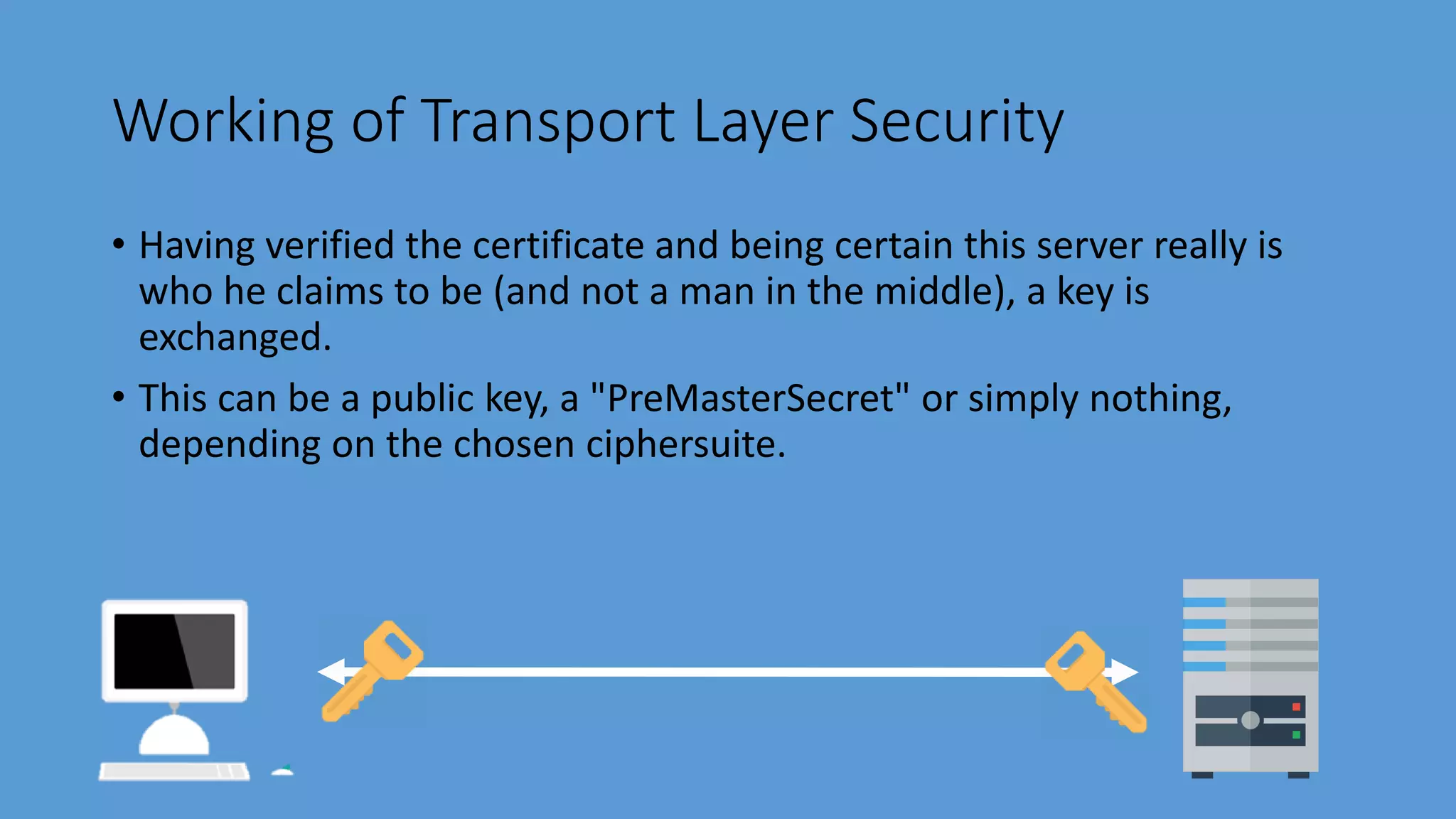
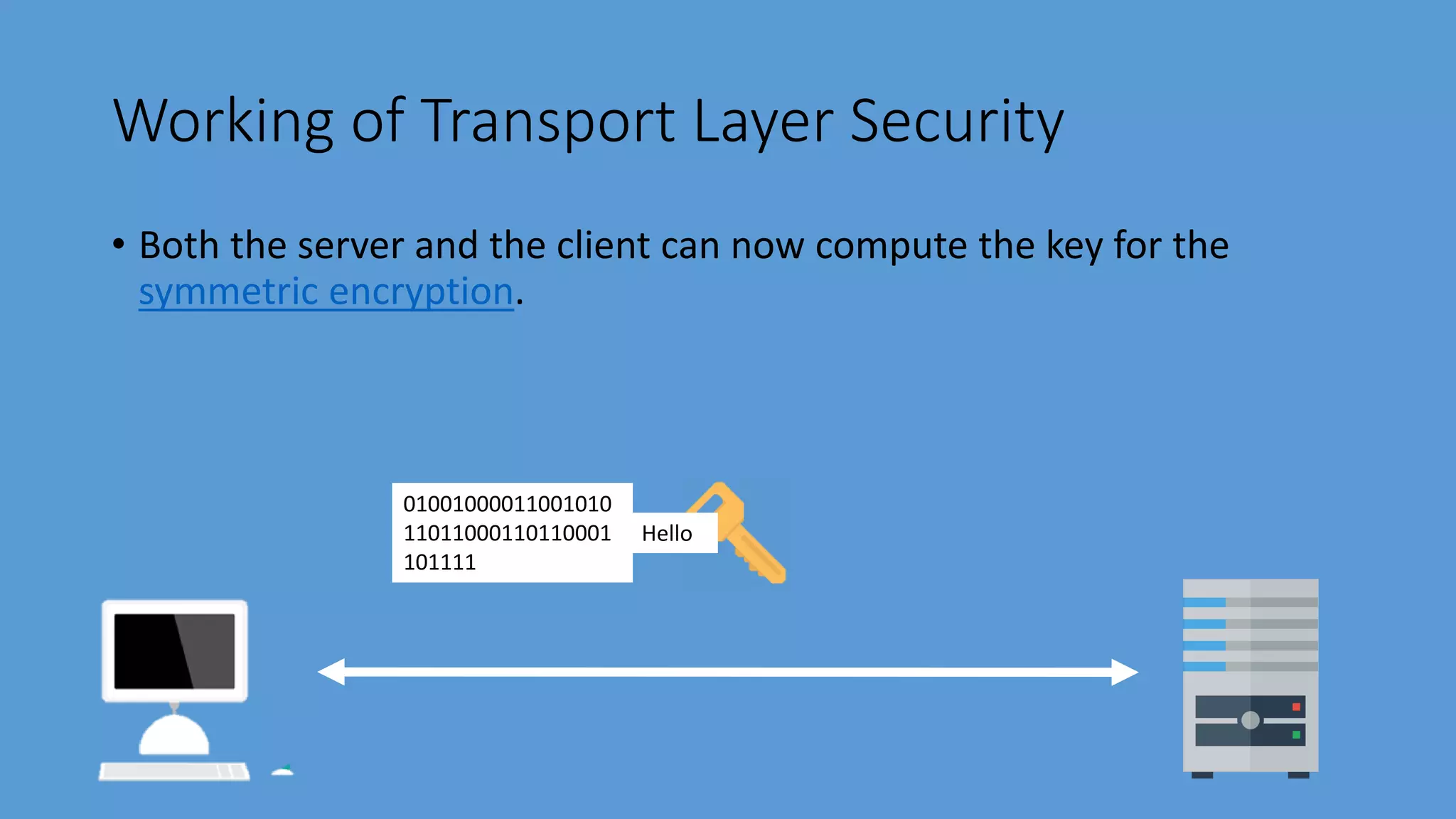
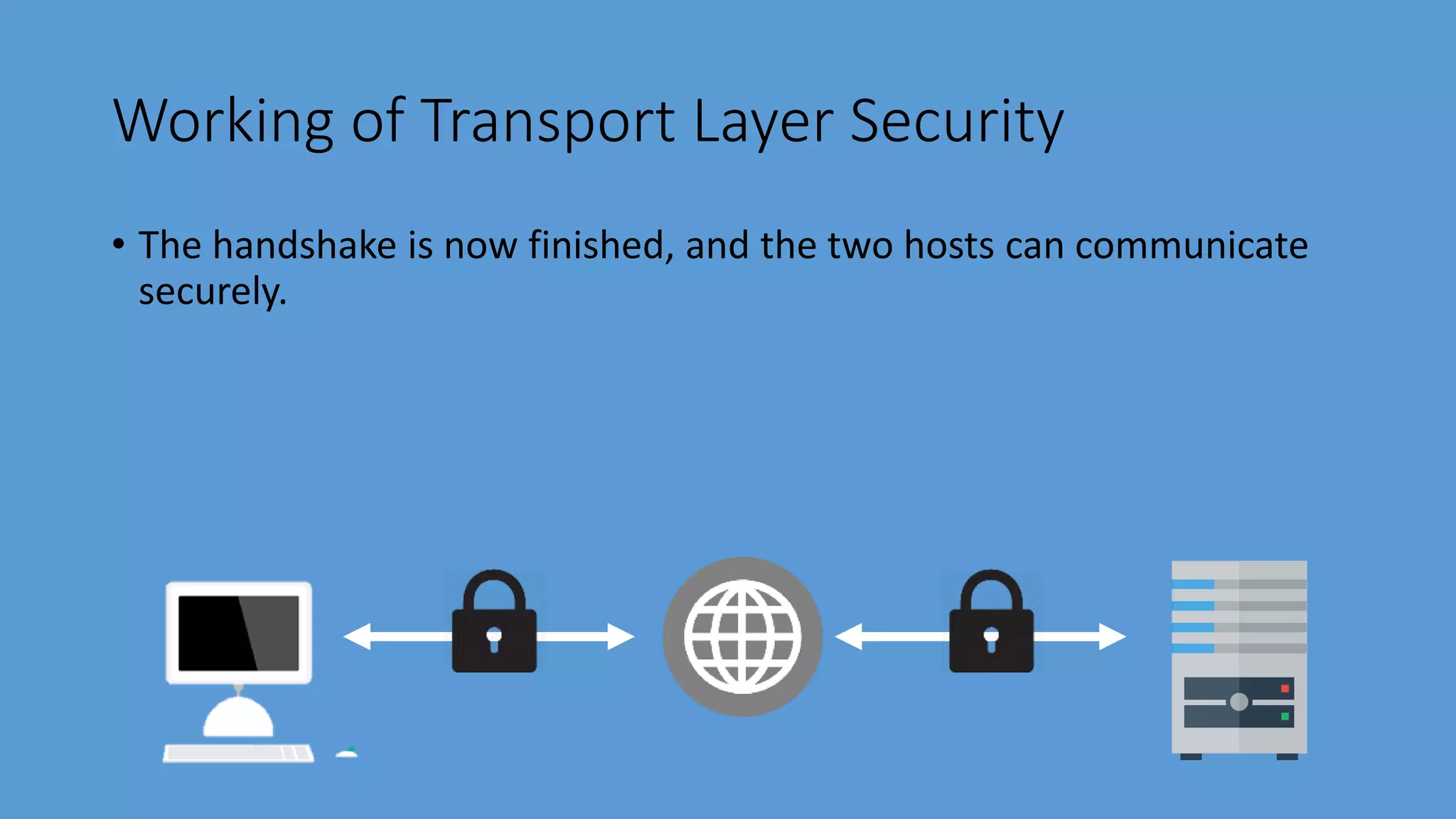
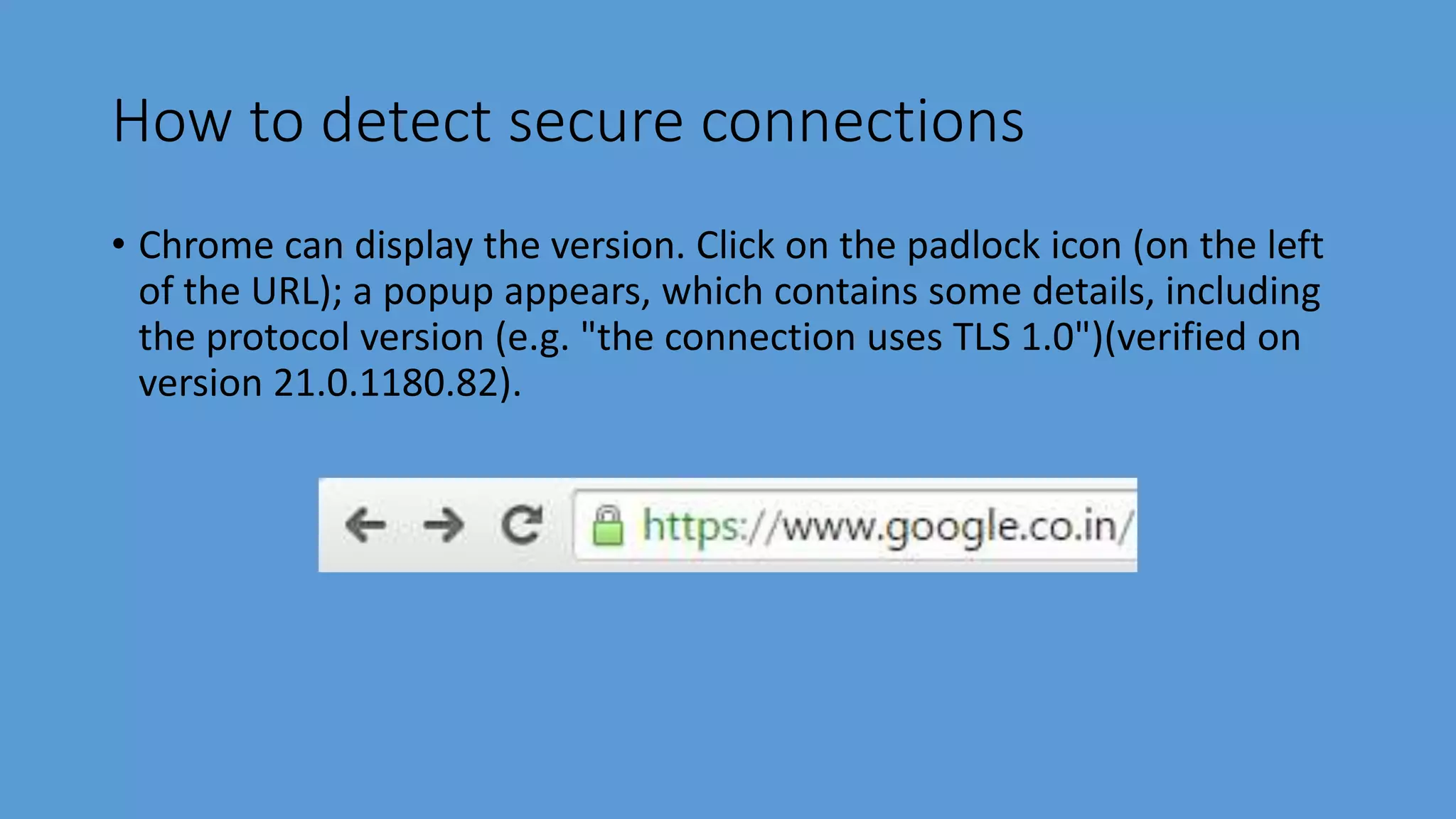
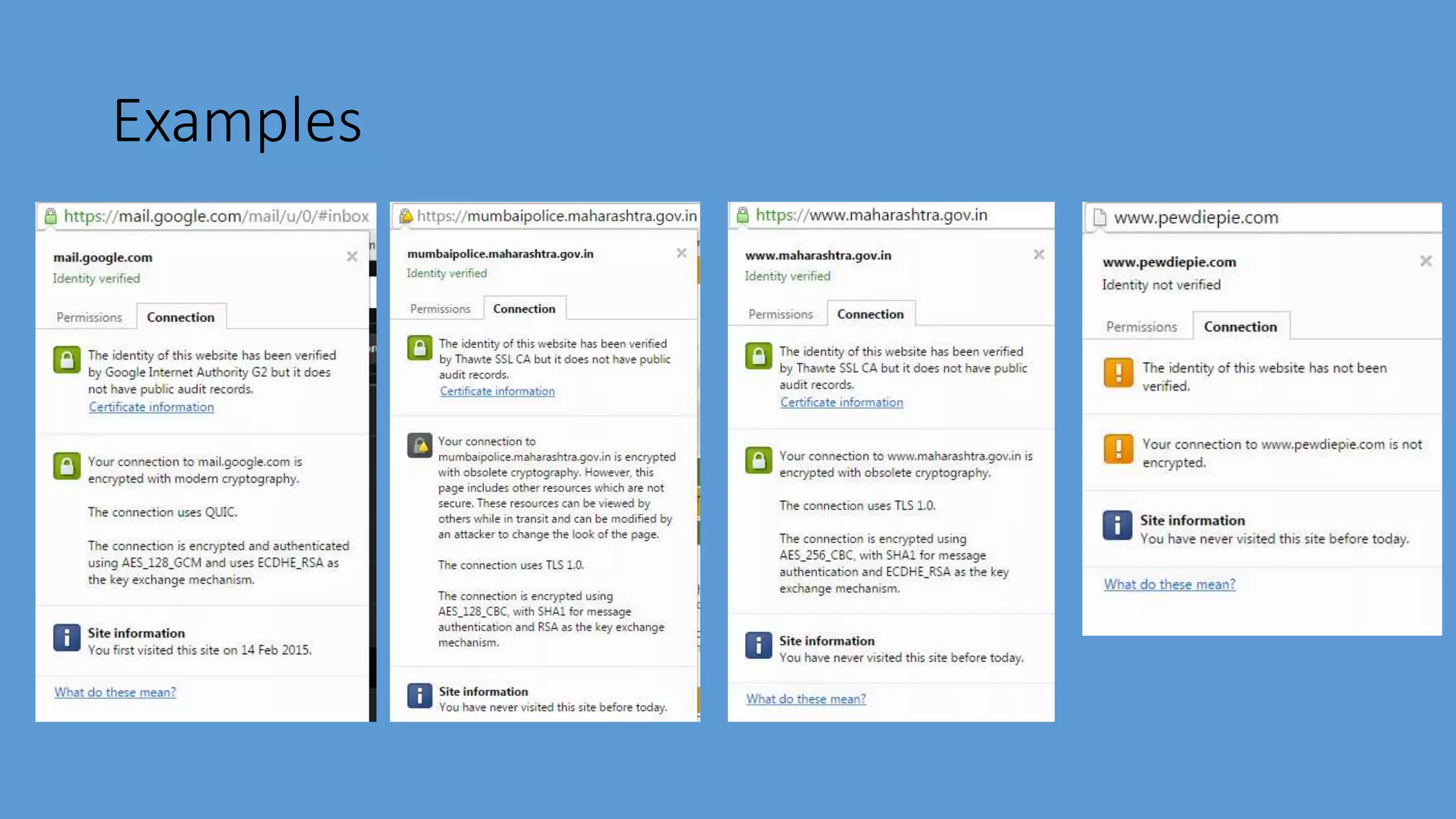
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a protocol that secures communications over the internet by preventing eavesdropping and tampering. It offers benefits such as encryption, interoperability with various browsers and operating systems, algorithm flexibility, and ease of deployment. The working of TLS involves a handshake process where client and server negotiate the security parameters and exchange keys to establish a secure connection.