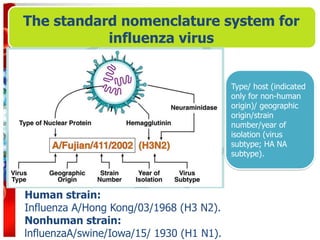
Influenza viruses are RNA viruses in the Orthomyxoviridae family that cause seasonal flu epidemics and pandemics. They are spherical, 80-120nm in size, with segmented negative-sense RNA and replicate in the nucleus. Influenza A has different subtypes based on its hemagglutinin and neuraminidase proteins that determine its antigenicity and ability to cause pandemics through genetic reassortment. Seasonal flu is associated with upper respiratory illness but can lead to pneumonia. Diagnosis involves PCR, antigen detection, virus isolation and serology. Treatment focuses on antivirals while vaccination provides moderate protection against matched strains. High risk groups like the elderly are more susceptible to flu complications.