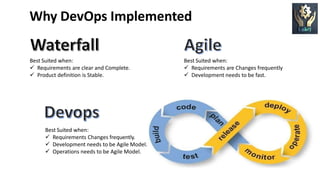
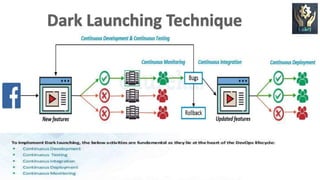
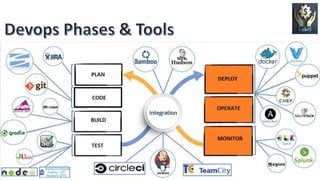
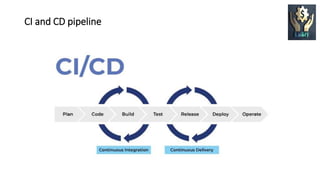
DevOps is a software development approach that aims to shorten the systems development life cycle and provide continuous delivery with high software quality. It focuses on collaboration between development and operations teams. Key aspects of DevOps include automation of the software delivery process through tools like Docker and Jenkins, continuous integration and deployment, and monitoring of applications in production. While DevOps can improve speed and collaboration, security challenges arise from development teams prioritizing speed over security and keeping up with the fast pace of changes. Adopting DevSecOps practices like automation, clear security policies, and vulnerability management can help integrate security into the DevOps process.