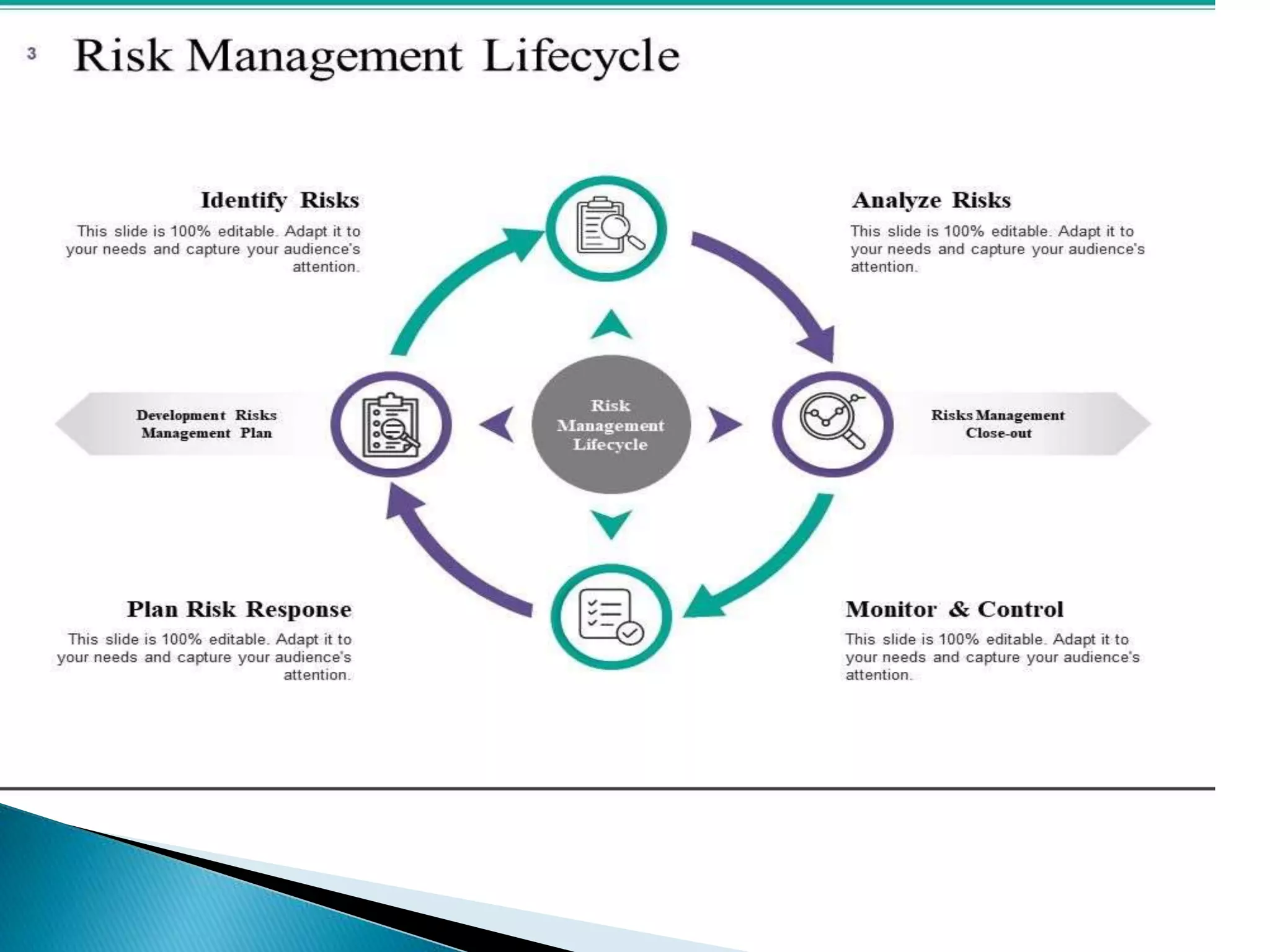
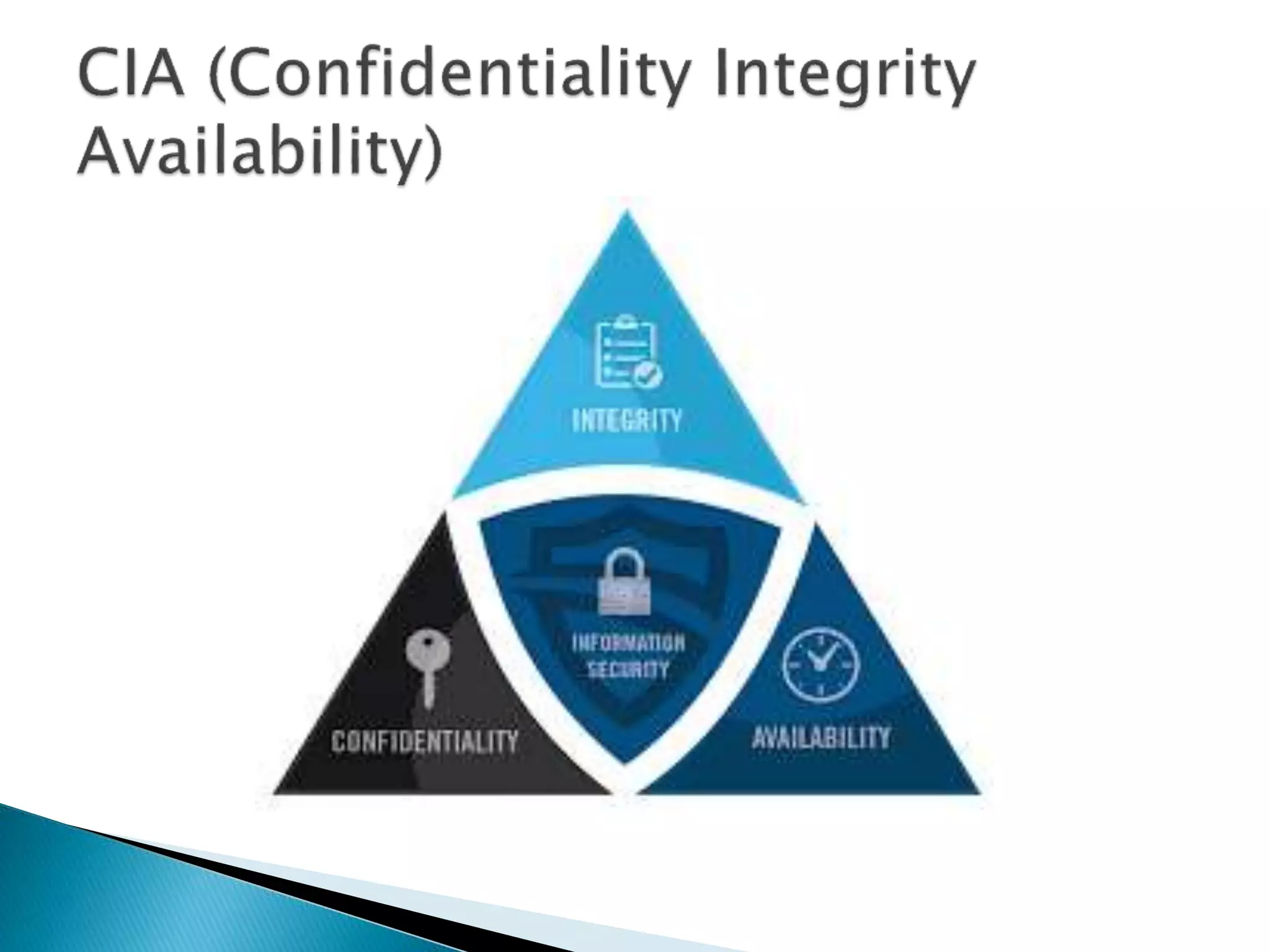
This document discusses cyber security risk assessments. It provides objectives for risk assessments such as determining organizational risk tolerance and identifying risks to confidentiality, integrity and availability of data. Risk is defined as the threat times vulnerability times information value. The benefits of risk assessments are outlined, including better organizational knowledge, avoidance of data breaches and regulatory issues. Types of risk assessments like qualitative and quantitative are described. Key aspects of confidentiality, integrity and availability are also summarized.