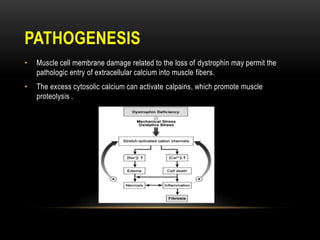
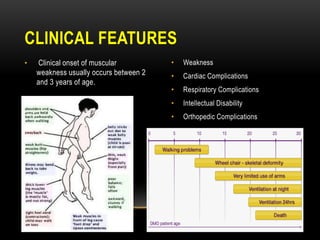
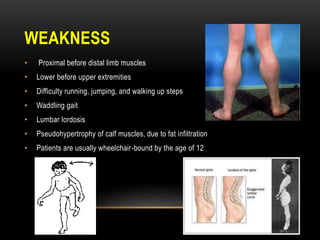
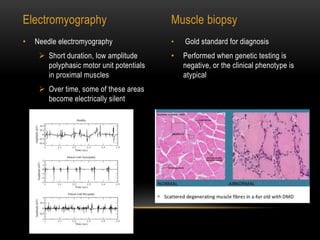
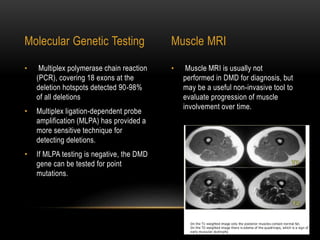
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene located on the X chromosome. It is characterized by progressive muscle weakness starting in early childhood. Clinical features include difficulty walking, cardiac complications like dilated cardiomyopathy, respiratory issues like sleep apnea and hypoventilation, intellectual disabilities in 30% of patients, and orthopedic problems like fractures and scoliosis. Diagnosis involves elevated creatine kinase levels, muscle biopsy, and genetic testing. Management focuses on cardiac, respiratory, orthopedic care as well as corticosteroid therapy to prolong ambulation and improve lung function. Emerging treatments include gene therapy using viral vectors and exon skipping to restore dystrophin production.