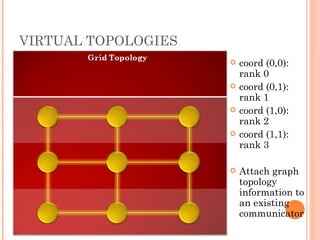
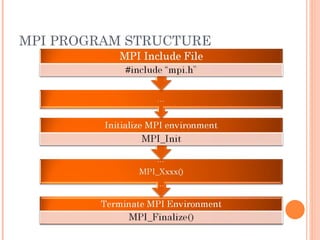
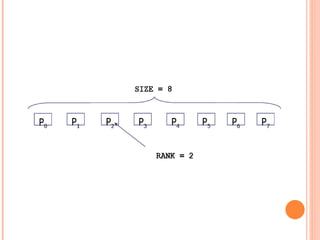
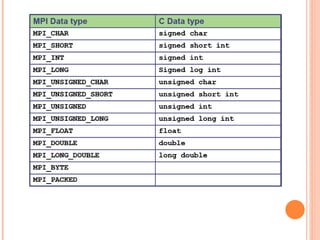
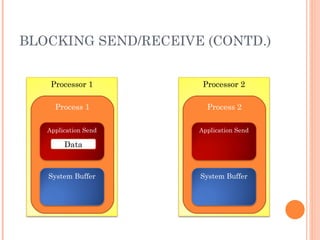
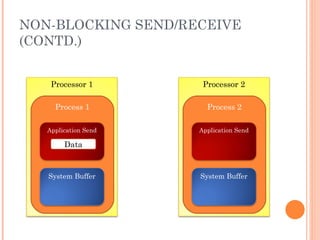
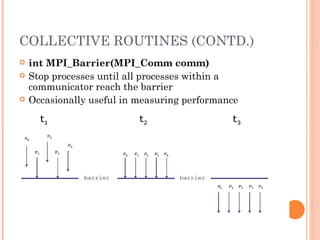
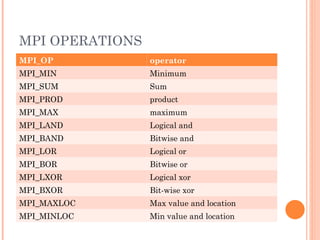
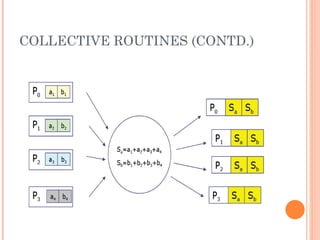
The document discusses the basics of MPI (Message Passing Interface), which is a standard for message passing parallel programming. It explains the basic model of MPI including communicators, groups, and ranks. It then covers point-to-point communication functions like blocking and non-blocking send/receive. Finally, it briefly introduces collective communication functions that involve groups of processes like broadcast and barrier.