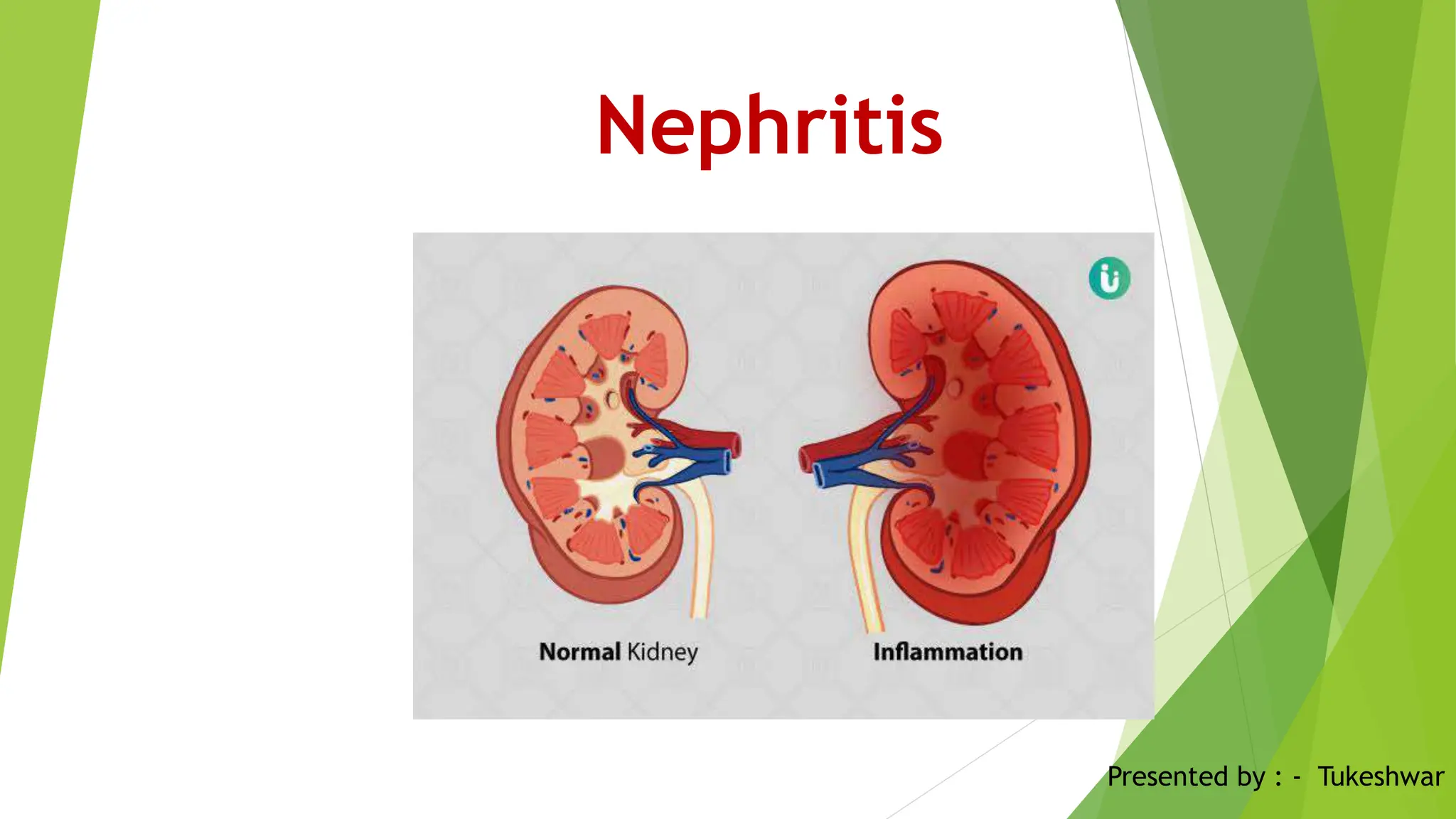
Nephritis is an inflammatory condition of the kidneys that impairs waste filtration, caused by infections or inflammatory disorders. It can be classified into acute nephritis, often triggered by drug sensitivity, and chronic nephritis, which arises from various causes like hypertension and renal diseases. Diagnosis involves history collection, tests, and biopsies, while management includes corticosteroids, antihypertensives, diuretics, and lifestyle modifications.