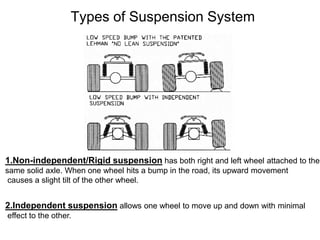
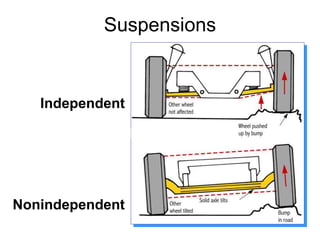
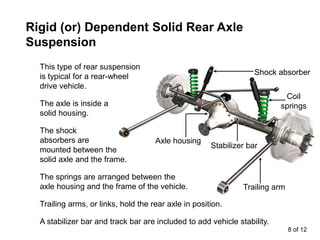
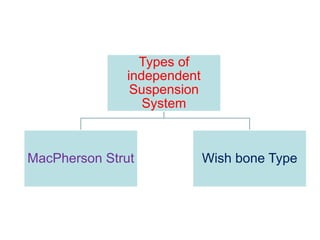
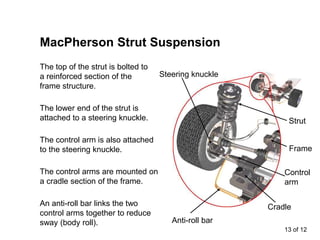
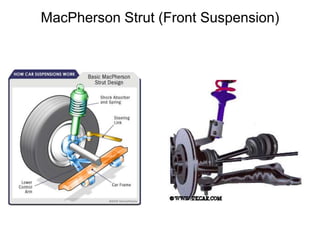
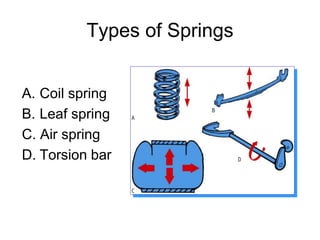
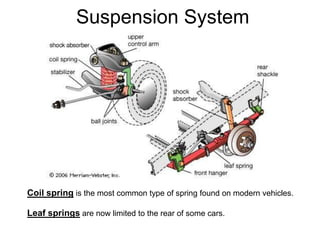
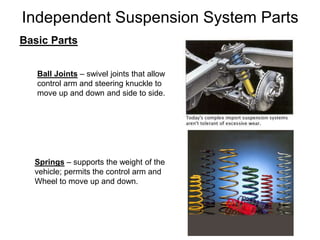
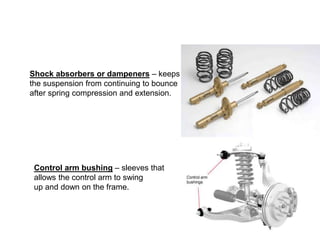
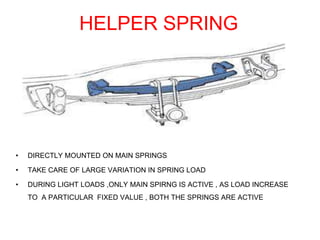
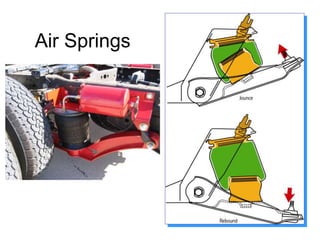
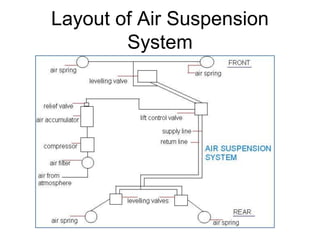
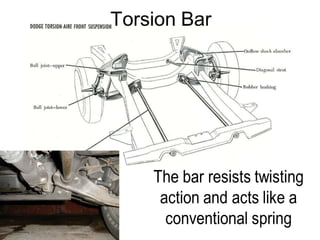
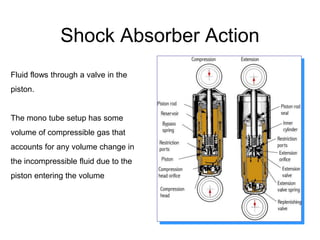
The suspension system connects a vehicle to its wheels using springs, shock absorbers, and linkages. It serves two purposes - contributing to handling and braking while also protecting the vehicle and cargo from road shocks. There are two main types of suspension systems - rigid/non-independent and independent. Rigid suspension connects both sides of the axle together while independent suspension allows each wheel to move independently. Common components of suspension systems include coil springs, shock absorbers, control arms, and sway bars which help provide cushioning, stability, and ride comfort.