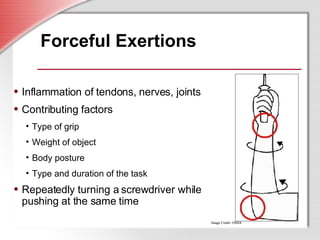
This document discusses ergonomics and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) in an industrial setting. It defines ergonomics as modifying jobs to fit people's capabilities in order to reduce MSDs caused by repetitive motions, forceful exertions, awkward postures, contact stress, and vibrations. It outlines general signs and symptoms of MSDs, common MSD types, and risk factors that can lead to MSDs like repetitive motions, forceful exertions, awkward postures, contact stress, and vibrations. The document recommends identifying and controlling MSD hazards through engineering controls, work practice changes, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment as part of an ergonomics management program.