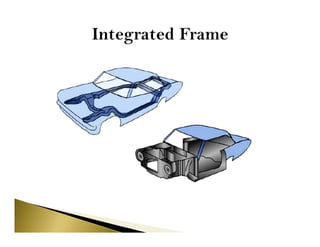
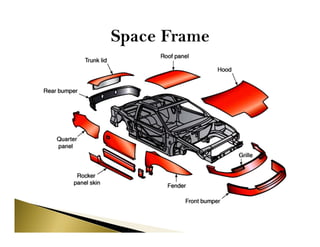
The document provides an overview of automotive chassis, detailing its definition, functions, and types, as well as the components that make it up, including the frame and various systems. It categorizes chassis based on control, engine fitting, drive wheel configuration, and wheelbase size while explaining different frame types, such as conventional and integral. Additionally, it discusses the materials used in frame construction and their specific applications.