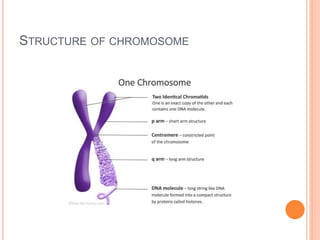
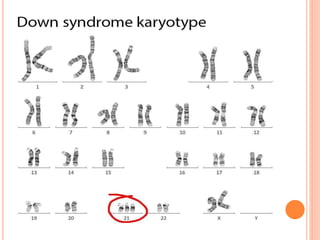
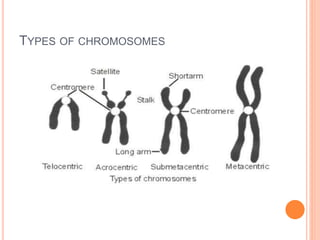
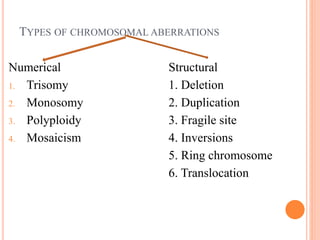
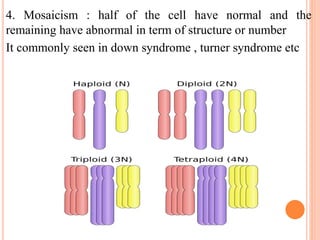
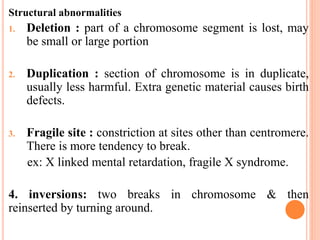
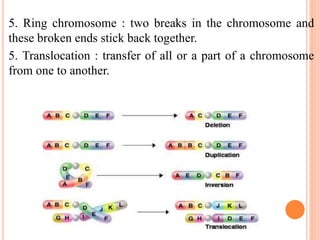
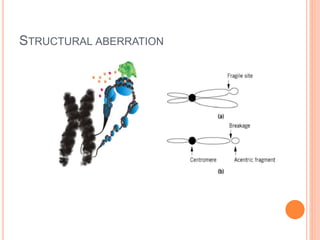
This document discusses chromosomal aberrations, beginning with their definition as any atypical number or structure of one or more chromosomes. It describes the basic terms like karyotyping, chromatid, and chromosome constituents. There are two main types of chromosomal aberrations - numerical involving an abnormal number of chromosomes, and structural involving changes in chromosome structure. Numerical aberrations include aneuploidy, trisomy, monosomy, and polyploidy. Structural aberrations comprise deletion, duplication, fragile sites, inversions, ring chromosomes, and translocations. The document outlines several methods for diagnosing chromosomal aberrations prenatally such as ultrasound, fetal echocardiography, and