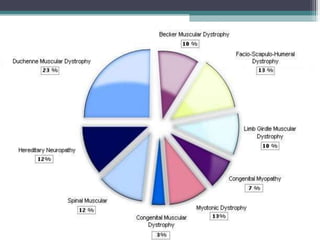
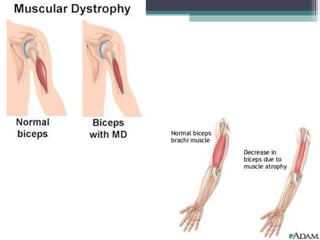
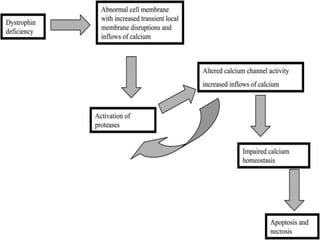
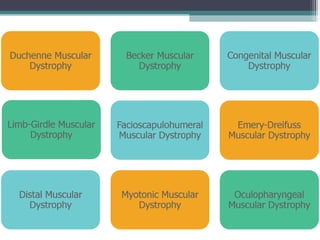
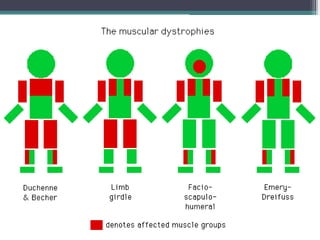
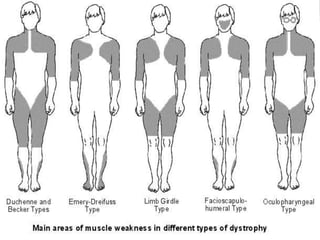
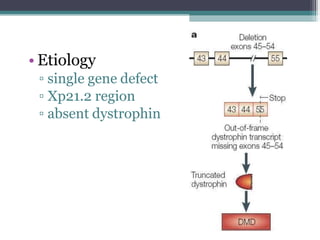
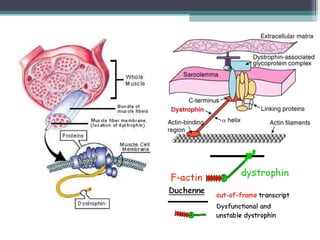
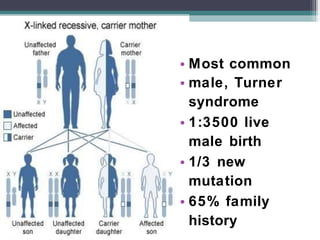
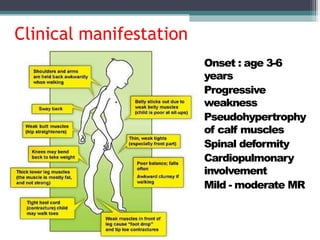
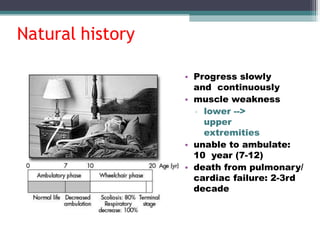
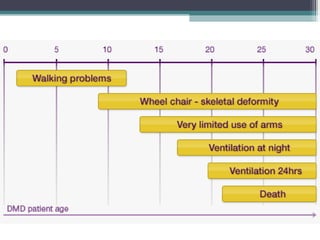
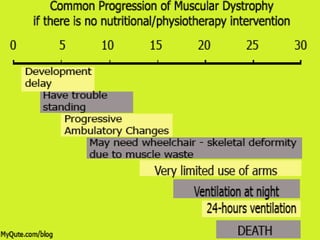
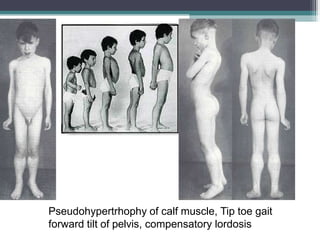
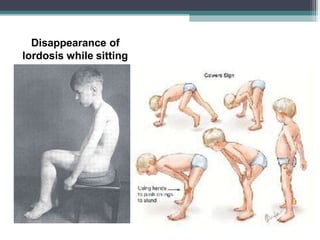
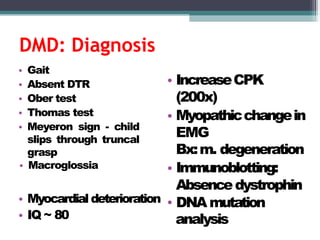
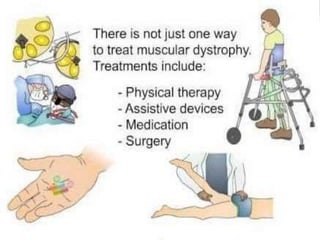
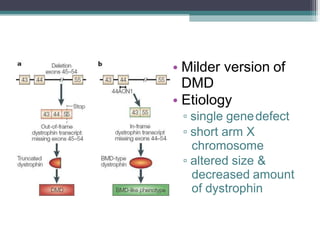
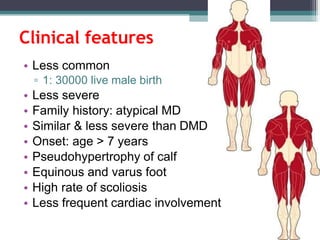
Muscular dystrophy is a heterogeneous group of inherited disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue from degenerative changes. The main types are Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), both of which are sex-linked recessive disorders caused by defects in the dystrophin gene on the X chromosome. DMD is the most common and severe form, affecting 1 in 3,500 live male births, with symptoms starting in early childhood and leading to death in the 2nd or 3rd decade without respiratory or cardiac support. BMD is a milder version of DMD with a later onset and slower progression.