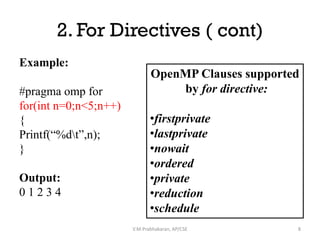
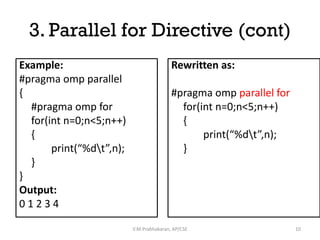
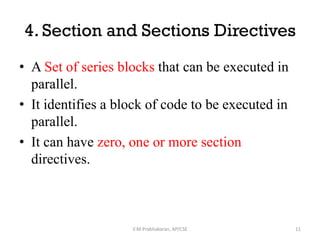
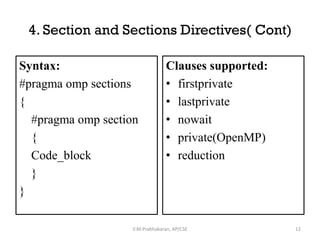
OpenMP directives are used to parallelize sequential programs. The key directives discussed include:
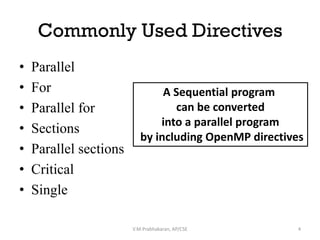
1. Parallel and parallel for to execute loops or code blocks across multiple threads.
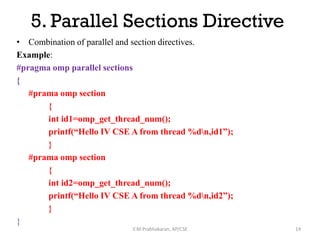
2. Sections and parallel sections to execute different code blocks simultaneously in parallel across threads.
3. Critical to ensure a code block is only executed by one thread at a time for mutual exclusion.
4. Single to restrict a code block to only be executed by one thread.
OpenMP makes it possible to easily convert sequential programs to leverage multiple threads and processors through directives like these.


![Introduction
• Insist which Instructions or Task to be
executed and distributed among multiple
threads.
• Understood only by OpenMP Compilers.
• In C and C++, the standard preprocessing
directive is starting with #pragma omp
• #pragma omp directive-name [optional_clauses]
3V.M.Prabhakaran, AP/CSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmpdirectives-181120110328/85/Open-mp-directives-3-320.jpg)
![1. Parallel Directives
• Executed in parallel using
multiple threads.
Syntax:
#pragma omp parallel[clauses]
{
// Block of code
}
• Clauses specified is optional
• OpenMP Clauses
– copyin
– default(OpenMP)
– firstprivate
– if(OpenMP)
– num_threads,
– private(OpenMP)
– reduction and
shared(OpenMP)
V.M.Prabhakaran, AP/CSE 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openmpdirectives-181120110328/85/Open-mp-directives-5-320.jpg)