This document discusses vehicle suspension systems. It describes how suspension systems have evolved from early leather springs to modern designs. Key points covered include:
- Early suspension systems used leather springs in 1665 and elliptical leaf springs in 1795. Hydraulic shock absorbers were introduced in 1919.
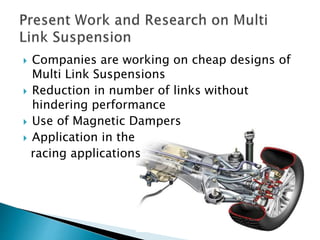
- Modern suspension types discussed include multi-link suspensions from 1960, MacPherson struts from the 1970s, and Bose automotive suspension from 2009.
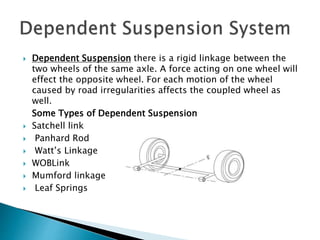
- The main components of suspension systems are identified as springs, shockers, and struts. Independent and dependent suspension systems are also defined.
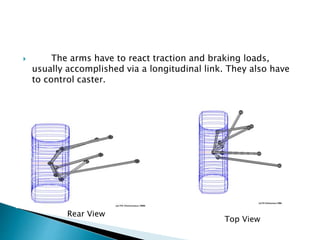
- Multi-link suspensions, which use three or more lateral arms and one or more longitudinal arms, provide improved