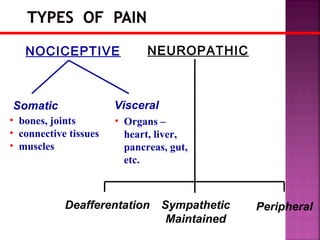
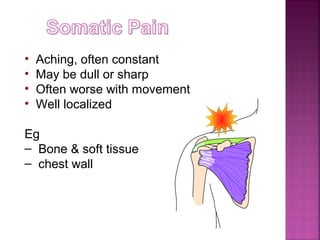
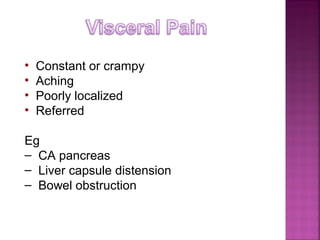
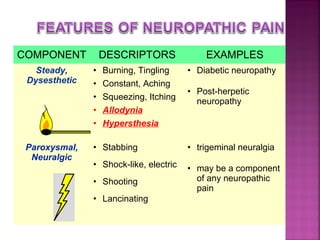
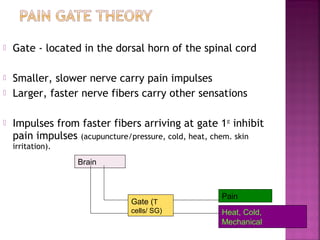
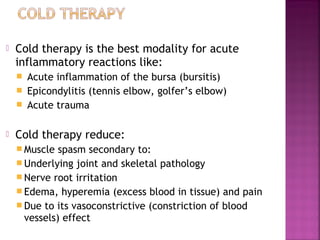
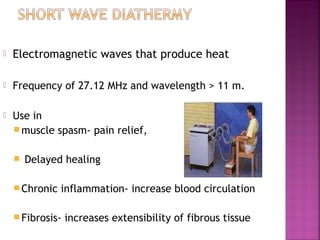
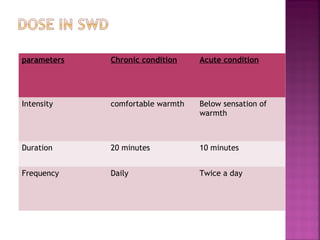
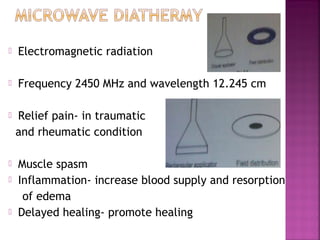
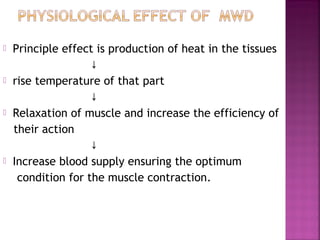
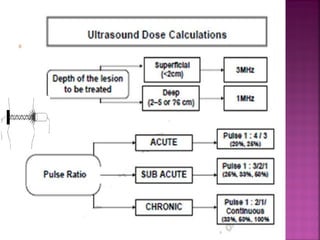
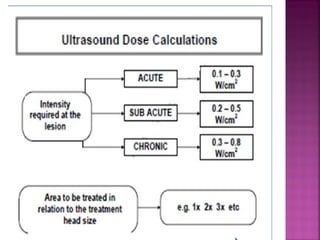
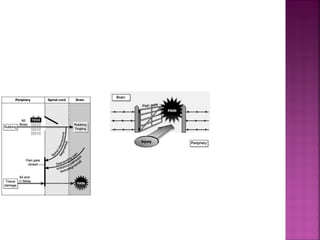
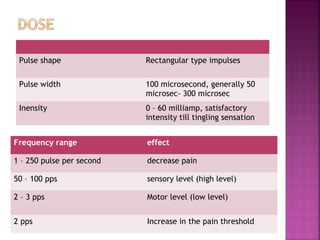
Somatic pain comes from skin and deep tissues, while visceral pain comes from internal organs. Both types of pain are detected by nociceptors and felt differently. Somatic pain is usually easier to locate and more intense, described as musculoskeletal pain. Visceral pain feels dull, vague, and hard to pinpoint, described as constant or crampy. The gate control theory proposes that stimulation of large diameter fibers can inhibit pain transmission through the substantia gelatinosa in the spinal cord. Various pain modulation techniques like TENS work through this mechanism.