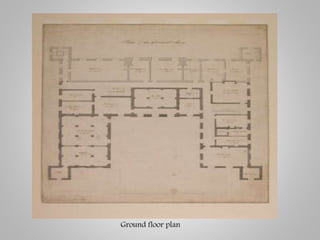
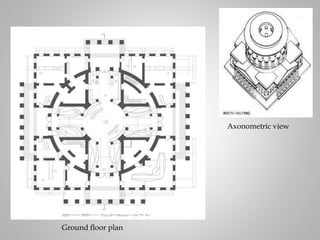
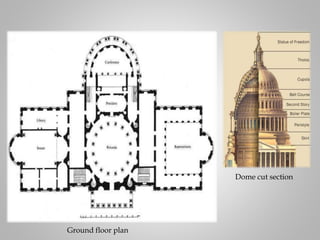
The document outlines the neoclassical movement in art, literature, and architecture, dating from 1660 to 1780, emphasizing a return to classical ideals in reaction to the baroque style and reflecting contemporary social and political changes. It details key characteristics, prominent artists, and significant works that illustrate the movement's impact on various creative fields, as well as discussing the evolution of literature defined by order and structure. The influence of historical events, such as the American and French revolutions, is connected to the styles and themes prevalent throughout the neoclassical period.