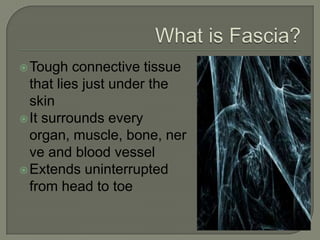
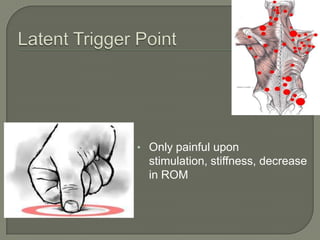
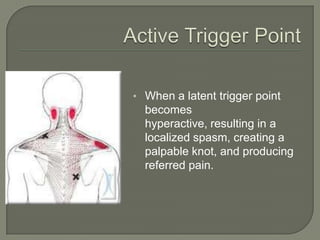
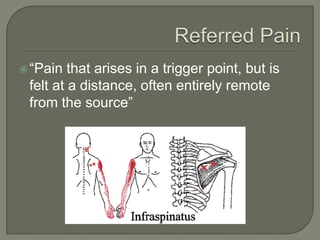
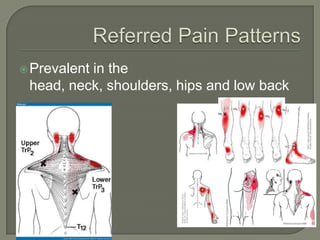
KSC RehabWorks, established in 1997, focuses on providing free physical medicine for work and sports-related injuries. The document highlights musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs), their prevalence, and the importance of injury prevention through education, proper ergonomics, and self-care techniques. It emphasizes the significance of addressing myofascial pain and trigger points, along with recommending effective prevention and treatment strategies, including exercise and microbreaks.