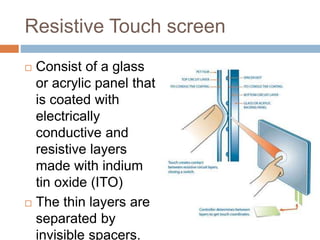
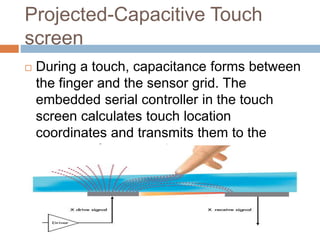
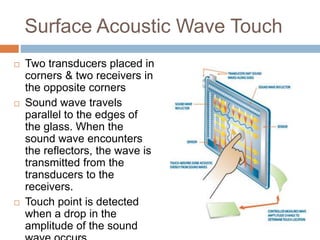
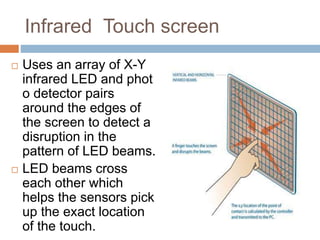
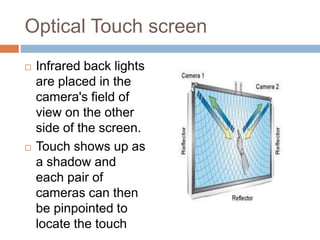
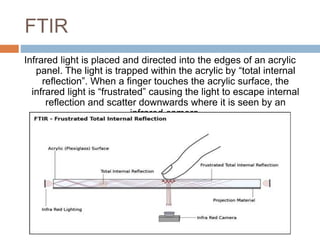
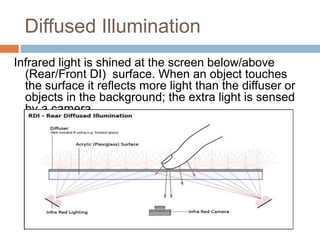
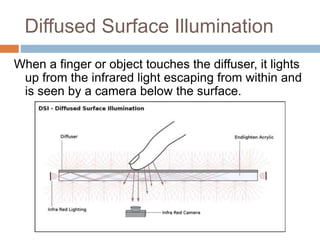
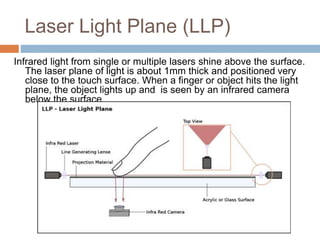
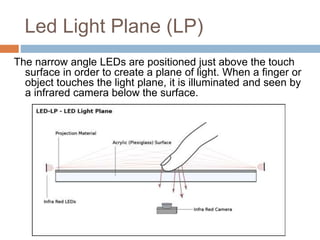
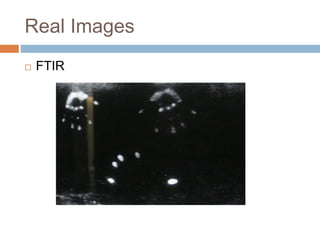
This document discusses multi-touch interaction and technologies. It describes how multi-touch allows for multiple simultaneous points of input detection on a touch surface. Various touch screen technologies are covered, including resistive, capacitive, surface acoustic wave, infrared, and optical. It also discusses techniques for optical touch sensing including FTIR, DI, DSI, LLP and LED LP. Programming for multi-touch involves using open-source libraries like CCV and TUIO protocols.