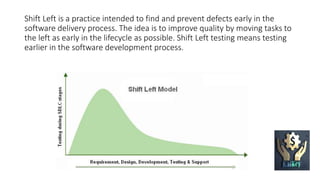
Shift left testing involves moving testing as far left or as early in the development process as possible to find and prevent defects early. This is opposed to traditional testing, which only occurred right before release. Shift left testing improves quality by identifying issues early when they are cheaper to fix. While shift left is often best, shift right testing post-production may also be useful in some cases to enhance customer experience and ensure proper test coverage and automation. To shift left, organizations can engage stakeholders early, do static testing of requirements and design, and see benefits like increased automation, delivery speed, and satisfaction.