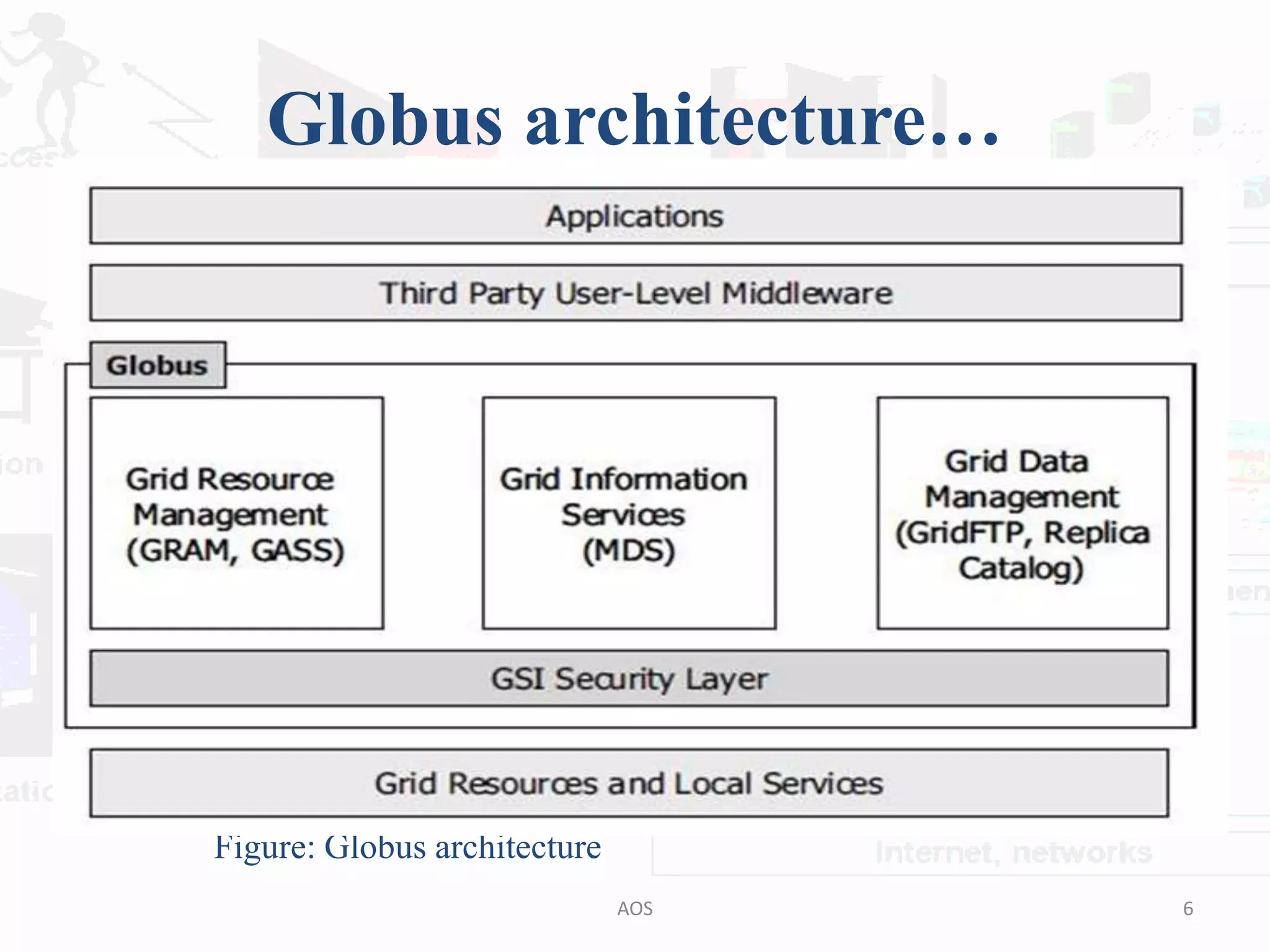
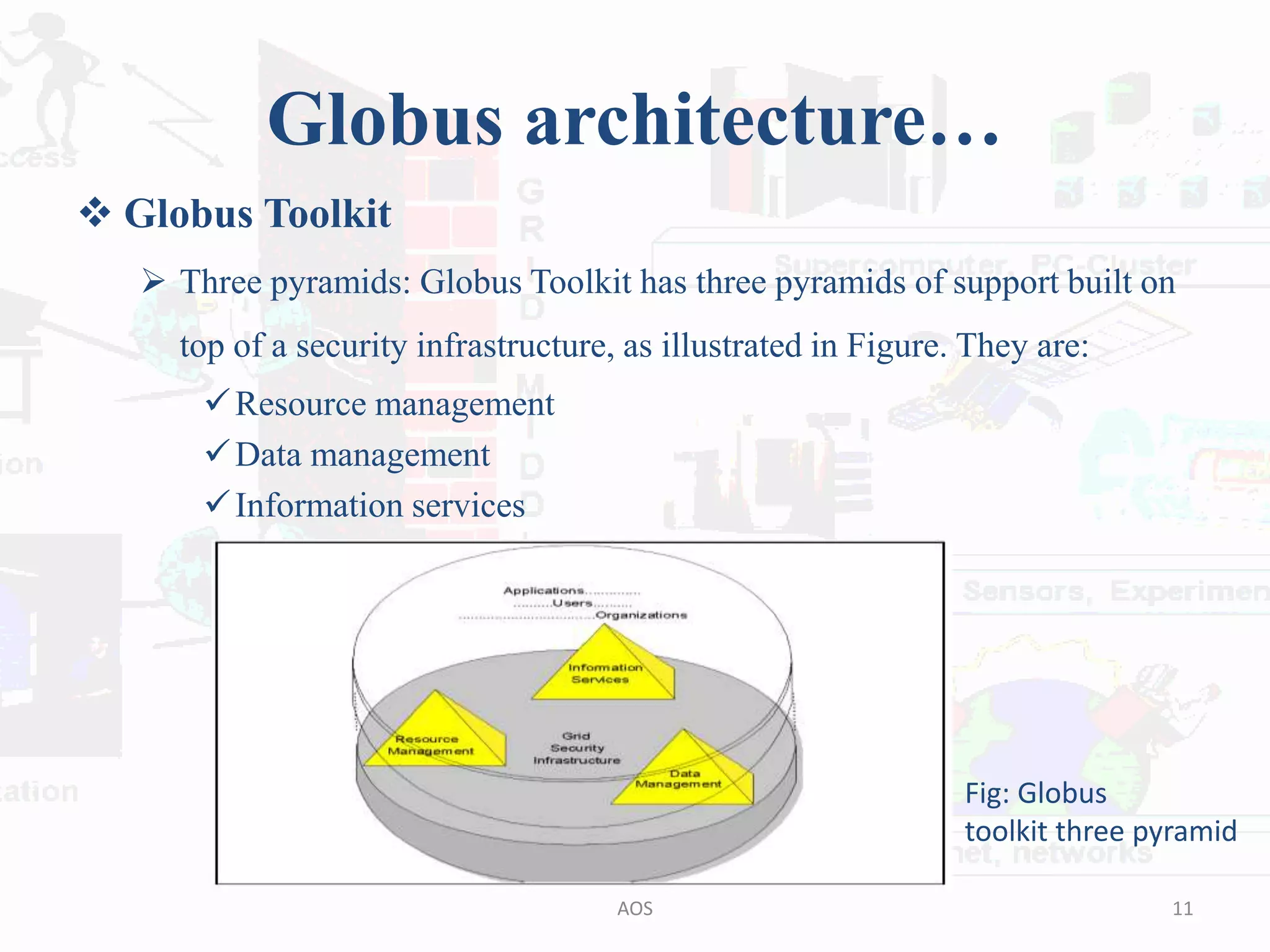
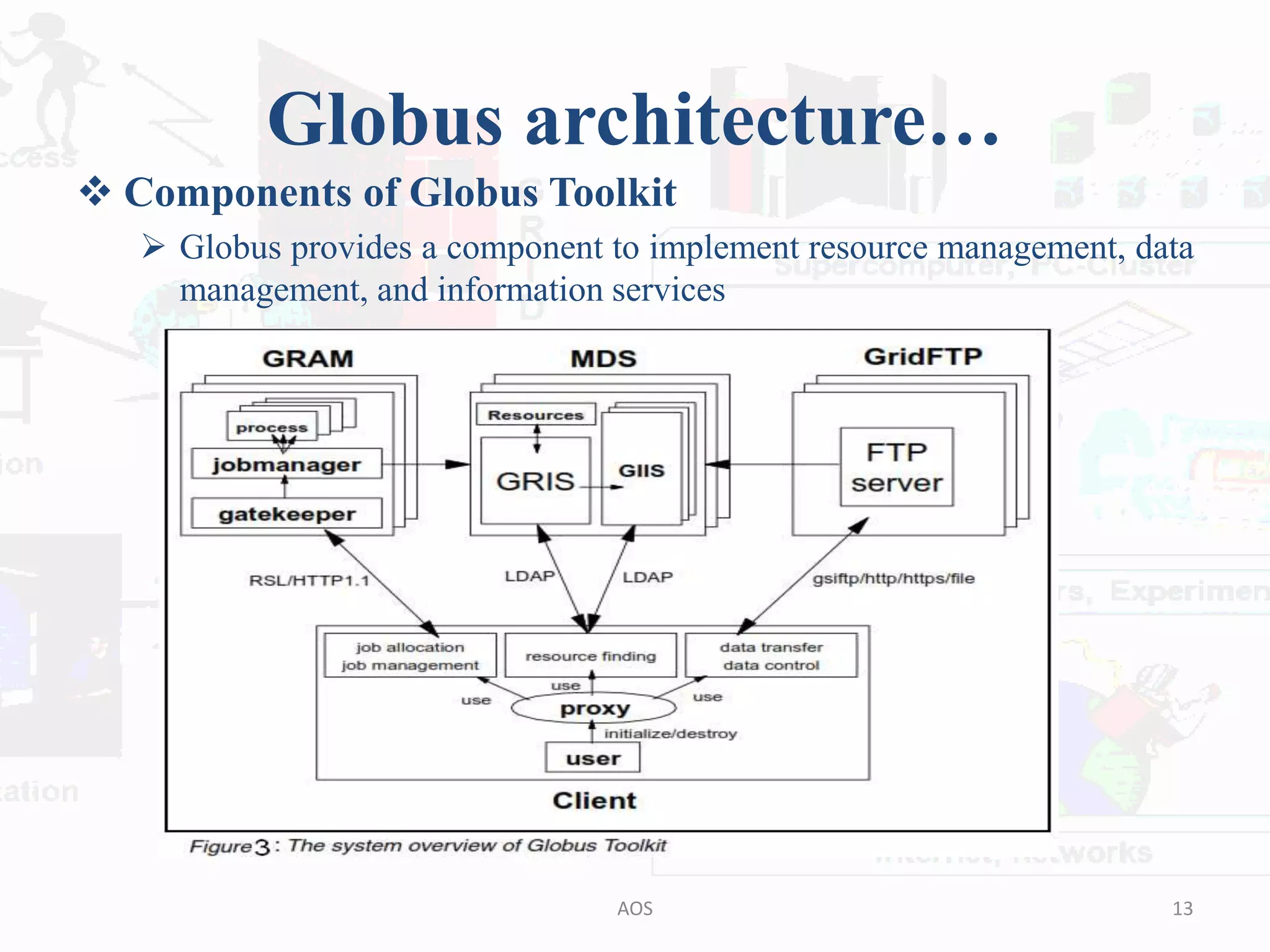
The document outlines the Globus and GridBus architectures, highlighting the Globus toolkit's components for building computational grids, including resource management, data management, and information services. It discusses the security layer, including the use of public key cryptography, and the challenges in creating a unified grid computing environment. Additionally, GridBus is presented as a solution to enhance service quality and manage distributed resources across various platforms.