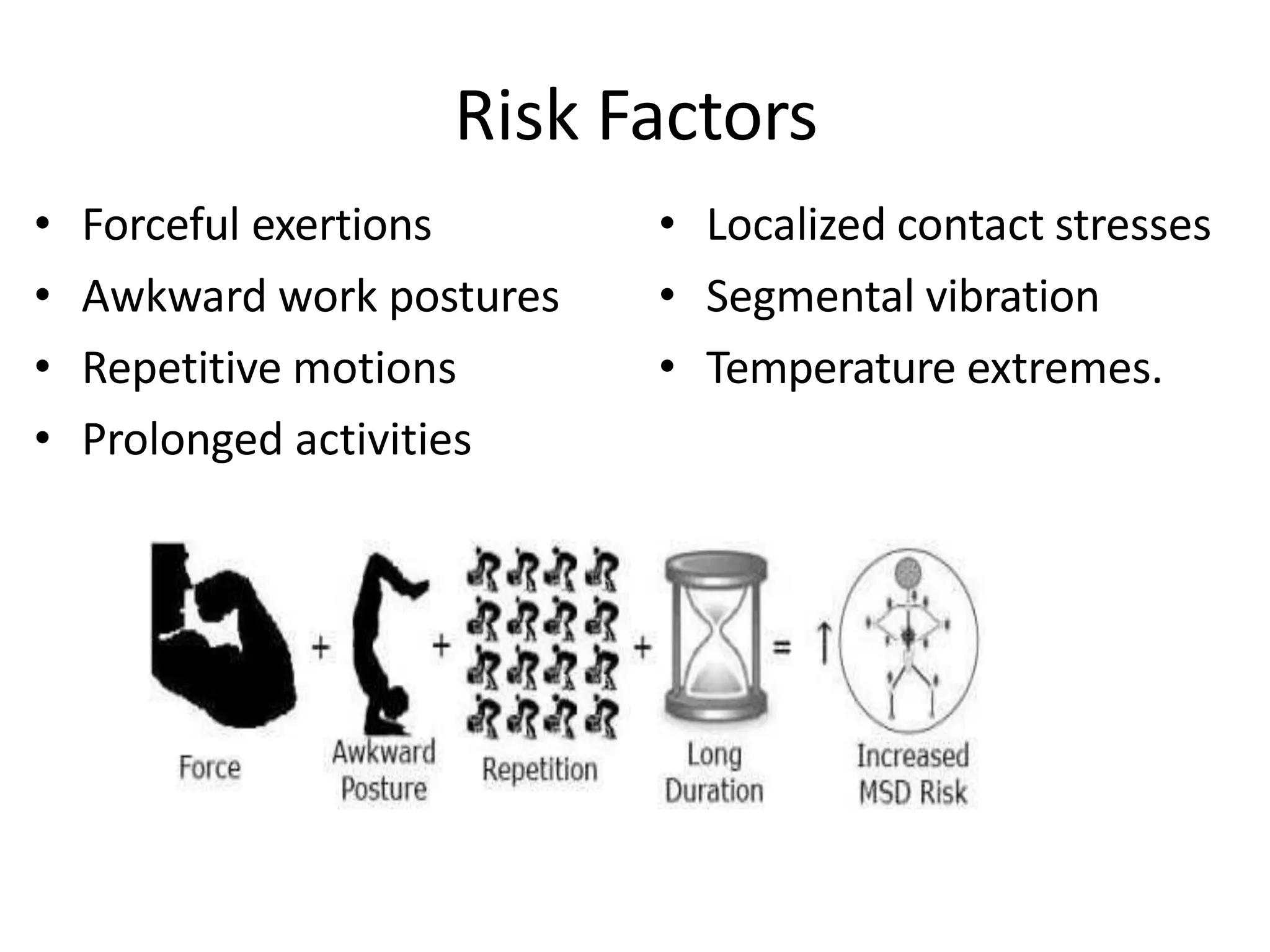
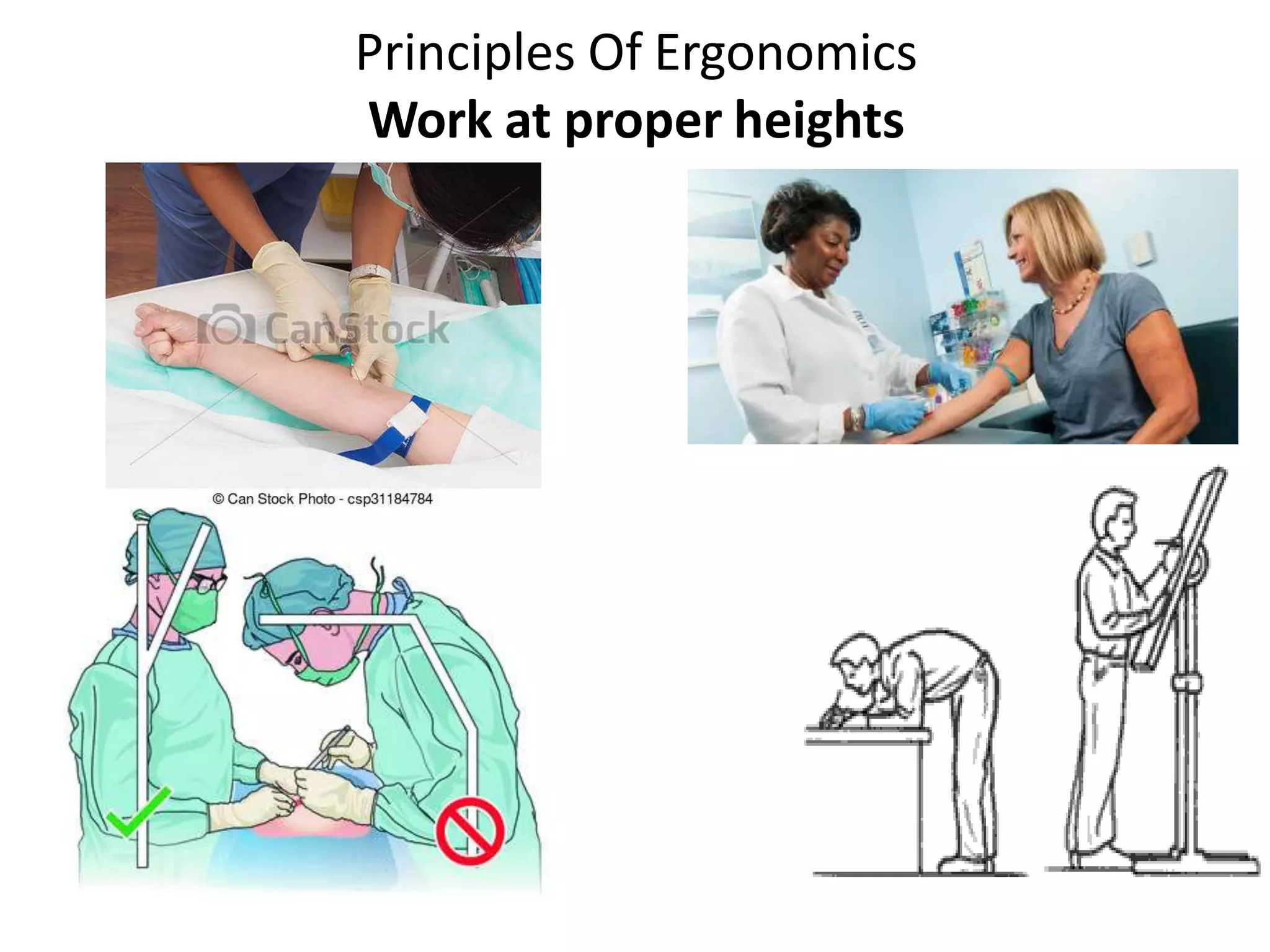
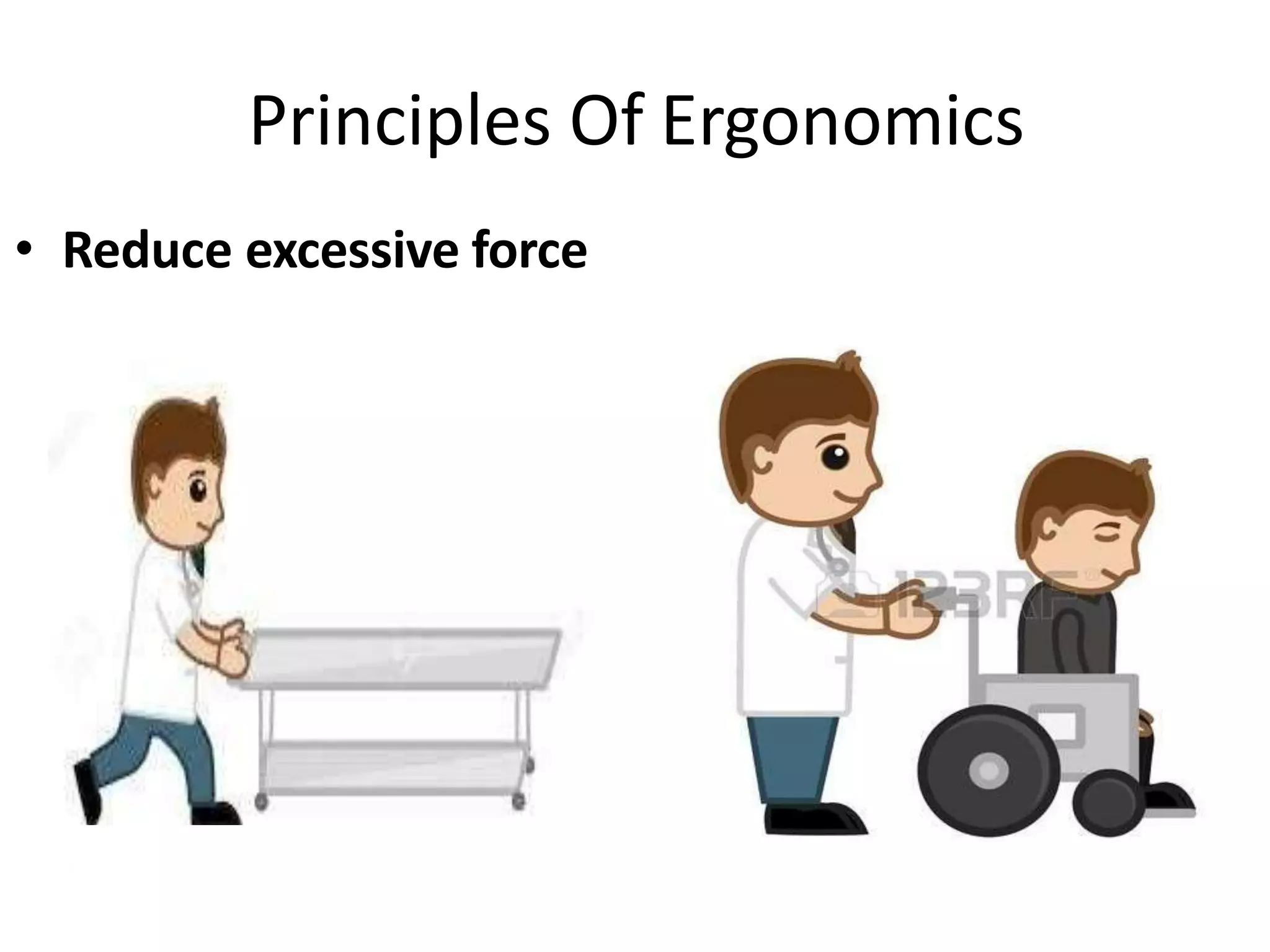
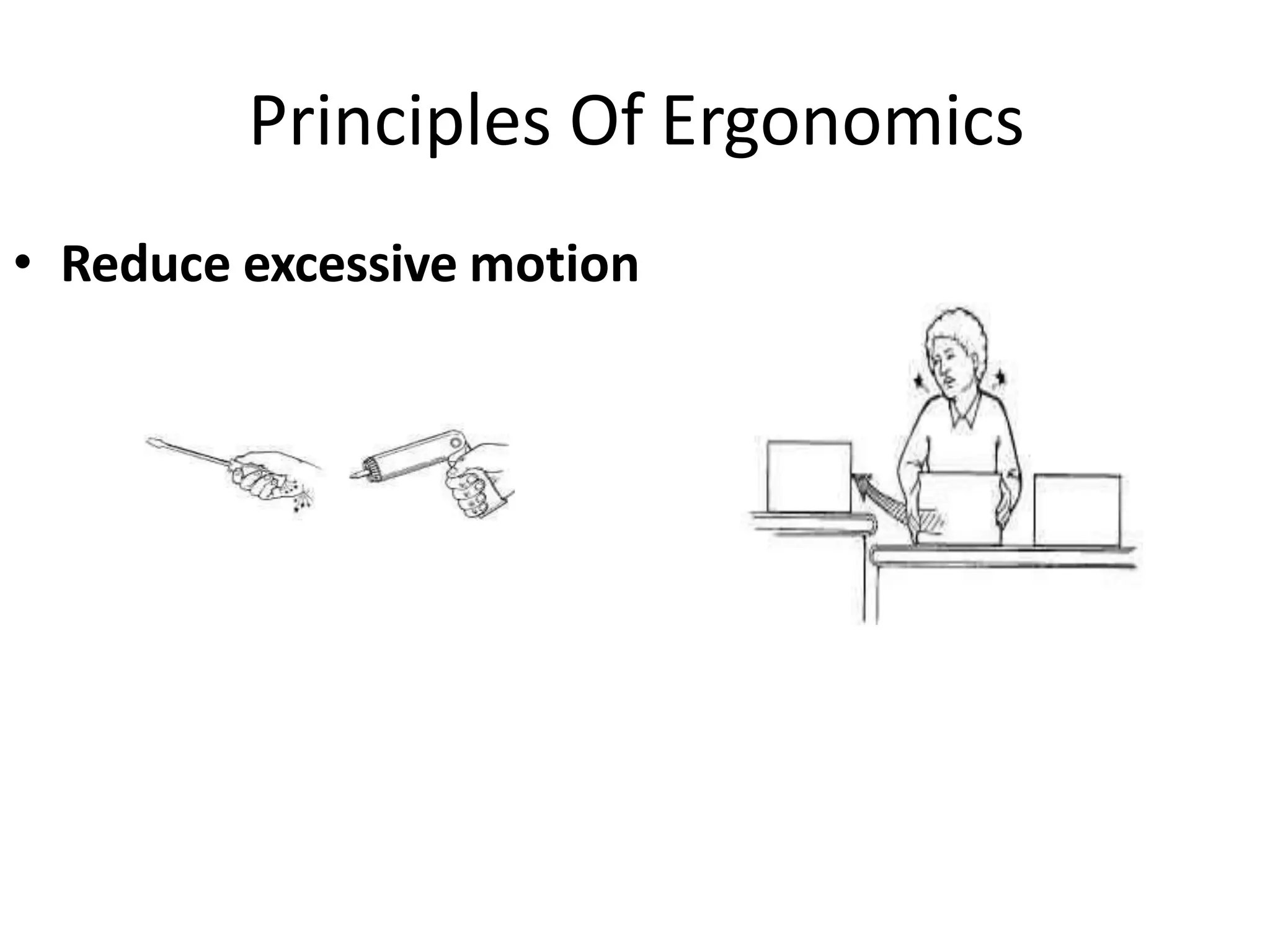
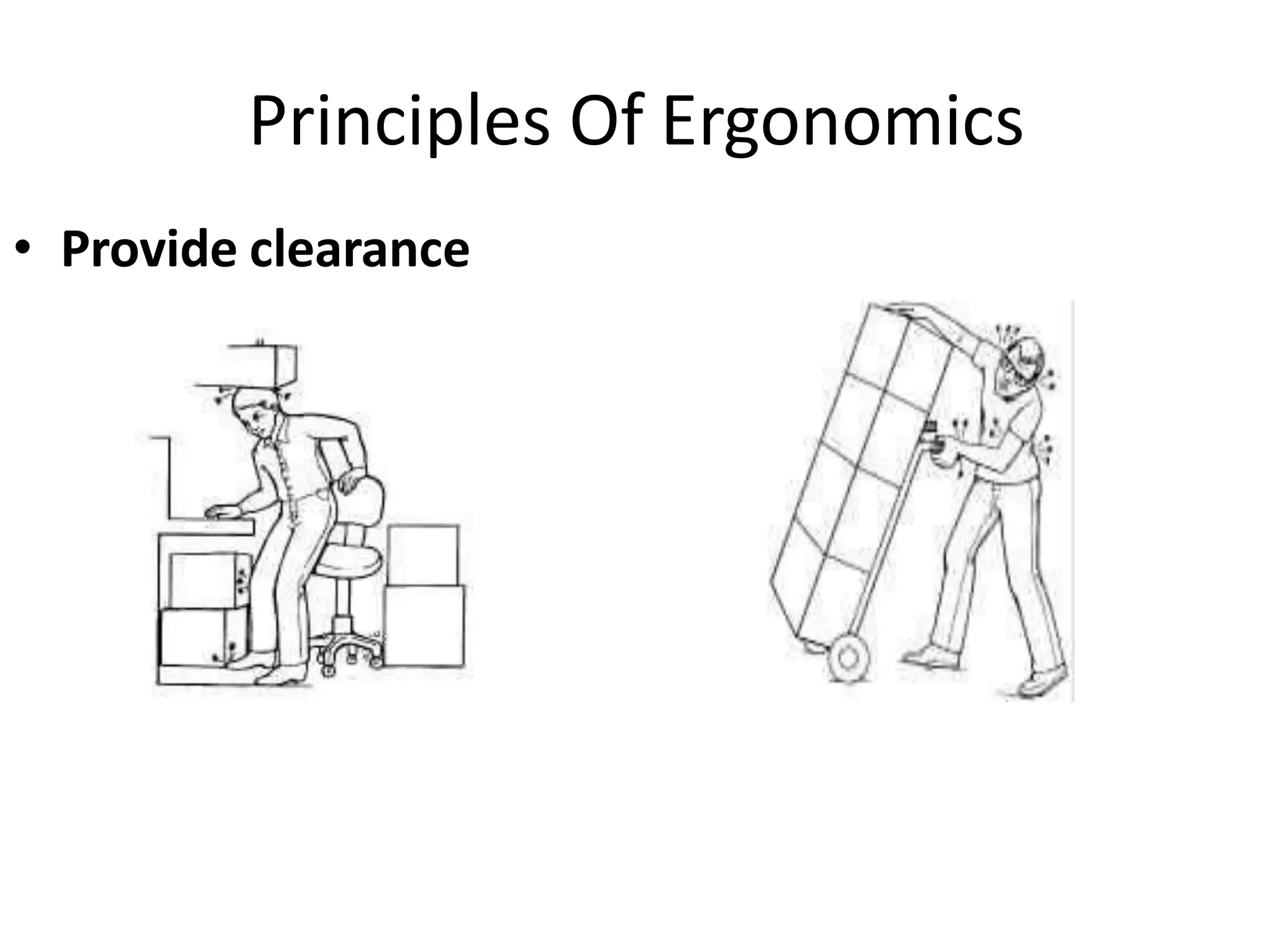
This document discusses musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) among healthcare professionals and the importance of ergonomics. It notes that MSDs like neck, back, shoulder, and wrist/hand pain are highly prevalent among healthcare workers due to long hours spent in ergonomically challenging postures, repetitive motions, and static positions. The document then defines ergonomics as designing a safe, comfortable workplace by matching jobs and products to humans. It describes the components of ergonomics including physical, cognitive, and organizational aspects. Finally, it outlines several principles of ergonomics like maintaining proper posture, keeping materials in easy reach, and reducing excessive force or motion to help prevent MSDs.