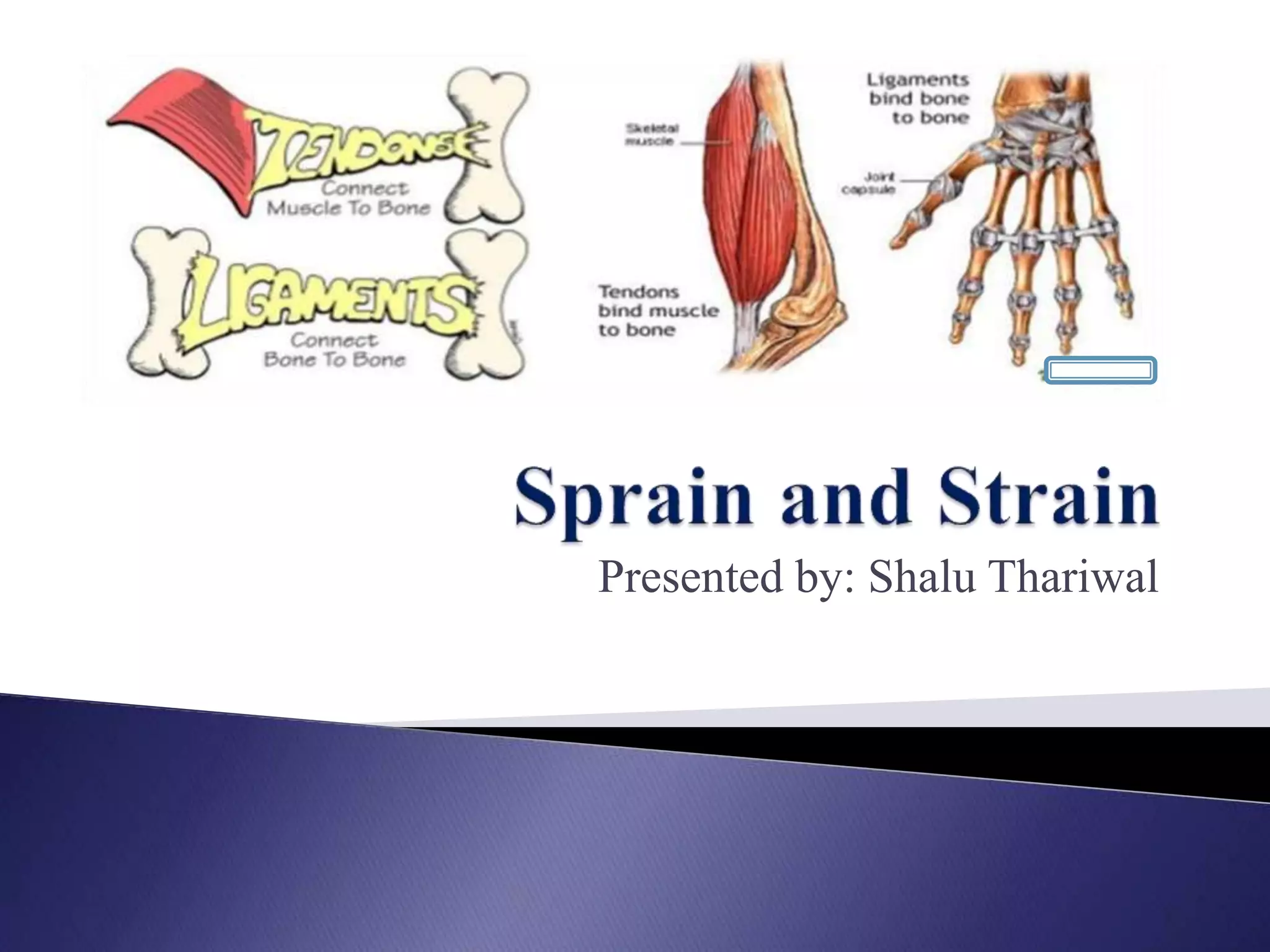
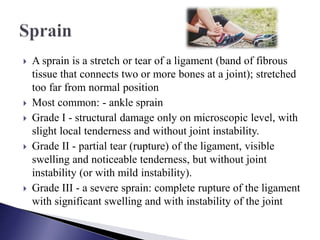
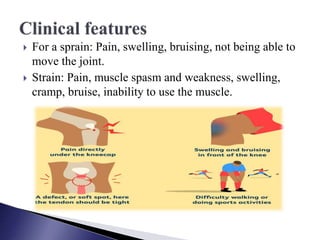
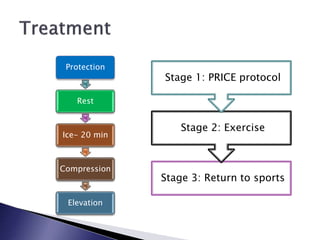
The document discusses different types and grades of sprains and strains. A sprain is a ligament injury caused by stretching or tearing from abnormal joint position. Ankle sprains are most common. Strains injure muscles or tendons. Back strains are most common. Grades range from minor fiber damage (Grade I) to complete rupture (Grade III). Treatment follows the PRICE protocol with rest, ice, compression and elevation. A three-stage recovery process focuses on PRICE, exercises and sports reintroduction. Recovery time depends on severity, from 3-6 weeks for mild to 8-12 months for severe injuries.