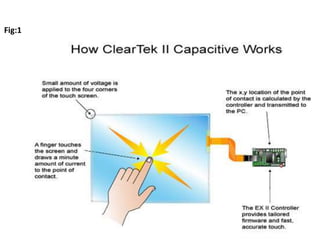
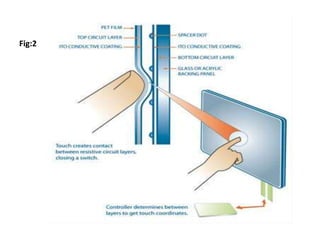
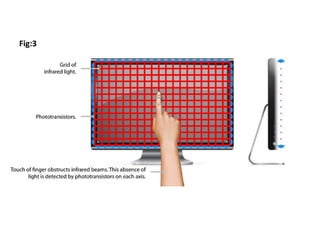
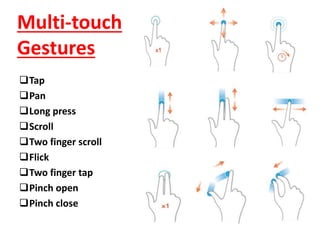
This document discusses multi-touch technology. It provides an overview of the history of multi-touch from 1982 onwards. It describes different types of multi-touch technologies including capacitive, resistive, optical and infrared. It outlines common multi-touch gestures and applications. It then focuses on frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR) as a new approach, describing how it works and its advantages over other methods like high resolution, low cost and scalability. It concludes that touch screens are the interface for the 21st century and FTIR provides a simple method for multi-touch displays.