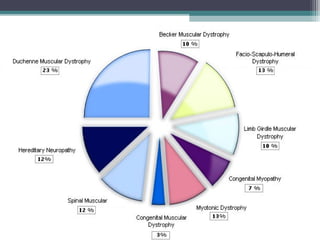
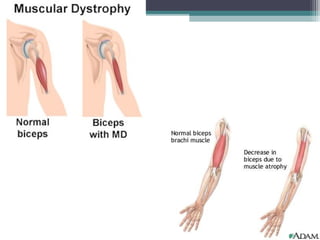
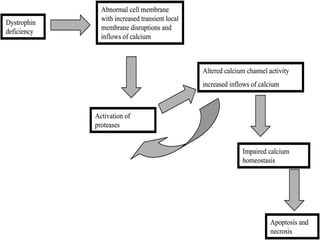
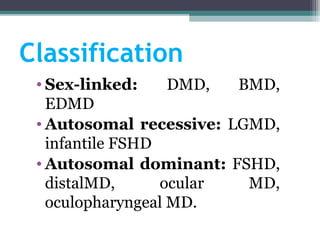
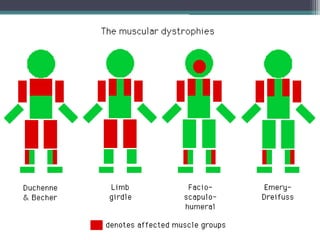
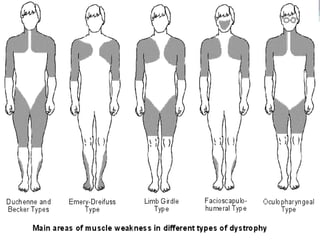
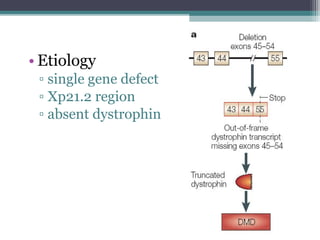
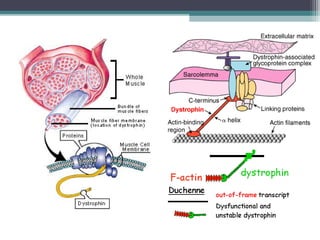
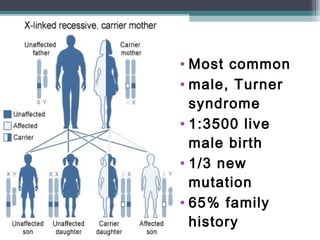
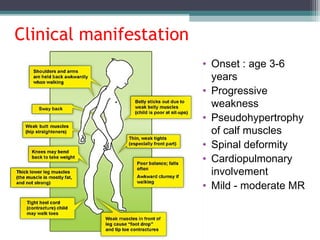
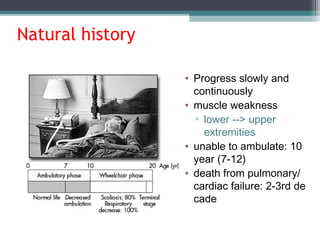
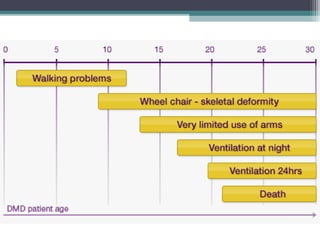
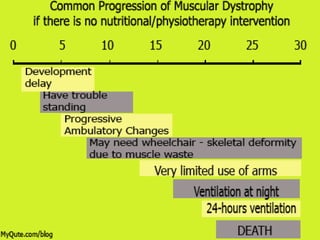
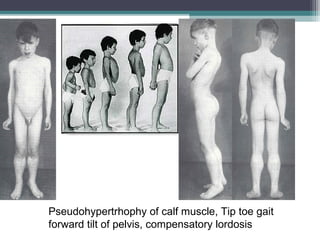
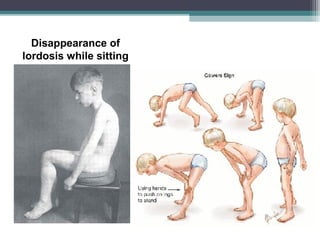
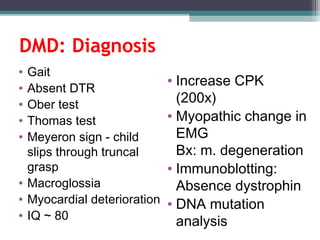
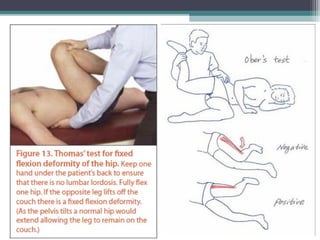
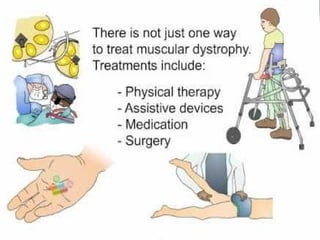
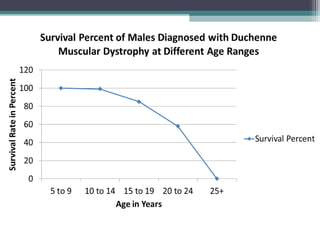
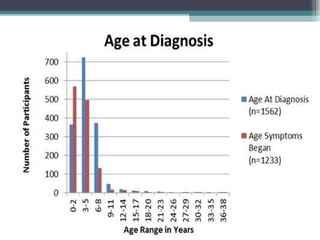
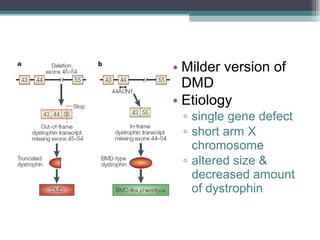
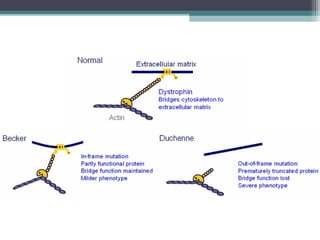
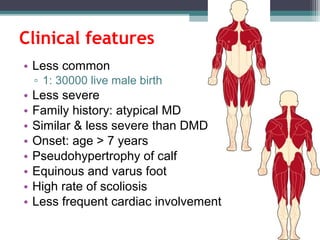
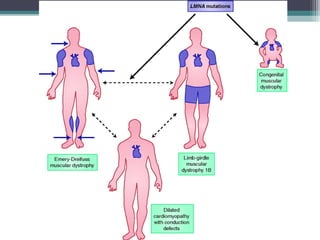
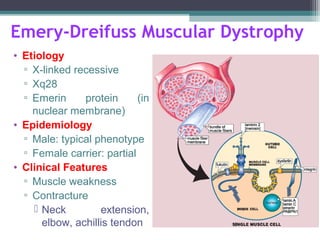
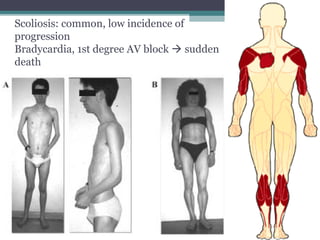
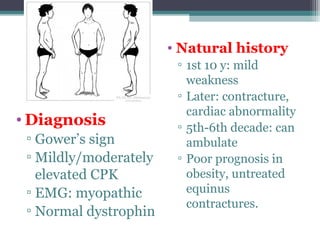
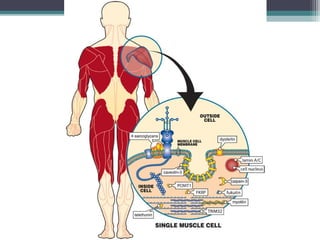
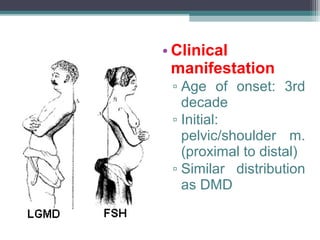
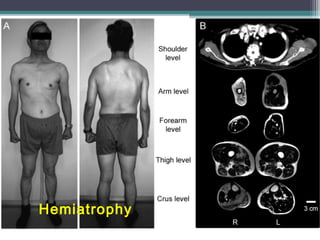
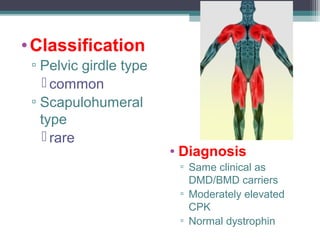
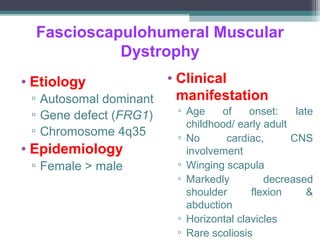
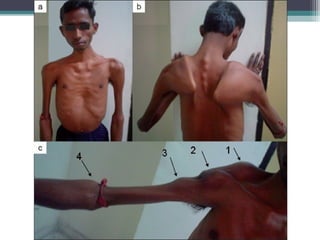
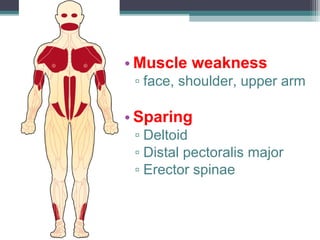
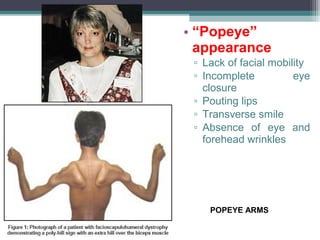
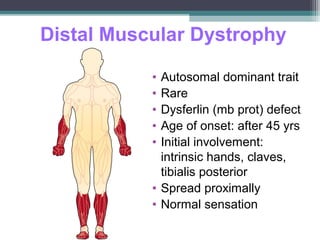
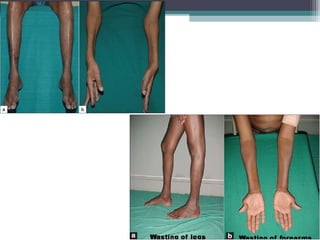
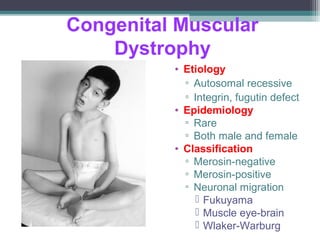
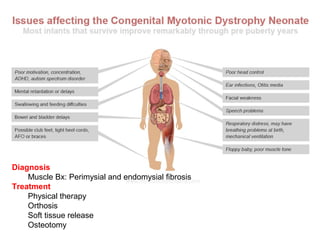
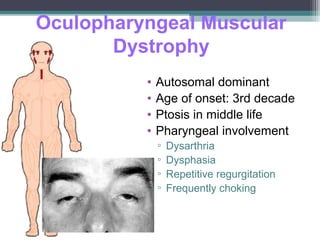
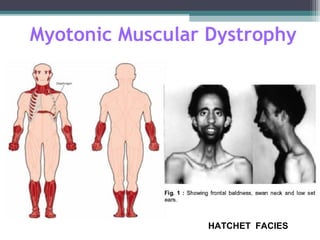
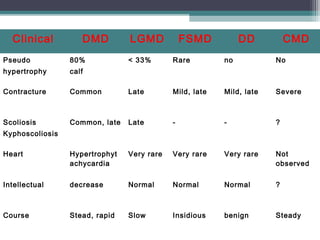
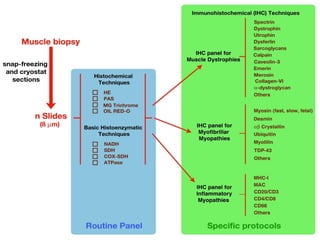
Muscular dystrophy is a heterogeneous group of inherited disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue. There are several classifications including sex-linked, autosomal recessive, and autosomal dominant forms that depend on the causative gene, age of onset, and symptoms. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is the most common and severe type that primarily affects males, causes muscle degeneration starting in childhood, and leads to death in the third decade without treatment. Other forms include limb-girdle, facioscapulohumeral, and congenital muscular dystrophies that have varying inheritance patterns, muscle involvement, and progression of symptoms. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications to maximize quality of life.