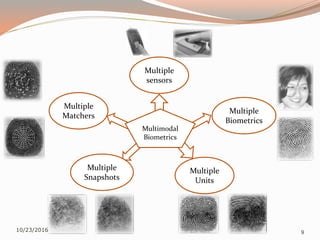
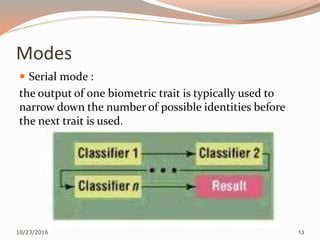
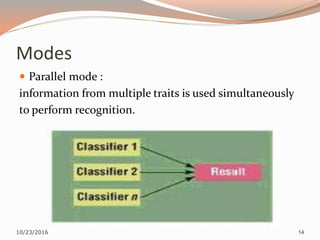
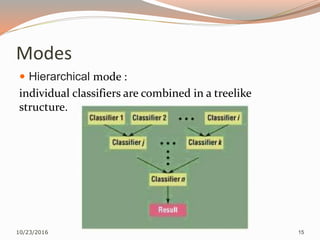
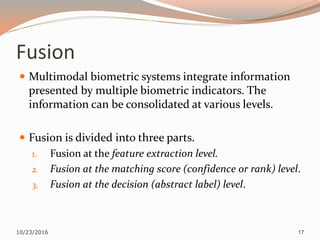
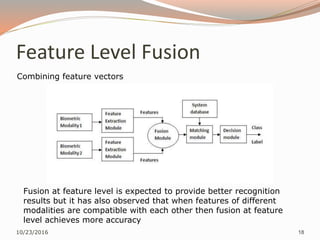
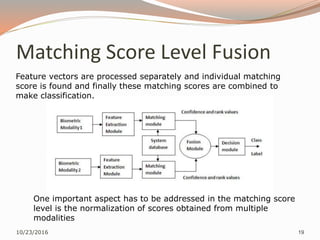
The document discusses the challenges of unimodal biometric systems, including issues such as noisy data, intra-class variation, inter-class similarities, non-universality, and spoofing. It introduces multimodal biometrics, which utilize multiple physical or behavioral characteristics to enhance accuracy and security, and outlines different operational modes (serial, parallel, hierarchical) along with the levels of fusion (feature extraction, matching score, decision level). Additionally, it highlights the advantages of multimodal systems, such as increased security and reduced error rates, as well as their disadvantages including cost and complexity.