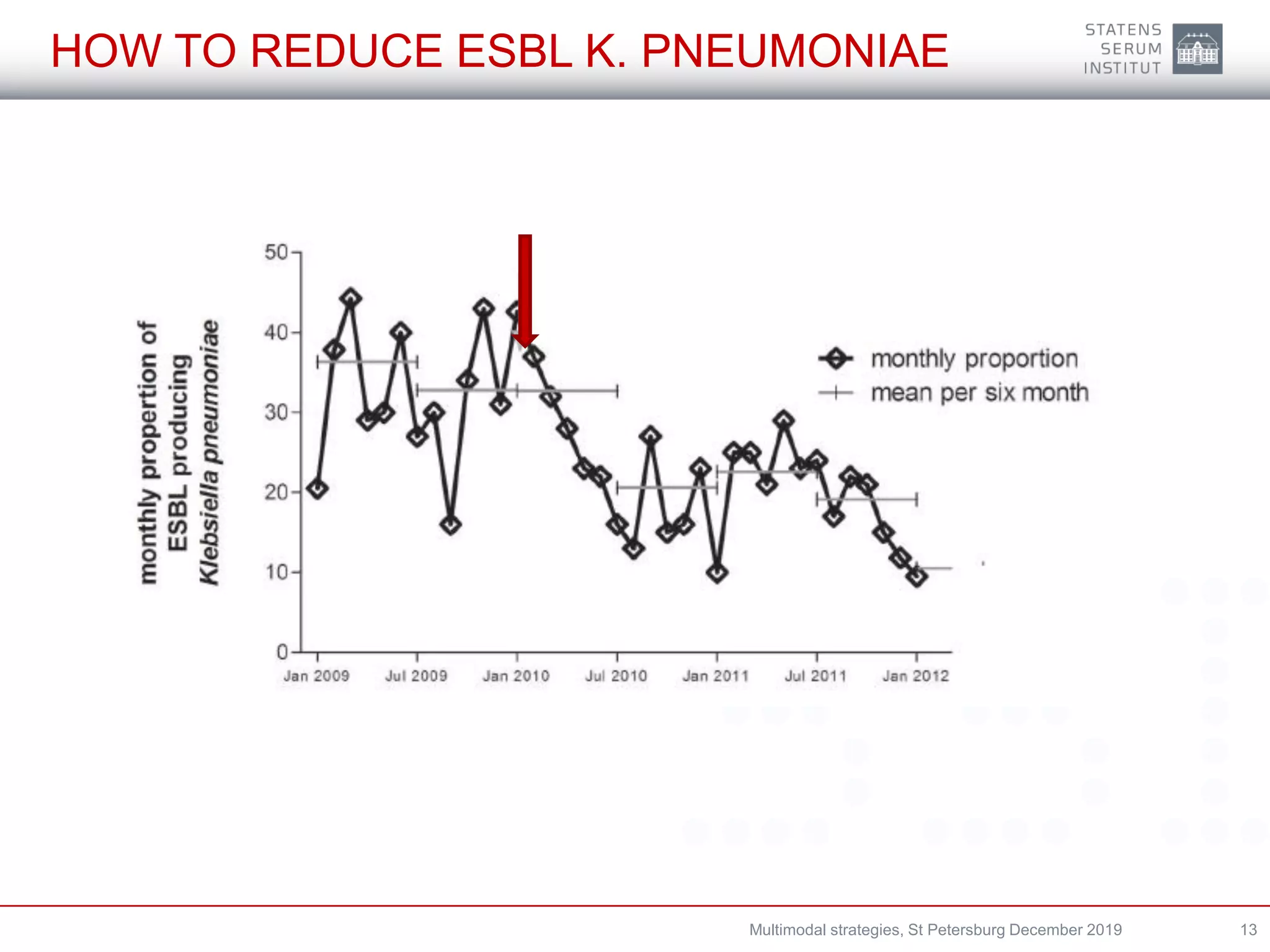
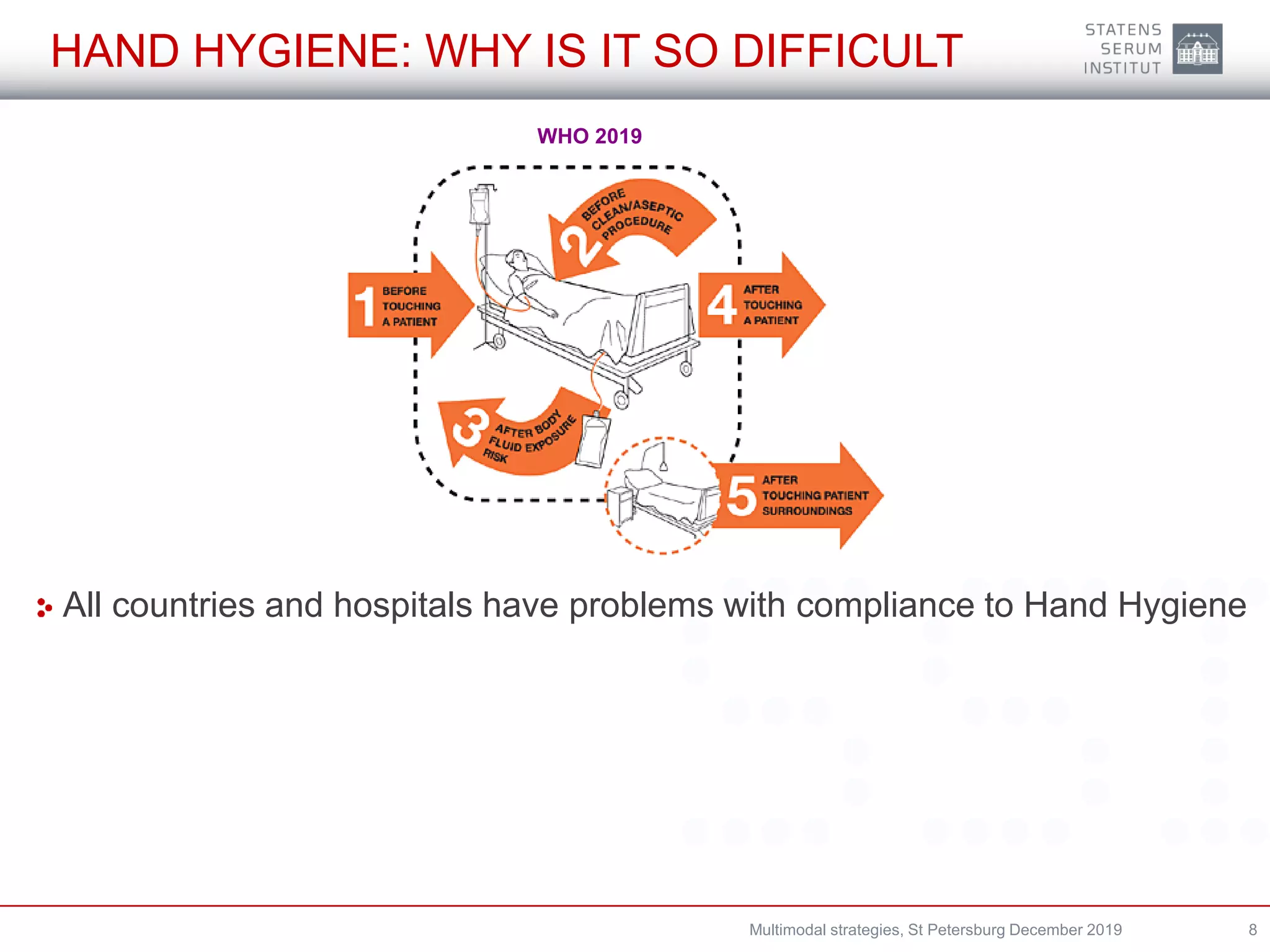
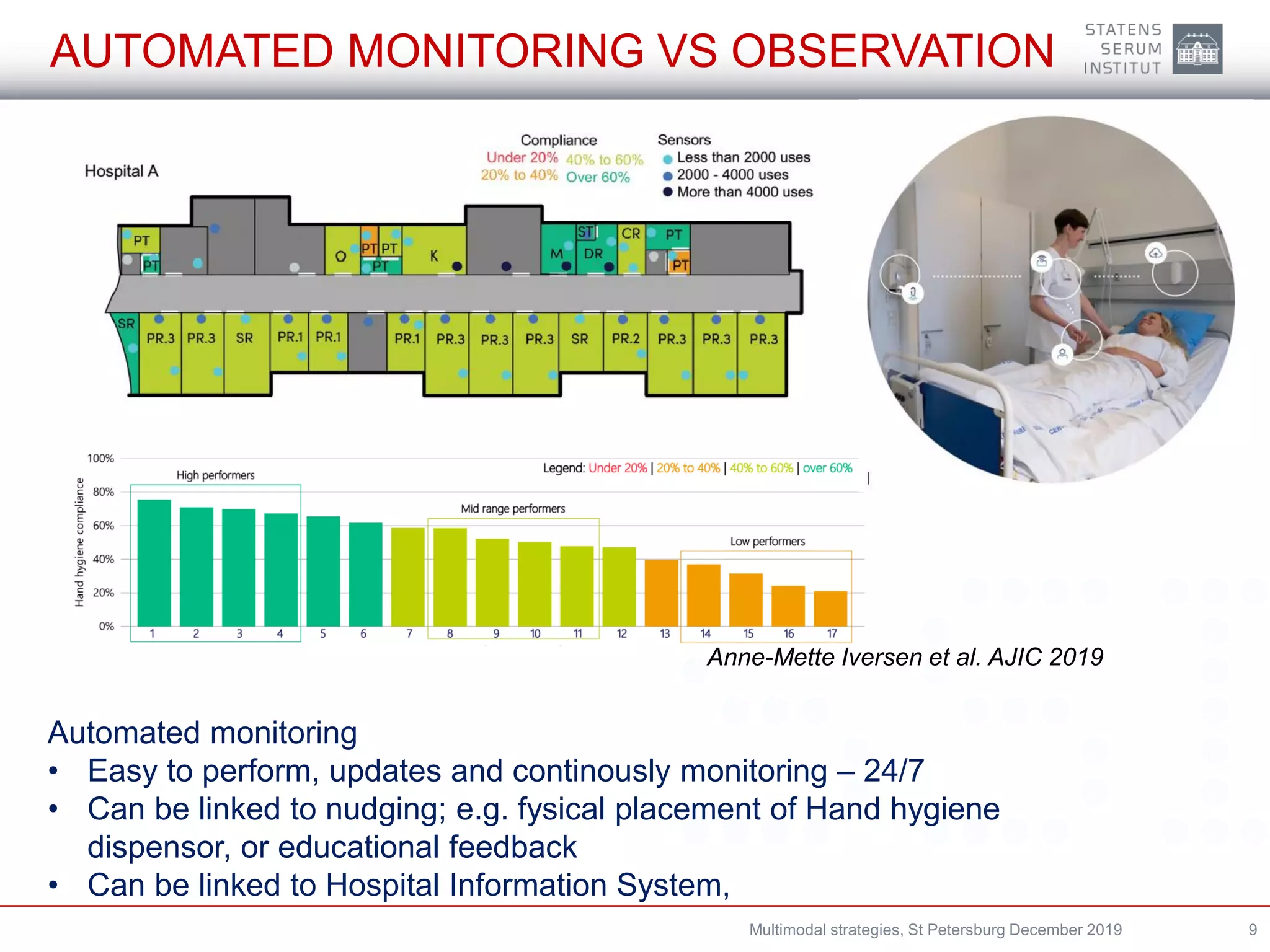
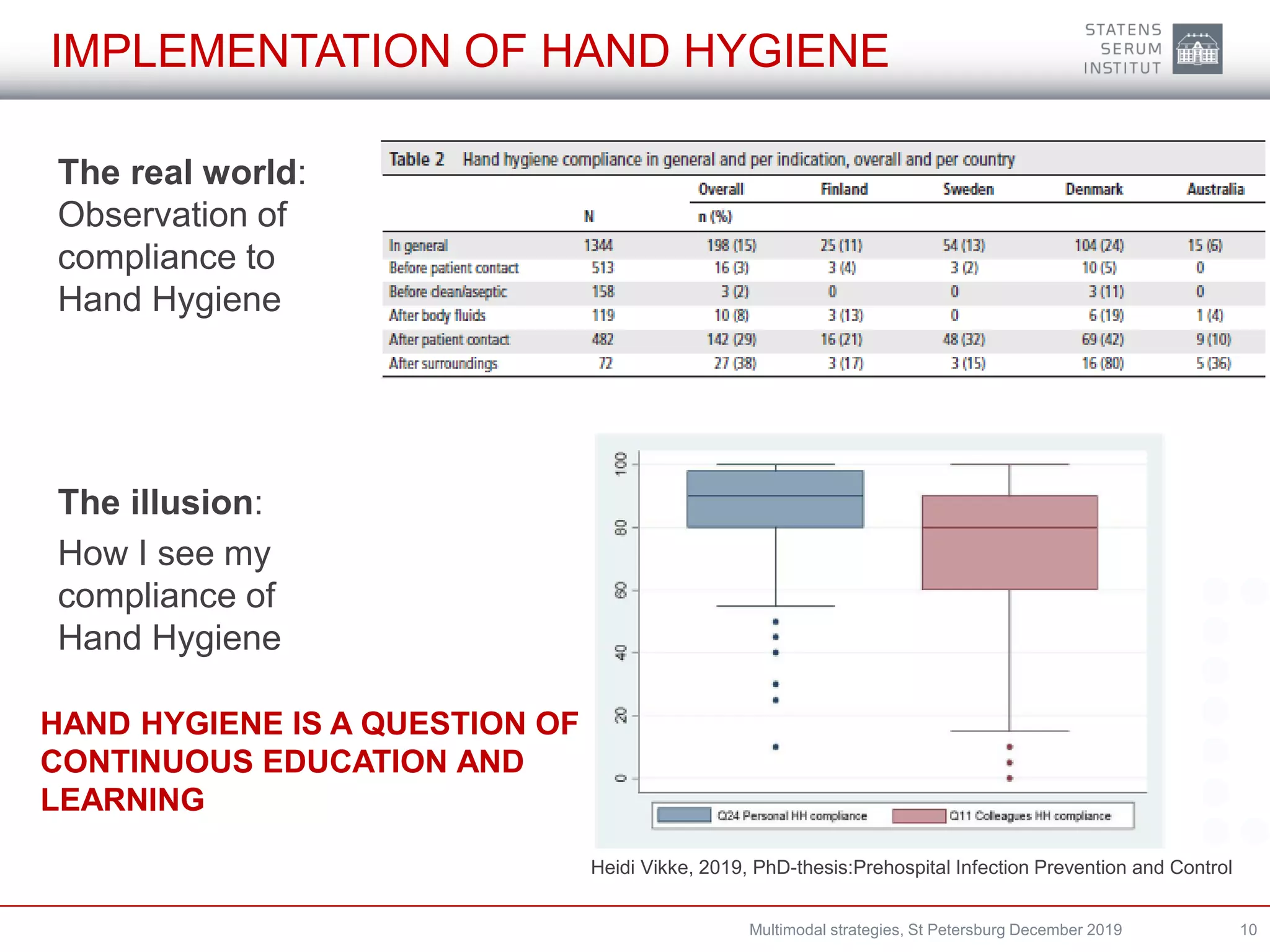
A multimodal strategy involves implementing several components together to improve outcomes and change behavior. For infection prevention and control, a multimodal approach is needed at both the national and hospital levels. It consists of system changes, education and training, monitoring practices and outcomes, reminders, and culture change. Hand hygiene is commonly addressed through multimodal strategies involving guidelines, education, automated monitoring, and reminders. Denmark has successfully used multimodal strategies including antimicrobial stewardship, isolation, communication, and establishing task forces to reduce antibiotic-resistant organisms like ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in hospitals.







![MULTIDISCIPLINARY INTERVENTION
The setting
- 5 hospital in Greater Copenhagen
• Approximately 1800 beds,
• Antibiotic consumption: approx. 800 DDD per 1000 bedday
The problem
- One (later two) hospitals noted an increase in ESBL-K. pneumoniae
The intervention (in one hospital, Bispebjerg)
- Antimicrobial stewardship and restrictions of ab-use (cephalosporins,
carbapenems and flouroquinoles)
- Isolation precautions
- Communication and education
- Establishing a task-force [pharmacologist, IC-nurses, Quality staff]
- Steering group [Hospital director, clin.microbiologists]
Strategy: involving all health care workers
Multimodal strategies, St Petersburg December 2019 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-200306094847/75/Multimodal-strategies-and-education-11-2048.jpg)