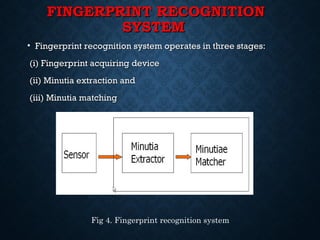
Fingerprint recognition involves comparing fingerprints to determine if they match. It operates by acquiring fingerprints, extracting minutiae features like ridge endings and bifurcations, and matching minutiae between fingerprints. It has high accuracy but can be affected by dirt or wounds. Applications include banking security, access control, and criminal identification. The presented algorithm accurately and quickly extracts minutiae and identifies corrupted regions for removal.