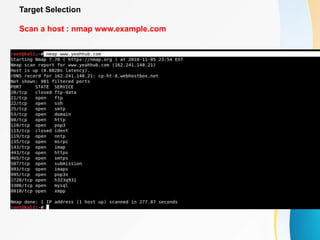
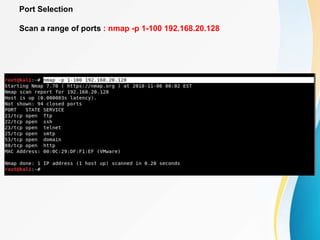
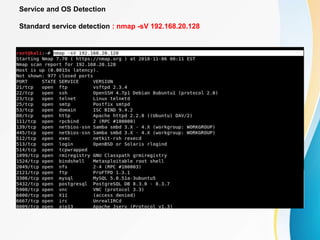
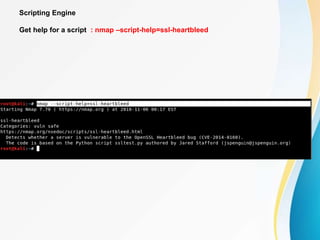
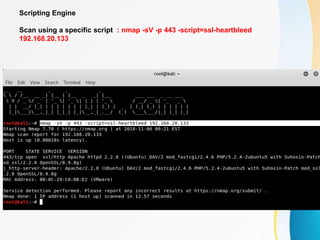
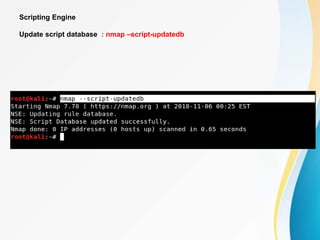
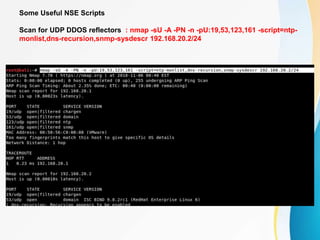
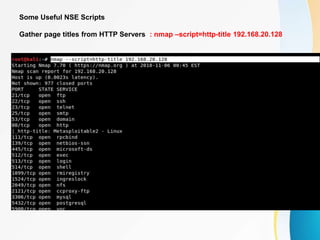
This document provides an overview of IP network scanning using the nmap tool. It describes how nmap can be used to discover active hosts on a network, identify open ports and services, determine operating system and software versions running on devices. Various scanning techniques are outlined, including host discovery, port scanning, and OS detection. The document also reviews common nmap commands and features such as target and port selection, different scan types, and using Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) scripts.