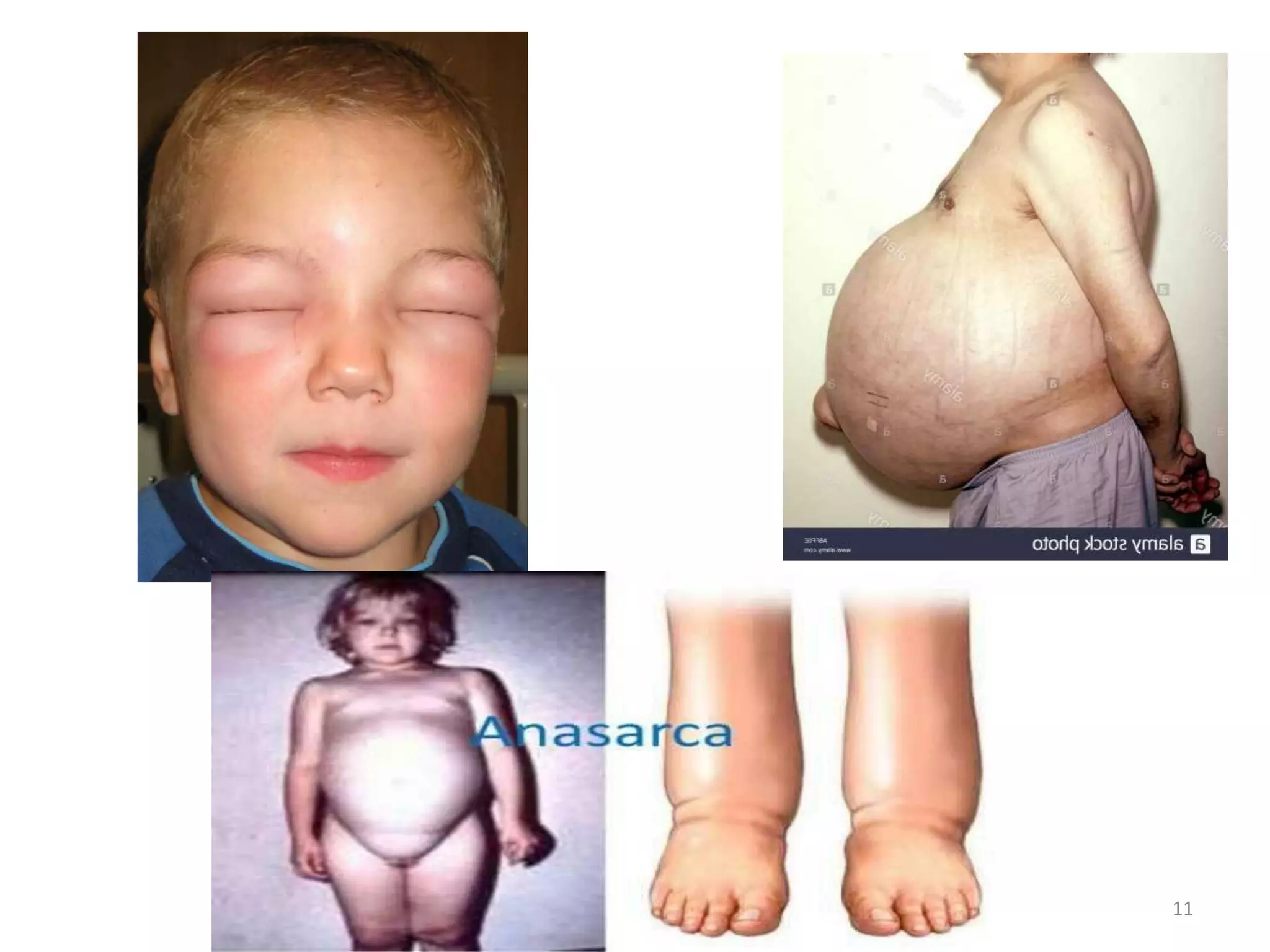
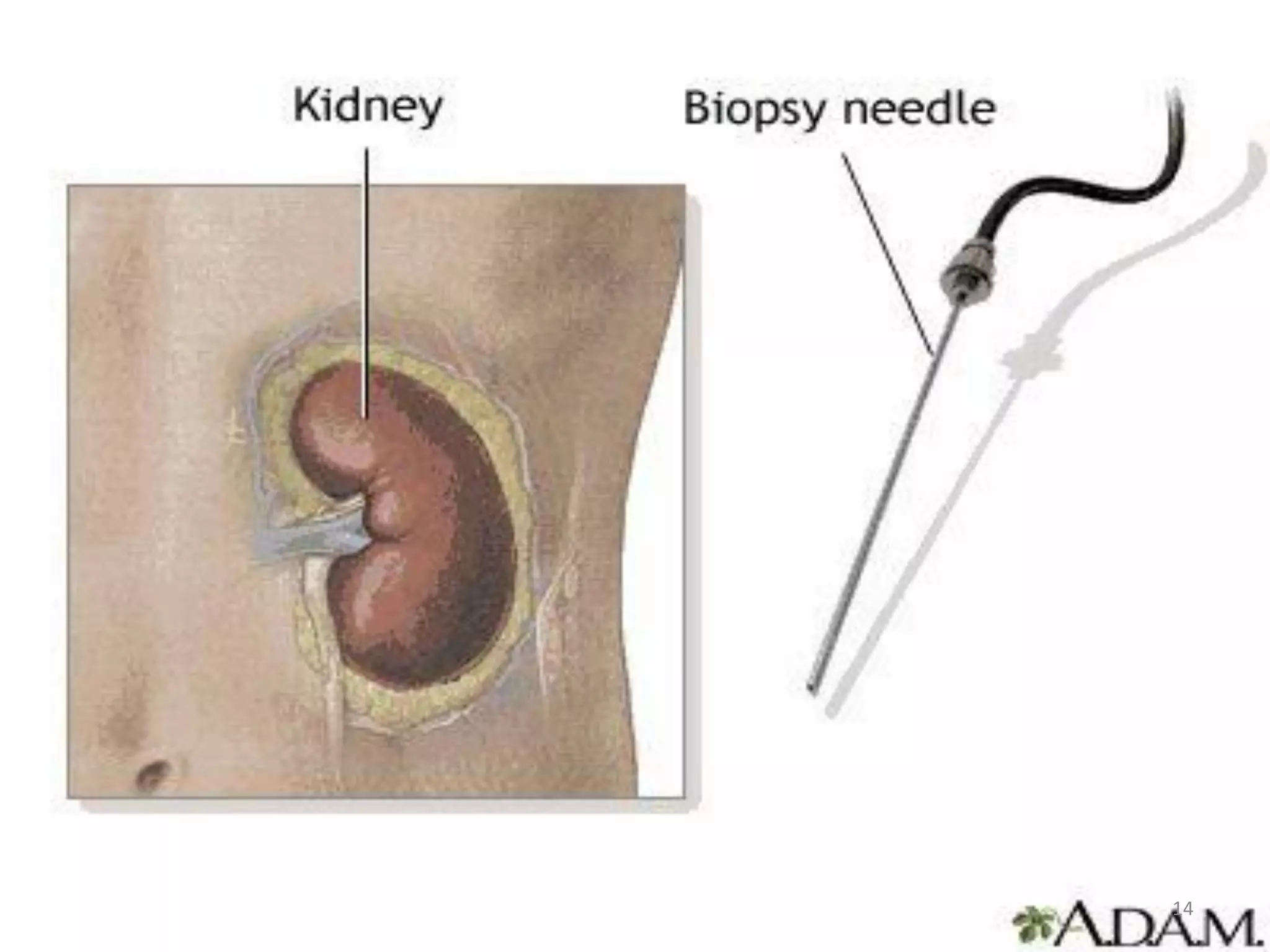
This document provides an overview of nephrotic syndrome, including its definition, incidence, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation, management, and complications. Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, and edema. It most commonly affects children ages 2-6 and has many potential causes, either primarily affecting the kidneys or secondarily from other conditions. Diagnosis involves urine and blood tests showing proteinuria and low albumin levels. Treatment focuses on controlling edema, promoting nutrition, and in some cases using corticosteroids, diuretics, or immunosuppressants.