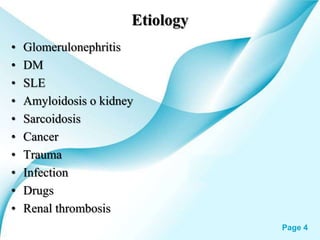
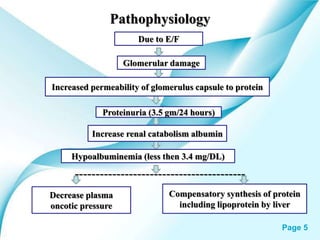
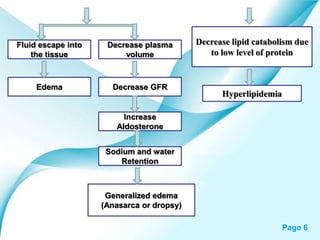
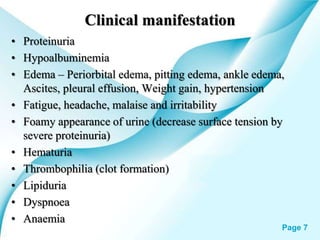
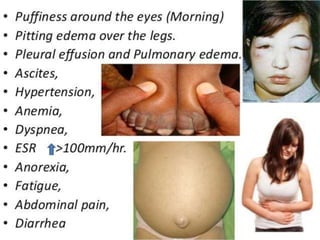
This powerpoint presentation covers Nephrotic Syndrome. It defines Nephrotic Syndrome as a clinical disorder characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, edema, and hyperlipidemia. It discusses the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, complications, and nursing management of Nephrotic Syndrome. It specifically examines the use of chlorambucil and corticosteroids in treating Nephrotic Syndrome and their potential behavioral side effects.