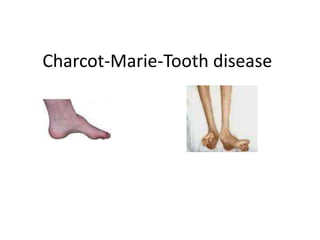
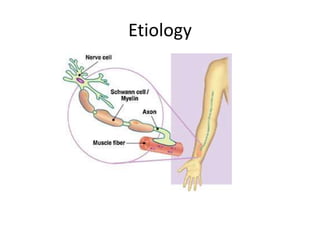
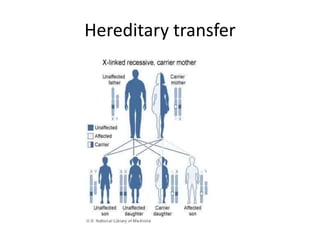
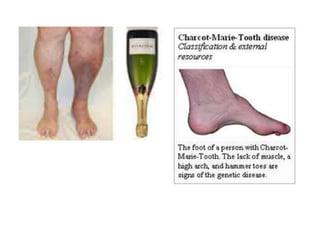
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is one of the most common inherited neurological disorders. It comprises a group of disorders that affect the peripheral nerves, causing their gradual degeneration. There are several types of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease that are caused by mutations in genes encoding proteins involved in the structure and function of the peripheral nerve axon or myelin sheath. Symptoms include weakness in the feet and lower legs, muscle wasting, and deformities of the feet. There is currently no cure for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, but treatment aims to correct deformities and muscle imbalances through procedures like tendon transfers and osteotomies.